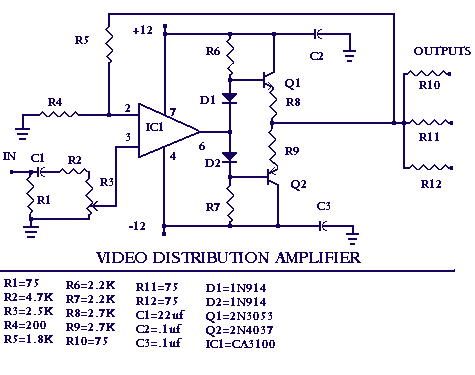
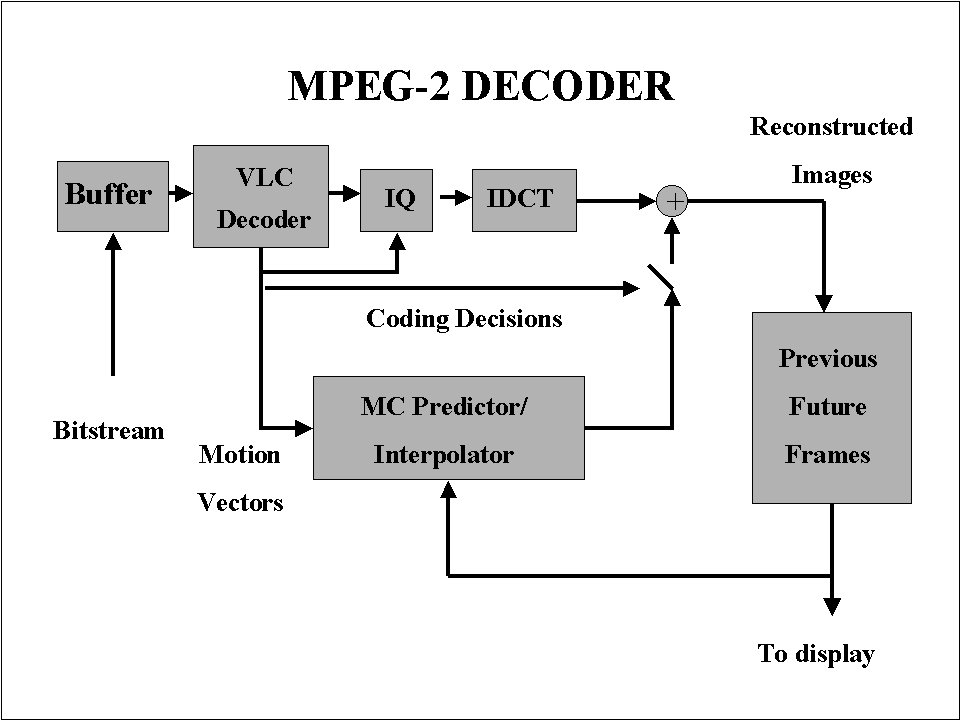
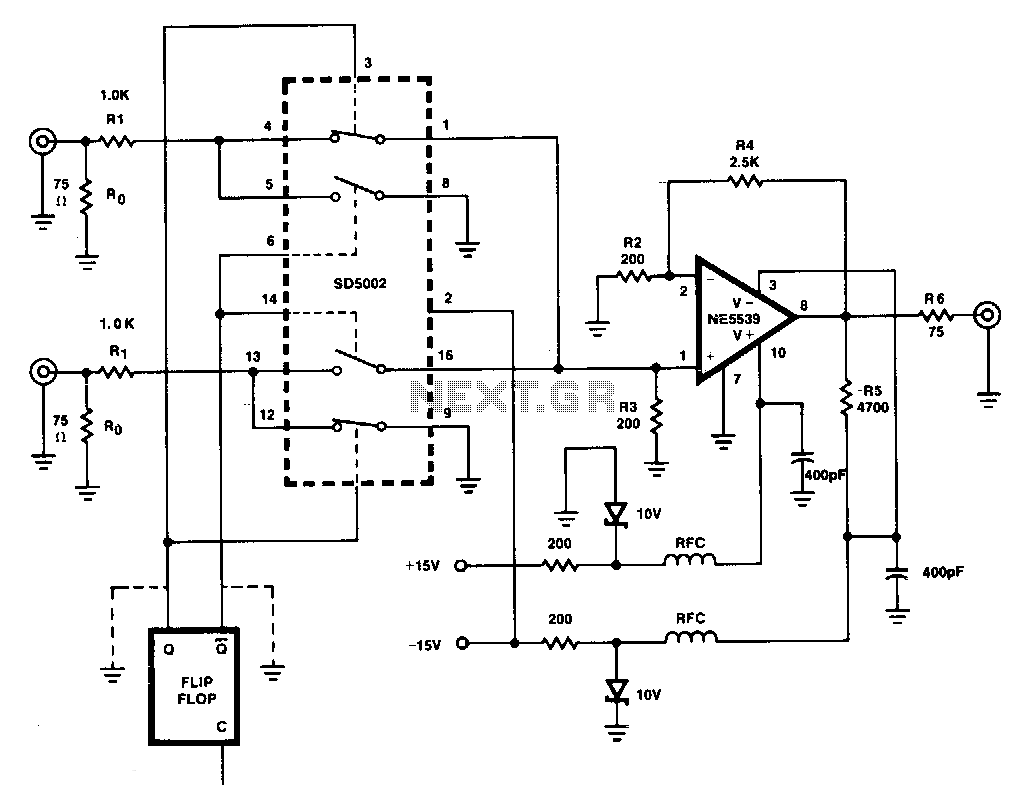
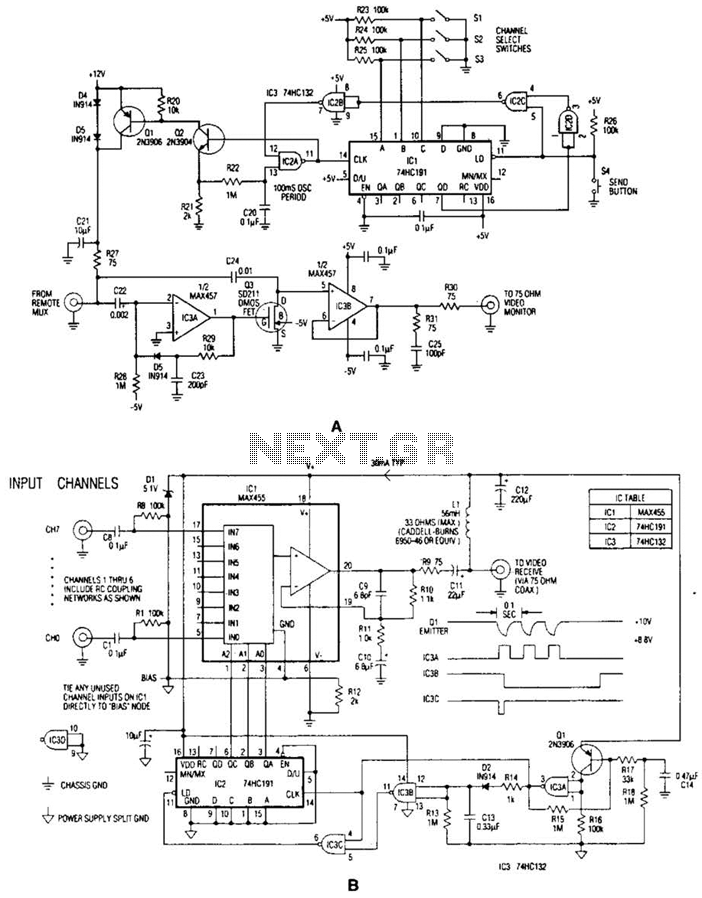
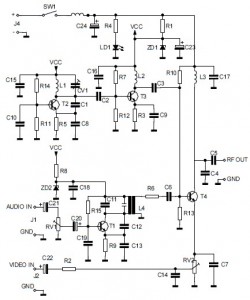
Video IsolatorCircuit

Nowadays, an increasing number of audio-visual devices in homes are interconnected. This is particularly true for televisions, which may be linked to DVD players.
In modern home entertainment systems, the integration of various audio-visual devices enhances user experience and convenience. A typical setup may include a television, DVD player, gaming console, streaming device, and sound system, all interconnected to provide seamless access to multimedia content.
The connection methods can vary, including HDMI, optical audio, component video, and composite video cables. HDMI (High Definition Multimedia Interface) is the most common due to its ability to transmit both high-definition video and audio signals through a single cable, simplifying connections and reducing clutter.
In a typical schematic for such a system, the television serves as the central hub, with multiple input ports for various devices. The DVD player connects via HDMI, allowing for high-quality video playback. If additional devices such as a gaming console are included, they can also connect through HDMI or other appropriate interfaces, depending on the available ports and desired functionality.
Audio output can be routed to an external sound system, which may utilize an optical audio connection or HDMI ARC (Audio Return Channel) to ensure high-fidelity sound. This setup allows users to enjoy enhanced audio quality, particularly important for cinematic experiences.
Furthermore, smart TVs may include built-in wireless connectivity, enabling them to connect to the internet and stream content from various online platforms. This capability enhances the versatility of the system, allowing users to access a wider range of media without the need for additional hardware.
Overall, a well-designed audio-visual system can significantly improve the home entertainment experience, providing flexibility, high-quality audio and video, and ease of use through interconnected devices.These days many more audio-visual devices in the home are connected together. This is especially the case with the TV, which may be connected to a DVD pla.. 🔗 External reference
In modern home entertainment systems, the integration of various audio-visual devices enhances user experience and convenience. A typical setup may include a television, DVD player, gaming console, streaming device, and sound system, all interconnected to provide seamless access to multimedia content.
The connection methods can vary, including HDMI, optical audio, component video, and composite video cables. HDMI (High Definition Multimedia Interface) is the most common due to its ability to transmit both high-definition video and audio signals through a single cable, simplifying connections and reducing clutter.
In a typical schematic for such a system, the television serves as the central hub, with multiple input ports for various devices. The DVD player connects via HDMI, allowing for high-quality video playback. If additional devices such as a gaming console are included, they can also connect through HDMI or other appropriate interfaces, depending on the available ports and desired functionality.
Audio output can be routed to an external sound system, which may utilize an optical audio connection or HDMI ARC (Audio Return Channel) to ensure high-fidelity sound. This setup allows users to enjoy enhanced audio quality, particularly important for cinematic experiences.
Furthermore, smart TVs may include built-in wireless connectivity, enabling them to connect to the internet and stream content from various online platforms. This capability enhances the versatility of the system, allowing users to access a wider range of media without the need for additional hardware.
Overall, a well-designed audio-visual system can significantly improve the home entertainment experience, providing flexibility, high-quality audio and video, and ease of use through interconnected devices.These days many more audio-visual devices in the home are connected together. This is especially the case with the TV, which may be connected to a DVD pla.. 🔗 External reference