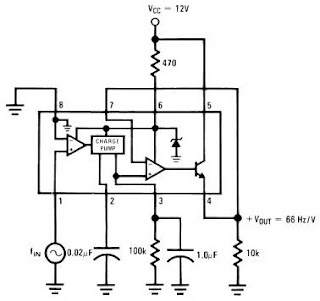
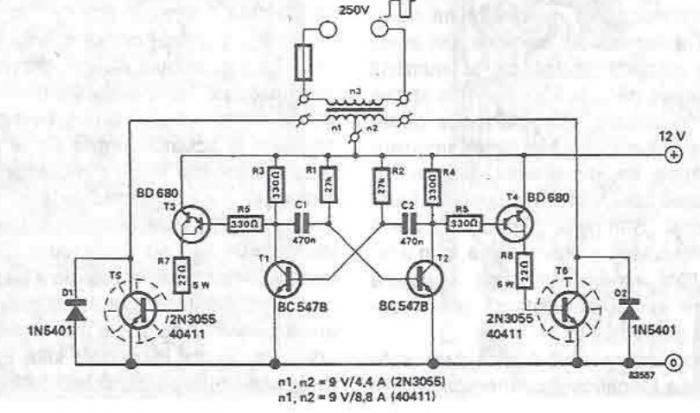
Voltage-to-Frequency And Frequency-to-Voltage Converter
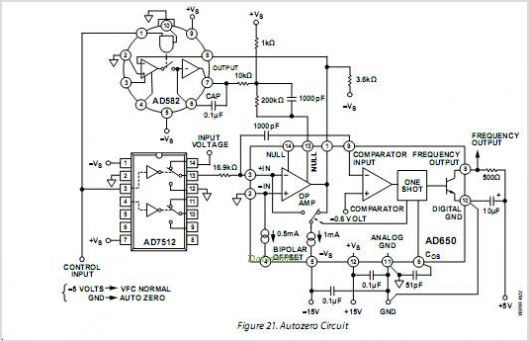
The AD652 Synchronous Voltage-to-Frequency Converter (SVFC) is a robust component designed for precision analog-to-digital conversion, featuring a typical nonlinearity of 0.002% (maximum of 0.005%) at an output frequency of 100 kHz. Its inherent monotonicity in the transfer function and the wide range of clock frequencies facilitate optimization of conversion time and resolution for various applications. The AD652 employs a variation of the well-known charge-balancing technique to execute the conversion process. It utilizes an external clock to establish the full-scale output frequency, instead of depending on the stability of an external capacitor. This approach yields a more stable and linear transfer function, offering significant advantages in both single-channel and multi-channel systems. Gain drift is minimized through the use of a precision low-drift reference and low temperature coefficient (TC) on-chip thin-film scaling resistors. Additionally, initial gain error is reduced to less than 0.5% by implementing laser-wafer-trimming. The design of the analog and digital sections of the AD652 enables operation from a single-ended power source, simplifying integration with isolated power supplies. The AD652 is available in five performance grades: the 20-pin PLCC packaged JP and KP grades are rated for operation over the commercial temperature range of 0°C to +70°C, while the 16-pin cerdip-packaged AQ and BQ grades are specified for the industrial temperature range of -40°C to +85°C. The AD652SQ variant is designed for operation across the extended temperature range of -55°C to +125°C.
The AD652 Synchronous Voltage-to-Frequency Converter is a highly versatile device utilized in applications requiring precise analog-to-digital conversion. The device's architecture is based on a synchronous operation that ensures low nonlinearity, making it suitable for high-accuracy applications. The typical nonlinearity of 0.002% ensures that the output frequency remains consistent with the input voltage across a wide range of conditions, which is critical in systems where precision is paramount.
The use of an external clock to define the full-scale output frequency is a key feature of the AD652. This design choice enhances stability and linearity, as it decouples the conversion process from the inherent variability of external capacitors. This feature is particularly beneficial in environments where temperature fluctuations and component aging could otherwise affect performance.
Gain drift is a critical parameter in precision applications; thus, the AD652 incorporates a low-drift reference and low TC thin-film scaling resistors on-chip. This design minimizes variations in gain over temperature and time, ensuring consistent performance. The implementation of laser-wafer-trimming to reduce initial gain error to below 0.5% further enhances the device's reliability and accuracy.
The operational flexibility of the AD652 is enhanced by its capability to function from a single-ended power source, which simplifies its integration into various systems. This feature is particularly useful in isolated power supply scenarios, where minimizing complexity is essential.
The AD652's availability in multiple performance grades allows for selection based on specific application requirements, including temperature range and packaging type. The 20-pin PLCC and 16-pin cerdip package options provide flexibility in design, catering to both commercial and industrial applications. The extended temperature range variant (AD652SQ) is particularly advantageous for applications in extreme environments, ensuring reliability and performance across a broad spectrum of operating conditions. Overall, the AD652 is an essential component for engineers seeking high precision in analog-to-digital conversion tasks.The AD652 Synchronous Voltage-to-Frequency Converter (SVFC) is a powerful building block for precision Analog-to-digital conversion, offering typical nonlinearity of 0. 002% (0. 005% maximum) at a 100 kHz output frequency. The inherent monotonicity of the transfer function and wide range of Clock frequencies allows the conversion time and resolution
to be optimized for specific applications. The AD652 uses a variation of the popular charge-balancing technique to perform the conversion function. The AD652 uses an external Clock to define the full-scale output frequency, rather than relying on the stability of an external capacitor.
The result is a more stable, more linear transfer function, with significant application benefits in both single and multichannel systems. Gain drift is minimized using a precision low drift reference and low TC on-chip thin-film scaling resistors.
Furthermore, the initial gain error is reduced to less than 0. 5% by the use of laser-wafer-trimming. The Analog and digital sections of the AD652 have been designed to allow operation from a single-ended power source, simplifying its use with isolated power supplies. The AD652 is available in five performance grades. The 20-pin PLCC packaged JP and KP grades are specified for operation over the 0C to +70C commercial temperature range.
The 16- pin cerdip-packaged AQ and BQ grades are specified for operation over the -40C to +85C industrial temperature range, and the AD652SQ is available for operation over the full -55C to +125C extended temperature range. 🔗 External reference
The AD652 Synchronous Voltage-to-Frequency Converter is a highly versatile device utilized in applications requiring precise analog-to-digital conversion. The device's architecture is based on a synchronous operation that ensures low nonlinearity, making it suitable for high-accuracy applications. The typical nonlinearity of 0.002% ensures that the output frequency remains consistent with the input voltage across a wide range of conditions, which is critical in systems where precision is paramount.
The use of an external clock to define the full-scale output frequency is a key feature of the AD652. This design choice enhances stability and linearity, as it decouples the conversion process from the inherent variability of external capacitors. This feature is particularly beneficial in environments where temperature fluctuations and component aging could otherwise affect performance.
Gain drift is a critical parameter in precision applications; thus, the AD652 incorporates a low-drift reference and low TC thin-film scaling resistors on-chip. This design minimizes variations in gain over temperature and time, ensuring consistent performance. The implementation of laser-wafer-trimming to reduce initial gain error to below 0.5% further enhances the device's reliability and accuracy.
The operational flexibility of the AD652 is enhanced by its capability to function from a single-ended power source, which simplifies its integration into various systems. This feature is particularly useful in isolated power supply scenarios, where minimizing complexity is essential.
The AD652's availability in multiple performance grades allows for selection based on specific application requirements, including temperature range and packaging type. The 20-pin PLCC and 16-pin cerdip package options provide flexibility in design, catering to both commercial and industrial applications. The extended temperature range variant (AD652SQ) is particularly advantageous for applications in extreme environments, ensuring reliability and performance across a broad spectrum of operating conditions. Overall, the AD652 is an essential component for engineers seeking high precision in analog-to-digital conversion tasks.The AD652 Synchronous Voltage-to-Frequency Converter (SVFC) is a powerful building block for precision Analog-to-digital conversion, offering typical nonlinearity of 0. 002% (0. 005% maximum) at a 100 kHz output frequency. The inherent monotonicity of the transfer function and wide range of Clock frequencies allows the conversion time and resolution
to be optimized for specific applications. The AD652 uses a variation of the popular charge-balancing technique to perform the conversion function. The AD652 uses an external Clock to define the full-scale output frequency, rather than relying on the stability of an external capacitor.
The result is a more stable, more linear transfer function, with significant application benefits in both single and multichannel systems. Gain drift is minimized using a precision low drift reference and low TC on-chip thin-film scaling resistors.
Furthermore, the initial gain error is reduced to less than 0. 5% by the use of laser-wafer-trimming. The Analog and digital sections of the AD652 have been designed to allow operation from a single-ended power source, simplifying its use with isolated power supplies. The AD652 is available in five performance grades. The 20-pin PLCC packaged JP and KP grades are specified for operation over the 0C to +70C commercial temperature range.
The 16- pin cerdip-packaged AQ and BQ grades are specified for operation over the -40C to +85C industrial temperature range, and the AD652SQ is available for operation over the full -55C to +125C extended temperature range. 🔗 External reference