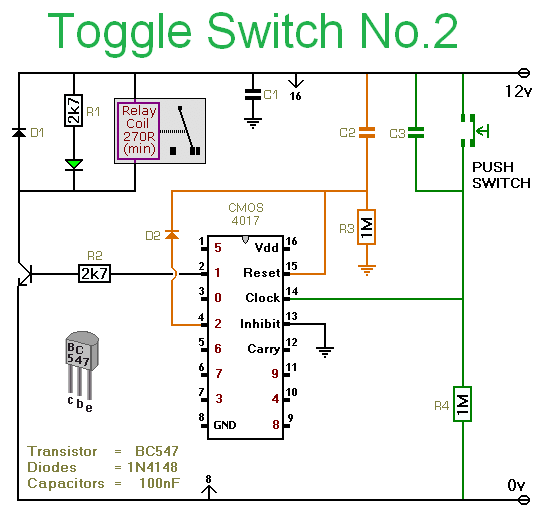
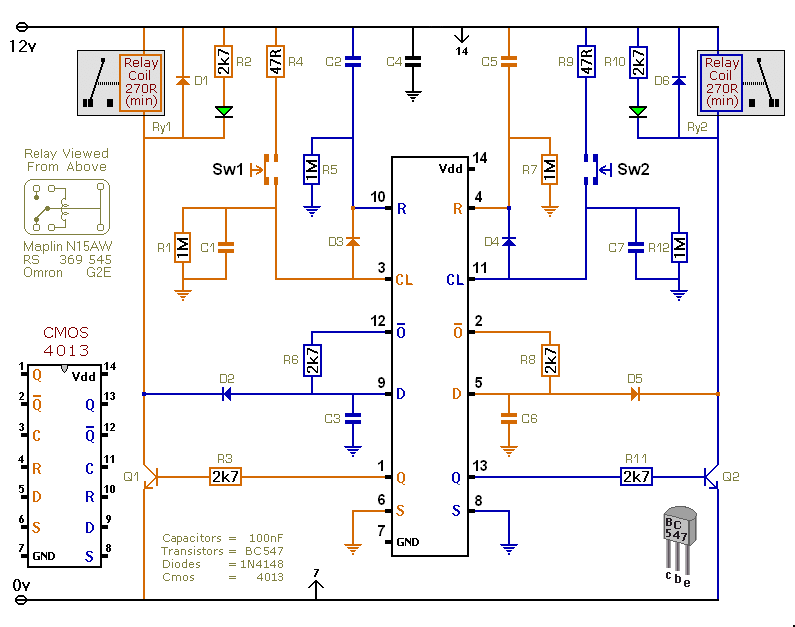
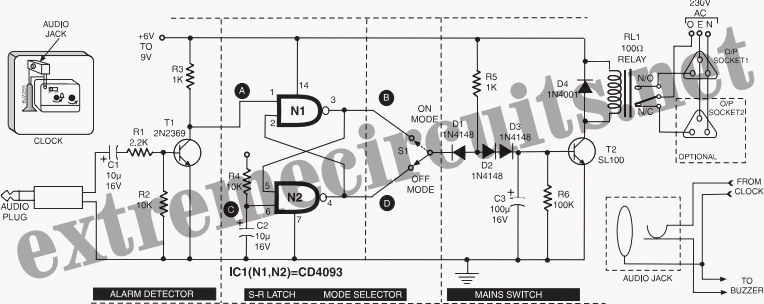
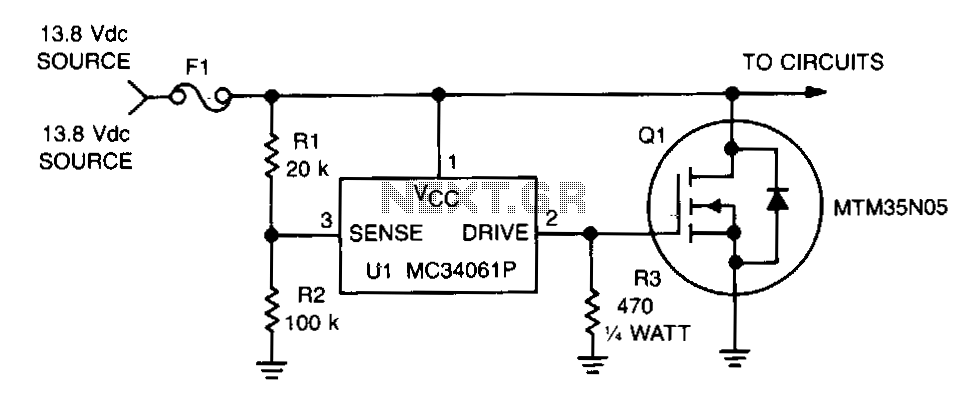
Voltage window switch
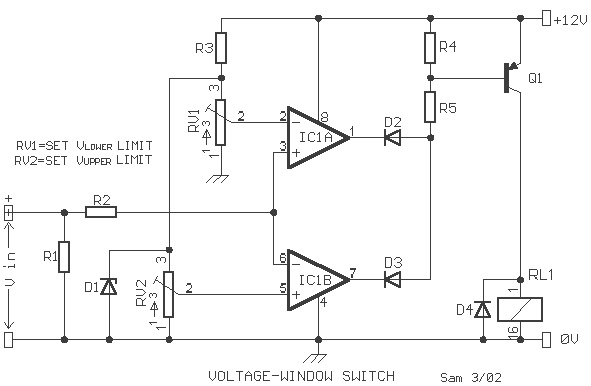
A voltage window switch is in practice the basic lower window limit of this circuit is roughly 3V and the upper limit is 9V. The window range can be extended by fitting a suitable range
Part List
R1-2=10Kohm D1=9V1/ 0.5W Zener IC1=TL072 R3=1Kohm D2-3=1N4148 Q1=BC214 R4=2.2Kohm D4=1N4001 RL1=12V >120ohm Relay R5=4.7Kohm RV1-2=47Kohm pot.
The voltage window switch circuit operates within a specified voltage range, with a lower limit of approximately 3V and an upper limit of around 9V. This functionality allows for the detection of voltage levels within the defined window, enabling various applications, such as over-voltage or under-voltage protection in electronic devices.
The circuit includes several key components:
- Resistors R1 and R2, both rated at 10 kΩ, are configured as a voltage divider, which helps set the reference voltage levels for the window limits.
- The Zener diode D1 (9V1/0.5W) serves to clamp the voltage at the upper limit, ensuring that the voltage does not exceed 9V, while diodes D2 and D3 (1N4148) are used for signal conditioning, providing rectification and protecting the circuit from reverse voltage spikes.
- The operational amplifier IC1 (TL072) is utilized for its high input impedance and low noise characteristics, making it suitable for precise voltage monitoring and comparison.
- Transistor Q1 (BC214) acts as a switching device that responds to the output of the operational amplifier, controlling the relay RL1 (12V, >120Ω) to activate or deactivate based on the input voltage conditions.
- Resistors R3 (1 kΩ), R4 (2.2 kΩ), and R5 (4.7 kΩ) are included to set various gain and biasing levels in the circuit, ensuring proper functionality and stability.
- Potentiometers RV1 and RV2 (47 kΩ each) allow for fine-tuning of the voltage levels, enabling the user to adjust the window limits as required for specific applications.
This voltage window switch circuit can be applied in numerous scenarios, such as battery management systems, power supply monitoring, or any application requiring voltage threshold detection and control. The design can be further modified by selecting different resistor and Zener diode values to expand the voltage window range according to specific requirements.A voltage window switch is in practice the basic lower window limit of this circuit is roughly 3V and the upper limit is 9V. The window range can be extended by fitting a suitable range Part List R1-2=10Kohm D1=9V1/ 0.5W Zener IC1=TL072 R3=1Kohm D2-3=1N4148 Q1=BC214 R4=2.2Kohm D4=1N4001 RL1=12V >120ohm Relay R5=4.7Kohm RV1-2=47Kohm pot. 🔗 External reference
Part List
R1-2=10Kohm D1=9V1/ 0.5W Zener IC1=TL072 R3=1Kohm D2-3=1N4148 Q1=BC214 R4=2.2Kohm D4=1N4001 RL1=12V >120ohm Relay R5=4.7Kohm RV1-2=47Kohm pot.
The voltage window switch circuit operates within a specified voltage range, with a lower limit of approximately 3V and an upper limit of around 9V. This functionality allows for the detection of voltage levels within the defined window, enabling various applications, such as over-voltage or under-voltage protection in electronic devices.
The circuit includes several key components:
- Resistors R1 and R2, both rated at 10 kΩ, are configured as a voltage divider, which helps set the reference voltage levels for the window limits.
- The Zener diode D1 (9V1/0.5W) serves to clamp the voltage at the upper limit, ensuring that the voltage does not exceed 9V, while diodes D2 and D3 (1N4148) are used for signal conditioning, providing rectification and protecting the circuit from reverse voltage spikes.
- The operational amplifier IC1 (TL072) is utilized for its high input impedance and low noise characteristics, making it suitable for precise voltage monitoring and comparison.
- Transistor Q1 (BC214) acts as a switching device that responds to the output of the operational amplifier, controlling the relay RL1 (12V, >120Ω) to activate or deactivate based on the input voltage conditions.
- Resistors R3 (1 kΩ), R4 (2.2 kΩ), and R5 (4.7 kΩ) are included to set various gain and biasing levels in the circuit, ensuring proper functionality and stability.
- Potentiometers RV1 and RV2 (47 kΩ each) allow for fine-tuning of the voltage levels, enabling the user to adjust the window limits as required for specific applications.
This voltage window switch circuit can be applied in numerous scenarios, such as battery management systems, power supply monitoring, or any application requiring voltage threshold detection and control. The design can be further modified by selecting different resistor and Zener diode values to expand the voltage window range according to specific requirements.A voltage window switch is in practice the basic lower window limit of this circuit is roughly 3V and the upper limit is 9V. The window range can be extended by fitting a suitable range Part List R1-2=10Kohm D1=9V1/ 0.5W Zener IC1=TL072 R3=1Kohm D2-3=1N4148 Q1=BC214 R4=2.2Kohm D4=1N4001 RL1=12V >120ohm Relay R5=4.7Kohm RV1-2=47Kohm pot. 🔗 External reference