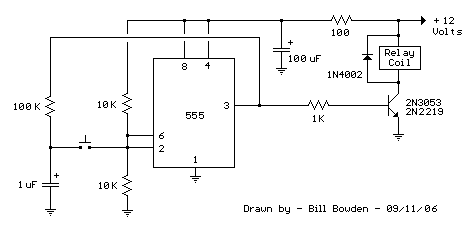
Water Activated Sensor Alarm Using 555 PCB

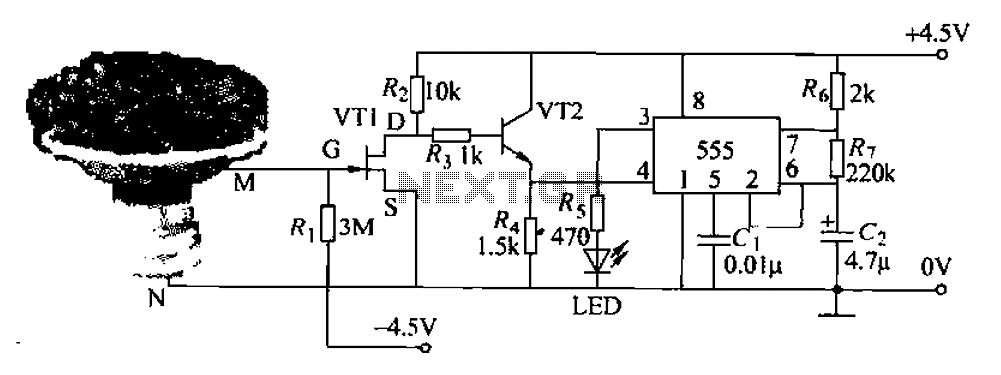
The circuit utilizes a 555 integrated circuit (IC) functioning as an astable multivibrator. When a positive 9 volts is applied to pin 8, the circuit generates sound through a speaker. The connection to pin 8 is routed through a transistor, specifically a BC 109C or BC 548. In this configuration, the base of the NPN transistor does not receive any positive voltage. However, when the resistance between the contacts decreases due to the presence of water, the transistor receives base voltage, activating the circuit to produce sound. The output from pin 3 of the 555 IC can be connected to a loudspeaker through a 100 µF electrolytic capacitor. Resistors R1 and R2 are employed for biasing the IC. The tone of the sound emitted from the speaker can be modified by adjusting the value of capacitor C1.
The described circuit operates as a water detection alarm system, leveraging the 555 timer's astable multivibrator configuration to generate an audible alert when moisture is detected. The 555 timer is a versatile component frequently used in timer, delay, pulse generation, and oscillator applications. In this specific design, it is configured to oscillate continuously, producing a square wave output at pin 3.
The circuit's functionality hinges on the behavior of the NPN transistor in response to changes in resistance caused by water. Under normal conditions, the base of the transistor is not biased, keeping it in the off state. Once water bridges the contacts, the resistance drops, allowing current to flow into the base of the transistor. This action turns the transistor on, enabling current to flow from the collector to the emitter, thus powering the speaker and generating sound.
The choice of a 100 µF electrolytic capacitor in series with the loudspeaker serves to block any DC component from the output while allowing the AC signal (the audio tone) to pass through. This configuration protects the speaker from potential damage due to DC voltage. The resistors R1 and R2 are critical for setting the operating point of the 555 timer, ensuring it functions correctly within its desired frequency range. The values of these resistors can be adjusted to change the frequency of oscillation, which in turn affects the pitch of the sound produced.
Capacitor C1 plays a significant role in determining the frequency of the output signal. By varying its capacitance, one can tune the circuit to produce different tones, allowing for customization of the alarm sound. This feature can be particularly useful in applications where distinct alerts are required for different types of detection.
Overall, this circuit provides a practical solution for water detection, combining simple components to create an effective alarm system that can be easily adapted for various applications.The circuit comprises a 555 IC as the core. This is designed to work as an astable multivibrator. When we connect a positive 9 volt to pin no. 8, the circuit will produce a sound through speaker. But here the connection to pin 8 goes through the transistor BC 109c or BC 548. In this condition, the base of the NPN transistor haven`t any positive vo ltage. But when the resistance between the "contacts" is lower due to water, the transistor get it base voltage and the circuit will produce a sound. We can connect the the 555 output pin no. 3 to loudspeaker through a 100uF electrolytic capacitor. The resistors, R1 and R2 are used for IC biasing. We can change the tone of the sound coming from the speaker by changing the value of capacitor C1. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit operates as a water detection alarm system, leveraging the 555 timer's astable multivibrator configuration to generate an audible alert when moisture is detected. The 555 timer is a versatile component frequently used in timer, delay, pulse generation, and oscillator applications. In this specific design, it is configured to oscillate continuously, producing a square wave output at pin 3.
The circuit's functionality hinges on the behavior of the NPN transistor in response to changes in resistance caused by water. Under normal conditions, the base of the transistor is not biased, keeping it in the off state. Once water bridges the contacts, the resistance drops, allowing current to flow into the base of the transistor. This action turns the transistor on, enabling current to flow from the collector to the emitter, thus powering the speaker and generating sound.
The choice of a 100 µF electrolytic capacitor in series with the loudspeaker serves to block any DC component from the output while allowing the AC signal (the audio tone) to pass through. This configuration protects the speaker from potential damage due to DC voltage. The resistors R1 and R2 are critical for setting the operating point of the 555 timer, ensuring it functions correctly within its desired frequency range. The values of these resistors can be adjusted to change the frequency of oscillation, which in turn affects the pitch of the sound produced.
Capacitor C1 plays a significant role in determining the frequency of the output signal. By varying its capacitance, one can tune the circuit to produce different tones, allowing for customization of the alarm sound. This feature can be particularly useful in applications where distinct alerts are required for different types of detection.
Overall, this circuit provides a practical solution for water detection, combining simple components to create an effective alarm system that can be easily adapted for various applications.The circuit comprises a 555 IC as the core. This is designed to work as an astable multivibrator. When we connect a positive 9 volt to pin no. 8, the circuit will produce a sound through speaker. But here the connection to pin 8 goes through the transistor BC 109c or BC 548. In this condition, the base of the NPN transistor haven`t any positive vo ltage. But when the resistance between the "contacts" is lower due to water, the transistor get it base voltage and the circuit will produce a sound. We can connect the the 555 output pin no. 3 to loudspeaker through a 100uF electrolytic capacitor. The resistors, R1 and R2 are used for IC biasing. We can change the tone of the sound coming from the speaker by changing the value of capacitor C1. 🔗 External reference