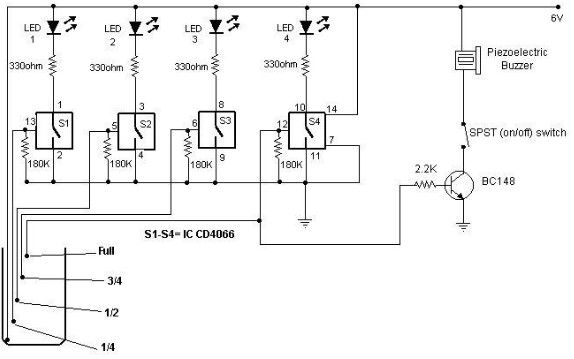
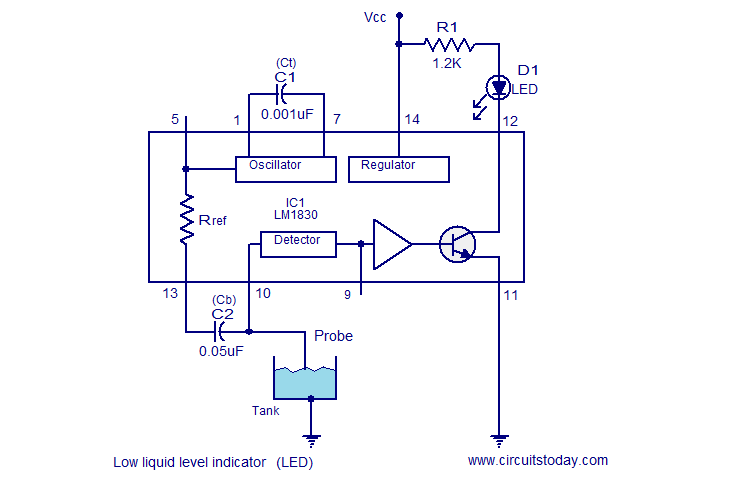
Water-level indicator
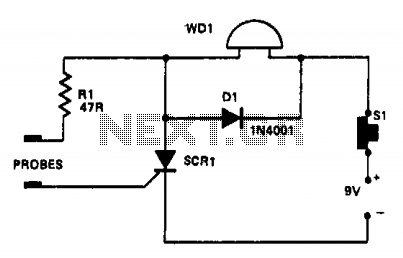
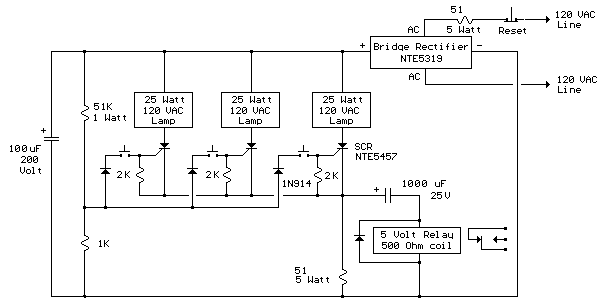
In this circuit, a warning device (WD1) is connected in series with a silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR1). When the liquid level creates a conductive path between the probes, the SCR becomes conductive, activating the warning device. The warning device can be a Sonalert (TM), a lamp, or a buzzer. Diode D1 functions as a transient suppressor.
Press switch SI to reset the circuit.
The circuit operates by monitoring the liquid level through two probes that detect conductivity. When the liquid reaches a certain level, it bridges the gap between the probes, allowing current to flow. This current triggers the SCR, which is a type of semiconductor device that can control power. Once the SCR is activated, it allows current to flow through the warning device (WD1), which then emits an audible or visual alert to notify users of the high liquid level.
The choice of the warning device can vary based on application requirements; a Sonalert provides an audible signal, while a lamp or buzzer can serve as visual or auditory alerts, respectively. The inclusion of diode D1 is critical for protecting the circuit from voltage spikes that may occur when the SCR switches off. This transient suppression helps to enhance the reliability and longevity of the circuit components.
To reset the system after an alert, the user must press switch SI. This action interrupts the circuit, allowing the SCR to turn off and the warning device to deactivate, thereby resetting the system to its initial state. The design ensures that the circuit remains operational and responsive to changes in liquid levels, providing essential monitoring capabilities in various applications, such as sump pumps, tanks, or other liquid storage systems.In this a warning device WD1 is in series with SCR1. When the liquid level causes a conductive path between the probes, the SCR conducts sounding WD1. The warning device may be a Sonalert (TM), a lamp or a buzzer.D1 acts as a transient suppressor. Press SI to reset the circuit.
Press switch SI to reset the circuit.
The circuit operates by monitoring the liquid level through two probes that detect conductivity. When the liquid reaches a certain level, it bridges the gap between the probes, allowing current to flow. This current triggers the SCR, which is a type of semiconductor device that can control power. Once the SCR is activated, it allows current to flow through the warning device (WD1), which then emits an audible or visual alert to notify users of the high liquid level.
The choice of the warning device can vary based on application requirements; a Sonalert provides an audible signal, while a lamp or buzzer can serve as visual or auditory alerts, respectively. The inclusion of diode D1 is critical for protecting the circuit from voltage spikes that may occur when the SCR switches off. This transient suppression helps to enhance the reliability and longevity of the circuit components.
To reset the system after an alert, the user must press switch SI. This action interrupts the circuit, allowing the SCR to turn off and the warning device to deactivate, thereby resetting the system to its initial state. The design ensures that the circuit remains operational and responsive to changes in liquid levels, providing essential monitoring capabilities in various applications, such as sump pumps, tanks, or other liquid storage systems.In this a warning device WD1 is in series with SCR1. When the liquid level causes a conductive path between the probes, the SCR conducts sounding WD1. The warning device may be a Sonalert (TM), a lamp or a buzzer.D1 acts as a transient suppressor. Press SI to reset the circuit.