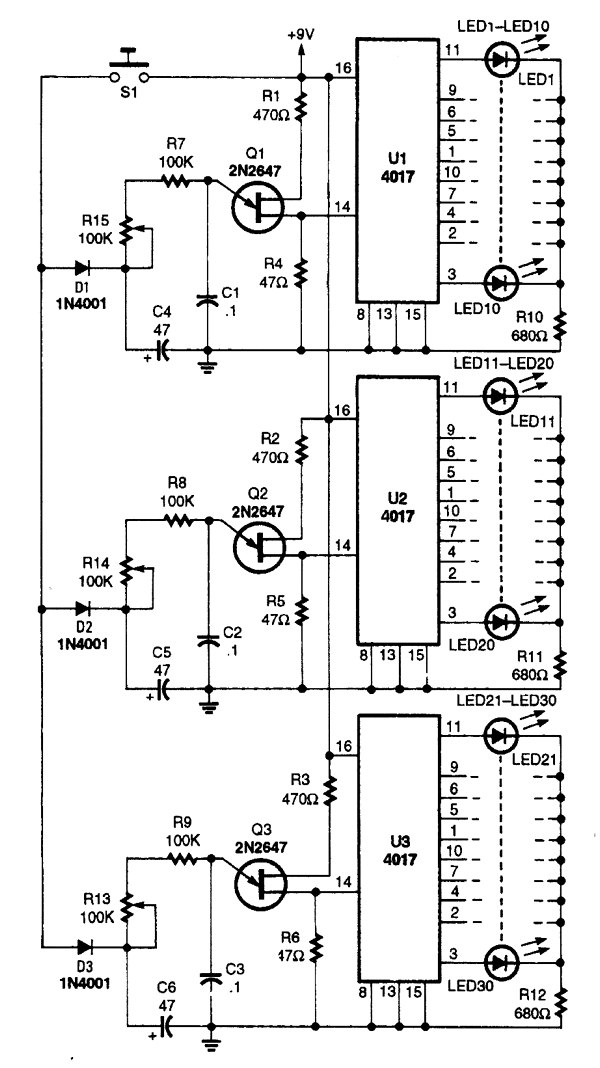
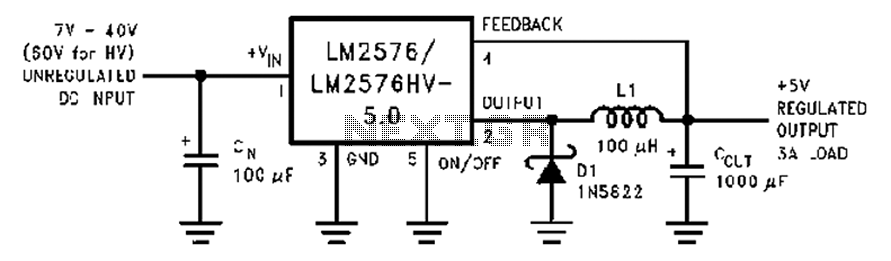
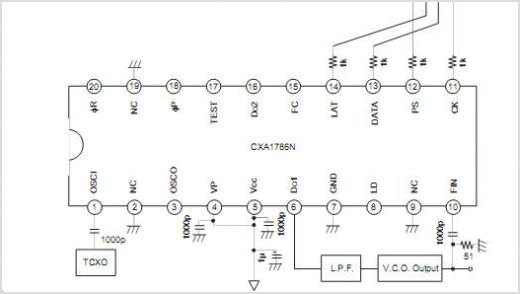
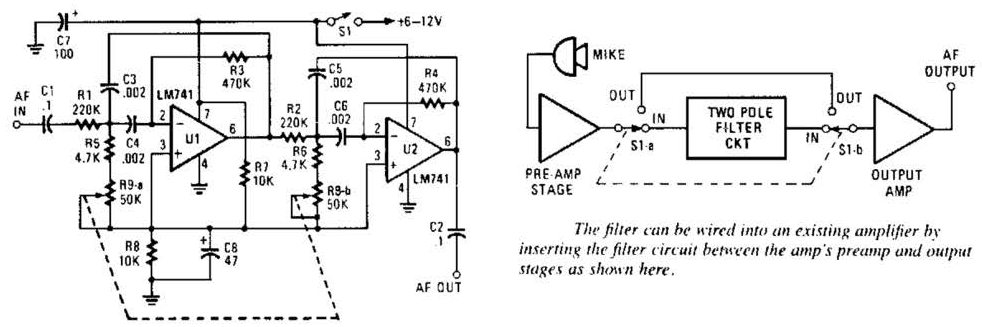
Wide band differential multiplexer
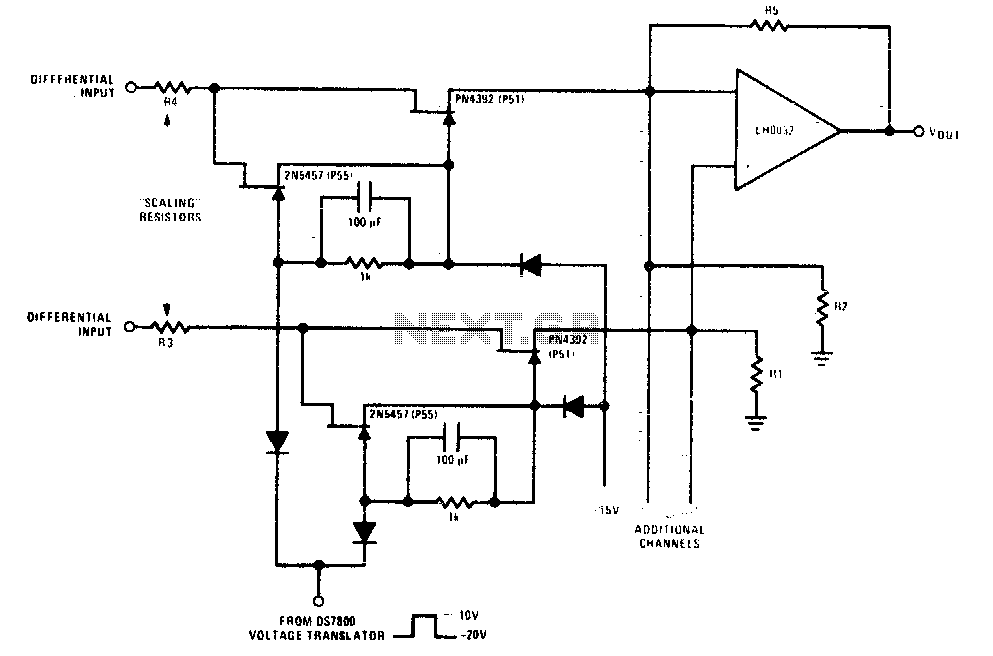
This design enables simultaneous handling of high-frequency signals and high toggle rates. Toggle rates of up to 1 MHz and megahertz signals are achievable with this circuit.
The circuit is designed to manage high-frequency signals effectively while maintaining rapid toggle rates, making it suitable for applications requiring quick signal processing and switching. The architecture typically employs high-speed transistors or operational amplifiers that can operate efficiently at frequencies reaching several megahertz.
In practical applications, this circuit can be utilized in digital communication systems, where data rates demand swift transitions between high and low states. The ability to toggle at rates up to 1 MHz ensures that the circuit can accommodate various modulation schemes, enhancing overall system performance.
To achieve the desired toggle rates, careful attention must be paid to the circuit layout, including minimizing parasitic capacitance and inductance, which can adversely affect performance at high frequencies. Components such as low-capacitance FETs or high-speed bipolar transistors are often selected to ensure rapid switching times and reliable operation.
Additionally, the circuit may incorporate feedback mechanisms to stabilize performance under varying load conditions, which is crucial for maintaining signal integrity. Proper decoupling of power supply lines and grounding techniques should also be implemented to reduce noise and improve the overall reliability of high-frequency operations.
Overall, this circuit design represents a robust solution for applications where both high-frequency signal processing and rapid switching capabilities are essential.This design allows high frequency signal handling and high toggle rates simultaneously Toggle rates up to 1 MHz and MHz signals are possible with this circuit. 🔗 External reference
The circuit is designed to manage high-frequency signals effectively while maintaining rapid toggle rates, making it suitable for applications requiring quick signal processing and switching. The architecture typically employs high-speed transistors or operational amplifiers that can operate efficiently at frequencies reaching several megahertz.
In practical applications, this circuit can be utilized in digital communication systems, where data rates demand swift transitions between high and low states. The ability to toggle at rates up to 1 MHz ensures that the circuit can accommodate various modulation schemes, enhancing overall system performance.
To achieve the desired toggle rates, careful attention must be paid to the circuit layout, including minimizing parasitic capacitance and inductance, which can adversely affect performance at high frequencies. Components such as low-capacitance FETs or high-speed bipolar transistors are often selected to ensure rapid switching times and reliable operation.
Additionally, the circuit may incorporate feedback mechanisms to stabilize performance under varying load conditions, which is crucial for maintaining signal integrity. Proper decoupling of power supply lines and grounding techniques should also be implemented to reduce noise and improve the overall reliability of high-frequency operations.
Overall, this circuit design represents a robust solution for applications where both high-frequency signal processing and rapid switching capabilities are essential.This design allows high frequency signal handling and high toggle rates simultaneously Toggle rates up to 1 MHz and MHz signals are possible with this circuit. 🔗 External reference