Wien-Bridge Sine-Wave Oscillator
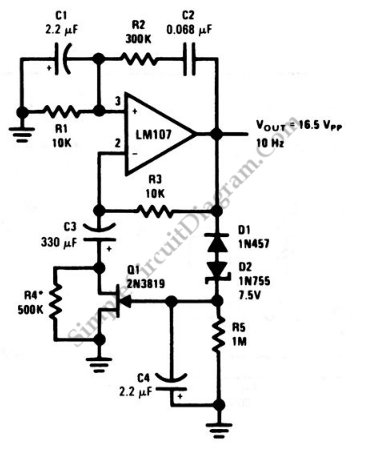
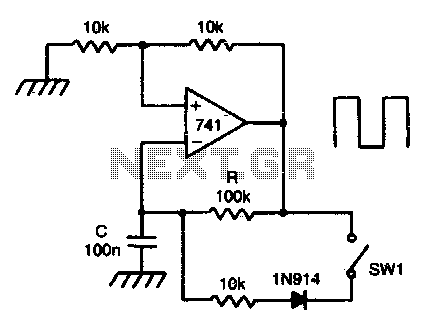
This is a Wien-bridge sine-wave oscillator circuit. This circuit utilizes negative-feedback stabilization to ensure that the gain does not exceed unity.
The Wien-bridge oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that generates sine waves. It consists of an amplifier and a frequency-selective network formed by resistors and capacitors. The circuit is notable for its ability to produce low-distortion sine waves across a range of frequencies.
The key components of a Wien-bridge oscillator include two resistors (R1 and R2) and two capacitors (C1 and C2) arranged in a bridge configuration. The resistors and capacitors are selected to set the desired frequency of oscillation, which can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1}{2\pi R \sqrt{C1 \cdot C2}} \]
where \( R \) is the resistance of R1 and R2 and \( C1 \) and \( C2 \) are the capacitances of C1 and C2.
In addition to the frequency-selective network, the Wien-bridge oscillator employs an operational amplifier (op-amp) configured in a feedback loop. The op-amp provides the necessary gain for oscillation. To ensure stable oscillation, a negative feedback mechanism is integrated into the circuit. This is typically achieved using a light bulb or thermistor, which adjusts the gain automatically. As the gain approaches unity, the circuit stabilizes, preventing oscillations from growing uncontrollably.
The output of the oscillator is a pure sine wave, making it suitable for various applications, including signal generation, audio testing, and function generation in laboratories. The simplicity and effectiveness of the Wien-bridge oscillator make it a popular choice among engineers and hobbyists alike.
In summary, the Wien-bridge sine-wave oscillator is a reliable circuit for generating high-quality sine waves, leveraging negative feedback to maintain stability and control over the gain, thus ensuring consistent performance across its operational frequency range.This is a Wien-bridge sine-wave oscillator circuit. This circuit uses negative-feedback stabilization to make sure the gain won`t go higher than unity to.. 🔗 External reference
The Wien-bridge oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that generates sine waves. It consists of an amplifier and a frequency-selective network formed by resistors and capacitors. The circuit is notable for its ability to produce low-distortion sine waves across a range of frequencies.
The key components of a Wien-bridge oscillator include two resistors (R1 and R2) and two capacitors (C1 and C2) arranged in a bridge configuration. The resistors and capacitors are selected to set the desired frequency of oscillation, which can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1}{2\pi R \sqrt{C1 \cdot C2}} \]
where \( R \) is the resistance of R1 and R2 and \( C1 \) and \( C2 \) are the capacitances of C1 and C2.
In addition to the frequency-selective network, the Wien-bridge oscillator employs an operational amplifier (op-amp) configured in a feedback loop. The op-amp provides the necessary gain for oscillation. To ensure stable oscillation, a negative feedback mechanism is integrated into the circuit. This is typically achieved using a light bulb or thermistor, which adjusts the gain automatically. As the gain approaches unity, the circuit stabilizes, preventing oscillations from growing uncontrollably.
The output of the oscillator is a pure sine wave, making it suitable for various applications, including signal generation, audio testing, and function generation in laboratories. The simplicity and effectiveness of the Wien-bridge oscillator make it a popular choice among engineers and hobbyists alike.
In summary, the Wien-bridge sine-wave oscillator is a reliable circuit for generating high-quality sine waves, leveraging negative feedback to maintain stability and control over the gain, thus ensuring consistent performance across its operational frequency range.This is a Wien-bridge sine-wave oscillator circuit. This circuit uses negative-feedback stabilization to make sure the gain won`t go higher than unity to.. 🔗 External reference