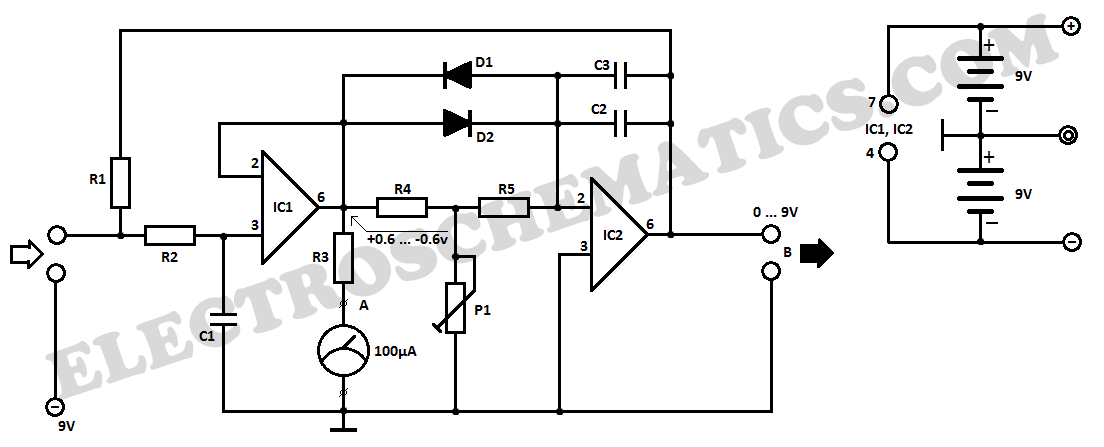
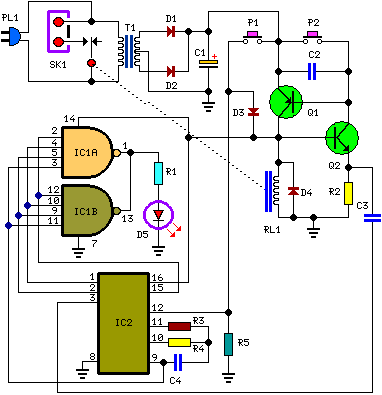
Wireless Ir Headphone Transmitter Circuit
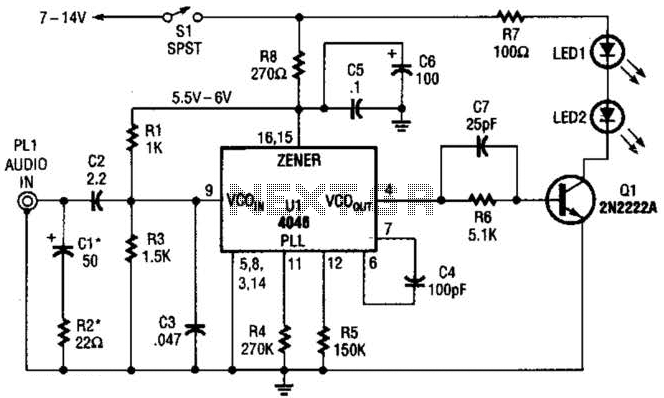
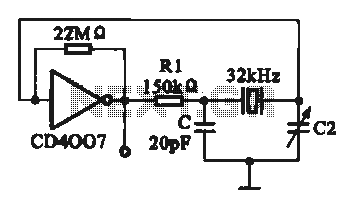
The transmitter for the wireless headphones is constructed using a CD4046 CMOS phase-locked loop, which is paired with a driver transistor and a set of infrared LEDs. While the CD4046 contains two phase comparators, a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO), a source follower, and a Zener reference, only the VCO is utilized in this application.
The circuit design employs the CD4046 as the central component, leveraging its VCO to generate a modulated signal that will be transmitted wirelessly. The VCO is capable of producing a frequency that varies based on the input voltage, making it suitable for audio transmission. The driver transistor serves to amplify the output from the VCO, ensuring that the signal strength is sufficient to drive the infrared LEDs effectively.
The infrared LEDs are configured to emit modulated light signals, which carry the audio information to the wireless headphones. The use of infrared technology allows for a line-of-sight communication method, minimizing interference from other electronic devices. The choice of infrared LEDs is critical, as they provide a reliable transmission medium with minimal noise.
In terms of power supply, the circuit typically requires a low-voltage DC source, which can be sourced from batteries. Proper decoupling capacitors should be included to filter out any noise that may affect the performance of the VCO and the overall circuit stability. Additionally, if the application requires, a simple low-pass filter can be implemented at the output stage to smooth the modulated signal before it reaches the infrared LEDs.
Overall, this transmitter design efficiently converts audio signals into modulated infrared light, enabling wireless audio transmission to headphones, while maintaining simplicity and reliability in its operation. The transmitter for the wireless headphones is built around a CD4046 CMOS phase-locked loop, coupled with a driver transistor, and a pair of infrared LEDs. Although the CD4046 is comprised of two phase comparators, a voltage-controlled oscillator (or VCO), a source follower, and a zencr reference, only its VCO is used in this application. 🔗 External reference
The circuit design employs the CD4046 as the central component, leveraging its VCO to generate a modulated signal that will be transmitted wirelessly. The VCO is capable of producing a frequency that varies based on the input voltage, making it suitable for audio transmission. The driver transistor serves to amplify the output from the VCO, ensuring that the signal strength is sufficient to drive the infrared LEDs effectively.
The infrared LEDs are configured to emit modulated light signals, which carry the audio information to the wireless headphones. The use of infrared technology allows for a line-of-sight communication method, minimizing interference from other electronic devices. The choice of infrared LEDs is critical, as they provide a reliable transmission medium with minimal noise.
In terms of power supply, the circuit typically requires a low-voltage DC source, which can be sourced from batteries. Proper decoupling capacitors should be included to filter out any noise that may affect the performance of the VCO and the overall circuit stability. Additionally, if the application requires, a simple low-pass filter can be implemented at the output stage to smooth the modulated signal before it reaches the infrared LEDs.
Overall, this transmitter design efficiently converts audio signals into modulated infrared light, enabling wireless audio transmission to headphones, while maintaining simplicity and reliability in its operation. The transmitter for the wireless headphones is built around a CD4046 CMOS phase-locked loop, coupled with a driver transistor, and a pair of infrared LEDs. Although the CD4046 is comprised of two phase comparators, a voltage-controlled oscillator (or VCO), a source follower, and a zencr reference, only its VCO is used in this application. 🔗 External reference