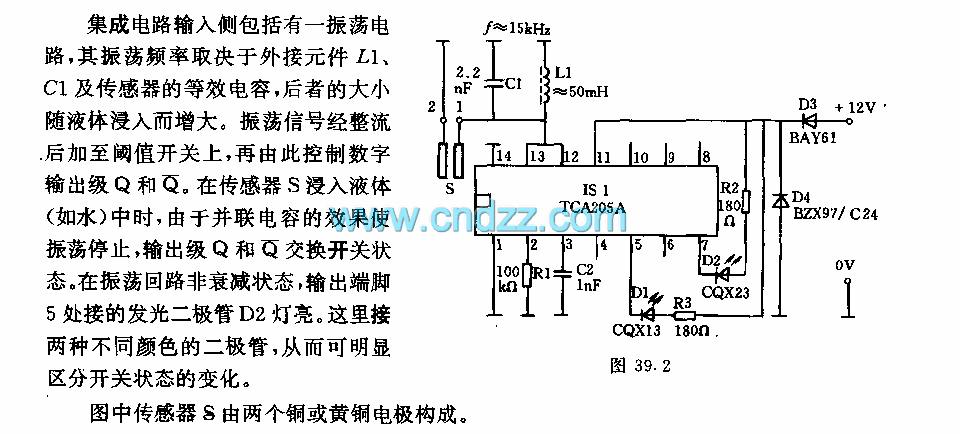
With FET amplifier output transformer circuit
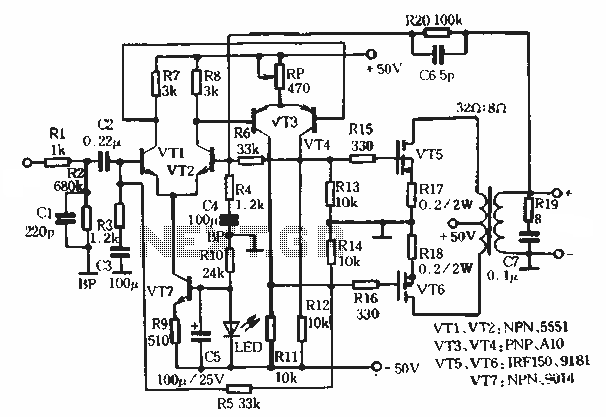
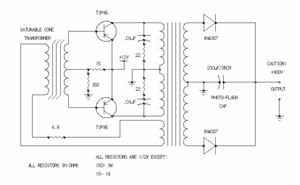
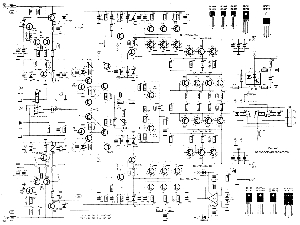
This article describes a transformer-based output FET amplifier, with tonal characteristics similar to those of tube amplifiers. It introduces various effects that are significant for audio enthusiasts. Power amplifier specifications include a rated output power of 50W (with an 8Ω load), a frequency response of 40Hz to 25kHz with a flat curve, harmonic distortion measured at 0.5% (at 1kHz), a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of 90dB, and an input sensitivity of 800mV. The power amplifier utilizes a double differential amplifier configuration with a preamp and an output transformer in the FET power amplifier stage, adhering to the "simplicity first" design principle. The circuit features a pair of NPN transistors (V1, V2) forming the first differential amplifier, while another pair of PNP transistors constitutes the second differential amplifier through mutual diodes (V3, V4). This arrangement, which employs transistors of different conductivity types, enhances power supply voltage utilization and improves thermal stability. Resistors R5 and R6 are configured to provide a two-way exchange of negative feedback, ensuring complementary symmetry within the circuit. This design promotes good DC stability and minimizes distortion, resulting in a wide frequency response. The output from the preceding stage (V3, V4) has opposite polarity at the collector, functioning as a complementary push-pull power amplification stage, with reference waveforms derived from two opposing odd signal sources.
The described transformer-based output FET amplifier is engineered to deliver high-fidelity audio reproduction, closely resembling the warm tonal qualities associated with traditional tube amplifiers. The design incorporates a transformer that plays a critical role in impedance matching and signal coupling, facilitating efficient power transfer while maintaining audio integrity.
The power amplifier's rated output of 50W at an 8Ω load ensures compatibility with a wide range of speakers, making it suitable for various audio applications. The frequency response extending from 40Hz to 25kHz allows the amplifier to reproduce low bass notes and high-frequency details effectively, contributing to a balanced audio output.
Harmonic distortion is kept to a minimum at 0.5% when measured at 1kHz, which is crucial for preserving the clarity and naturalness of the audio signal. The SNR of 90dB indicates that the amplifier can produce a clean sound with minimal background noise, enhancing the listening experience.
The double differential amplifier configuration is pivotal in achieving high performance. By utilizing both NPN and PNP transistors, the design capitalizes on their complementary characteristics, which not only improves voltage utilization but also enhances the thermal stability of the amplifier. This is particularly important in audio applications where temperature fluctuations can affect performance.
Negative feedback provided by resistors R5 and R6 plays a significant role in stabilizing the circuit and reducing distortion. This feedback mechanism contributes to the overall linearity of the amplifier, ensuring that the output signal closely follows the input signal without unwanted alterations.
In summary, this transformer-based output FET amplifier exemplifies a well-thought-out design that prioritizes simplicity, stability, and audio fidelity. Its robust specifications make it an excellent choice for audio enthusiasts seeking a reliable amplifier with tube-like tonal qualities.This article describes a transformer with output FET amplifier production, its tone has been very close to the tube amp effects introduced to the circuit for the majority of audio enthusiasts reference. Power amplifier Specifications: Rated output power: 50w (load 8n); Frequency response: 4 0Hz ~ 25Hz curve flat; harmonic distortion: 0.5 (measured under lkHz); SNR: 90d13; input sensitivity: 800n1V o the power amplifier by a double differential amplifier with a preamp and output transformer FET power amplifier stage configuration, the design idea of "simplicity first" principle. Figure 7-15 can be seen from a pair of NPN type transistor Vl.v2 constitutes a first differential amplifier, the other a pair of PNP type.
Mutual diode V3, V4 constitute _r second differential amplifier. Two different conductivity type transistors increases the power supply voltage utilization, but have different temperature characteristics, so that significantly improve the stability of the whole machine. FIG resistors R5, R6-oriented stage circuit provides a two-way exchange of negative feedback, and the circuit full complementary symmetry, so good DC stability of the circuit, while reducing the degree of distortion, wide forehead noon.
Circuit the output of the preceding stage V3, V4 polarity opposite the collector, as a complementary push-pull power amplifying stage after the reference waveforms for the two opposite odd signal source
The described transformer-based output FET amplifier is engineered to deliver high-fidelity audio reproduction, closely resembling the warm tonal qualities associated with traditional tube amplifiers. The design incorporates a transformer that plays a critical role in impedance matching and signal coupling, facilitating efficient power transfer while maintaining audio integrity.
The power amplifier's rated output of 50W at an 8Ω load ensures compatibility with a wide range of speakers, making it suitable for various audio applications. The frequency response extending from 40Hz to 25kHz allows the amplifier to reproduce low bass notes and high-frequency details effectively, contributing to a balanced audio output.
Harmonic distortion is kept to a minimum at 0.5% when measured at 1kHz, which is crucial for preserving the clarity and naturalness of the audio signal. The SNR of 90dB indicates that the amplifier can produce a clean sound with minimal background noise, enhancing the listening experience.
The double differential amplifier configuration is pivotal in achieving high performance. By utilizing both NPN and PNP transistors, the design capitalizes on their complementary characteristics, which not only improves voltage utilization but also enhances the thermal stability of the amplifier. This is particularly important in audio applications where temperature fluctuations can affect performance.
Negative feedback provided by resistors R5 and R6 plays a significant role in stabilizing the circuit and reducing distortion. This feedback mechanism contributes to the overall linearity of the amplifier, ensuring that the output signal closely follows the input signal without unwanted alterations.
In summary, this transformer-based output FET amplifier exemplifies a well-thought-out design that prioritizes simplicity, stability, and audio fidelity. Its robust specifications make it an excellent choice for audio enthusiasts seeking a reliable amplifier with tube-like tonal qualities.This article describes a transformer with output FET amplifier production, its tone has been very close to the tube amp effects introduced to the circuit for the majority of audio enthusiasts reference. Power amplifier Specifications: Rated output power: 50w (load 8n); Frequency response: 4 0Hz ~ 25Hz curve flat; harmonic distortion: 0.5 (measured under lkHz); SNR: 90d13; input sensitivity: 800n1V o the power amplifier by a double differential amplifier with a preamp and output transformer FET power amplifier stage configuration, the design idea of "simplicity first" principle. Figure 7-15 can be seen from a pair of NPN type transistor Vl.v2 constitutes a first differential amplifier, the other a pair of PNP type.
Mutual diode V3, V4 constitute _r second differential amplifier. Two different conductivity type transistors increases the power supply voltage utilization, but have different temperature characteristics, so that significantly improve the stability of the whole machine. FIG resistors R5, R6-oriented stage circuit provides a two-way exchange of negative feedback, and the circuit full complementary symmetry, so good DC stability of the circuit, while reducing the degree of distortion, wide forehead noon.
Circuit the output of the preceding stage V3, V4 polarity opposite the collector, as a complementary push-pull power amplifying stage after the reference waveforms for the two opposite odd signal source