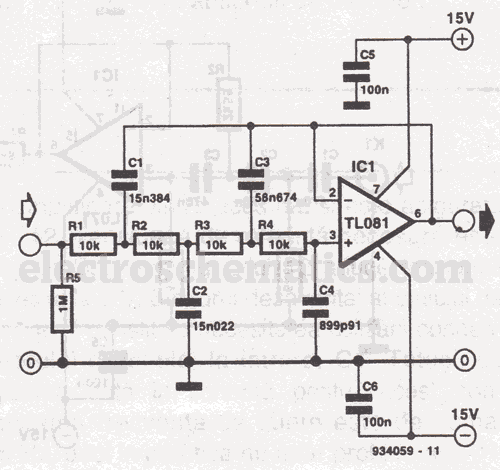
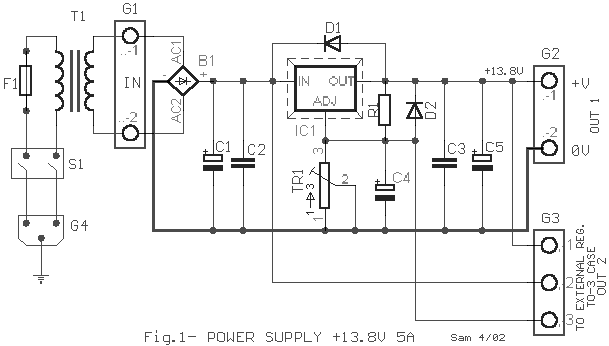
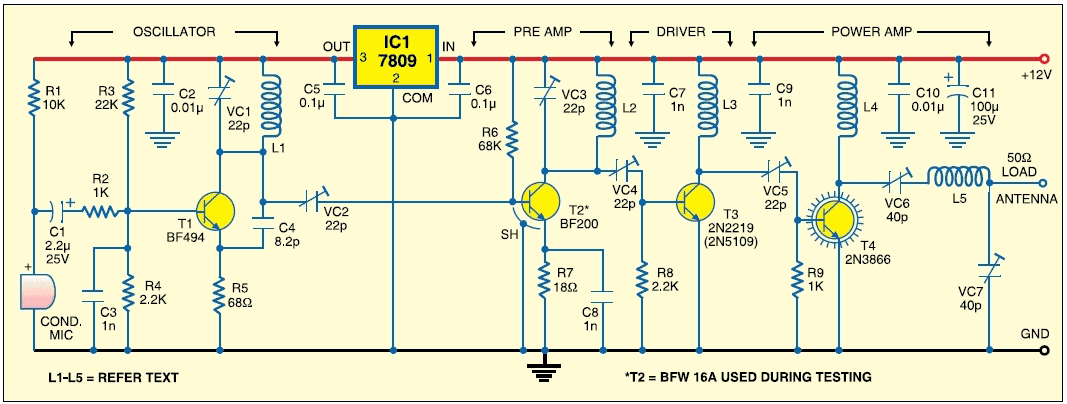
555 astable multivibrator circuit diagram
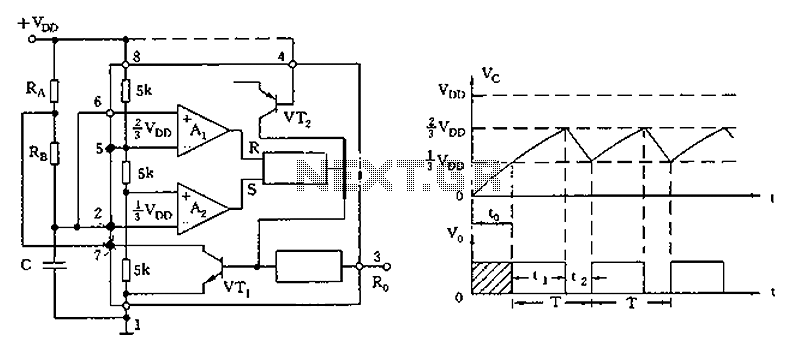
The circuit diagram illustrates the 555 timer (or 556 timer in half configuration) configured in astable multivibrator mode. It features three resistive and capacitive elements connected as shown. In one-shot mode, the trigger terminal (pin 2) is connected to the charge and discharge circuit of capacitor C, rather than being controlled by an external trigger.
The 555 timer is a versatile integrated circuit commonly used in various applications, including timing, pulse generation, and oscillation. In astable mode, the 555 timer continuously switches between its high and low states, generating a square wave output. This mode is characterized by the absence of a stable state, making it ideal for applications such as clock pulses for digital circuits or LED flashing.
The configuration involves connecting two resistors (R1 and R2) and a capacitor (C) to the 555 timer. The resistors determine the charge and discharge times of the capacitor, which in turn sets the frequency and duty cycle of the output waveform. The output frequency (f) can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1.44}{(R1 + 2R2)C} \]
The duty cycle (D) is given by:
\[ D = \frac{R2}{R1 + 2R2} \]
In one-shot mode, the 555 timer generates a single pulse when triggered. In this case, the trigger input on pin 2 is connected to the charge and discharge circuit of capacitor C, allowing the capacitor to control the timing interval for the output pulse. The duration of the output pulse is determined by the resistor (R) connected to the discharge pin (pin 7) and the capacitor (C) connected to the threshold pin (pin 6). The pulse width (T) can be calculated as:
\[ T = 1.1 \times R \times C \]
This configuration allows for precise control over timing applications without the need for external triggering mechanisms, making it suitable for various electronic projects, including timers, pulse-width modulation, and frequency generation.As illustrated, the 555 (or 556 1/2) and three resistive, capacitive element connected as shown, constitute astable multivibrator mode. And one-shot mode except that only the t rigger terminal (pin 2) connected to the charge and discharge circuit C, rather than by external trigger control.
The 555 timer is a versatile integrated circuit commonly used in various applications, including timing, pulse generation, and oscillation. In astable mode, the 555 timer continuously switches between its high and low states, generating a square wave output. This mode is characterized by the absence of a stable state, making it ideal for applications such as clock pulses for digital circuits or LED flashing.
The configuration involves connecting two resistors (R1 and R2) and a capacitor (C) to the 555 timer. The resistors determine the charge and discharge times of the capacitor, which in turn sets the frequency and duty cycle of the output waveform. The output frequency (f) can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1.44}{(R1 + 2R2)C} \]
The duty cycle (D) is given by:
\[ D = \frac{R2}{R1 + 2R2} \]
In one-shot mode, the 555 timer generates a single pulse when triggered. In this case, the trigger input on pin 2 is connected to the charge and discharge circuit of capacitor C, allowing the capacitor to control the timing interval for the output pulse. The duration of the output pulse is determined by the resistor (R) connected to the discharge pin (pin 7) and the capacitor (C) connected to the threshold pin (pin 6). The pulse width (T) can be calculated as:
\[ T = 1.1 \times R \times C \]
This configuration allows for precise control over timing applications without the need for external triggering mechanisms, making it suitable for various electronic projects, including timers, pulse-width modulation, and frequency generation.As illustrated, the 555 (or 556 1/2) and three resistive, capacitive element connected as shown, constitute astable multivibrator mode. And one-shot mode except that only the t rigger terminal (pin 2) connected to the charge and discharge circuit C, rather than by external trigger control.