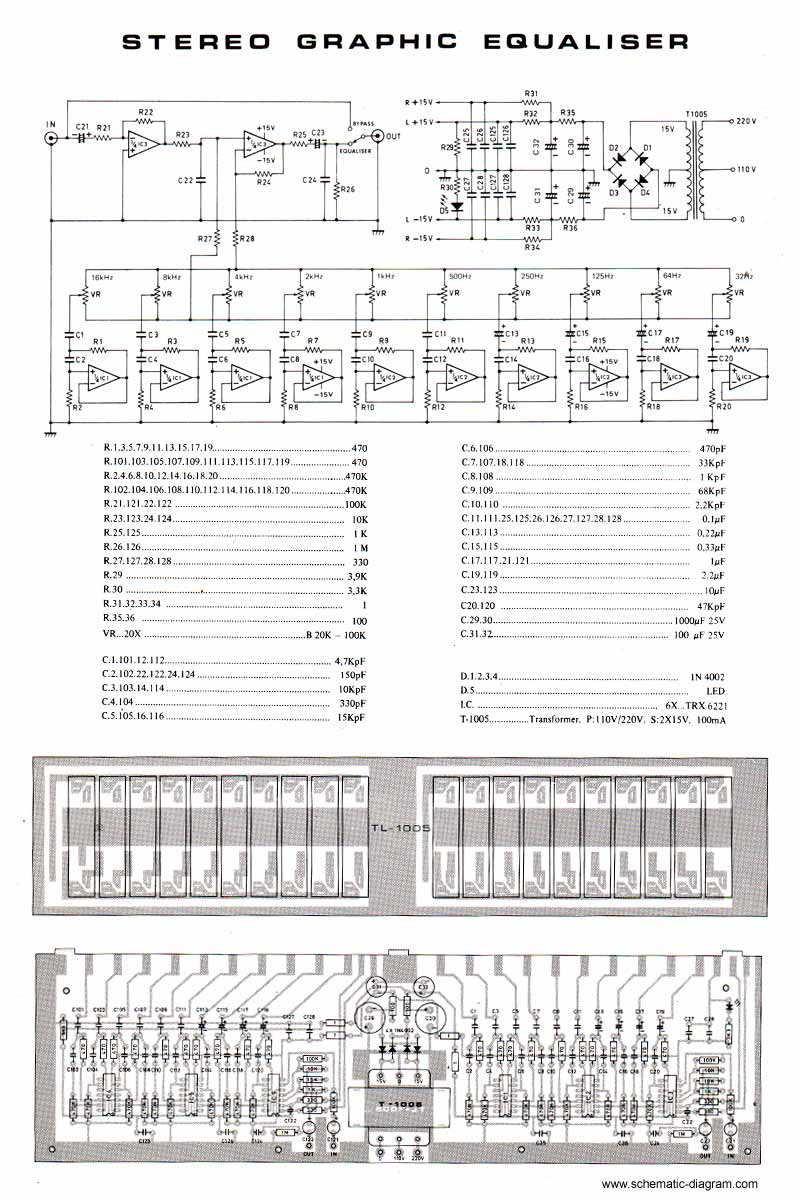
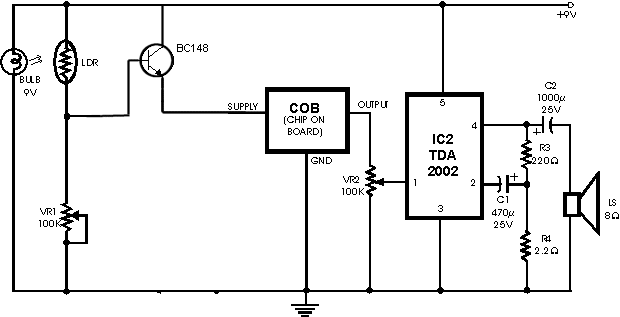
1.5V Joule Thief 2.0 circuit
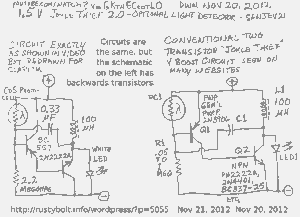
A schematic of a two-transistor Joule Thief was presented in a YouTube video by Sanjev21, which has since been removed.
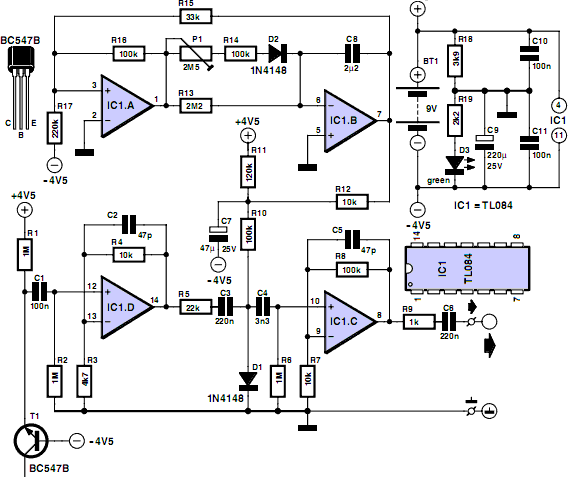
The two-transistor Joule Thief is a compact and efficient circuit designed to extract energy from low-voltage sources, such as depleted batteries. This circuit typically consists of two NPN transistors, a few passive components, and a transformer. The main purpose of the Joule Thief is to boost the voltage from a low-power source to a usable level, making it particularly useful for powering small electronic devices.
In the schematic, each transistor plays a crucial role in the oscillation process. The first transistor is responsible for initiating the oscillation by turning on and allowing current to flow through the primary winding of the transformer. This current generates a magnetic field, which induces a voltage in the secondary winding. As the magnetic field collapses, the induced voltage can be significantly higher than the original input voltage. The second transistor acts as a feedback mechanism that helps sustain the oscillation by providing additional current to the first transistor when the voltage at the base of the first transistor exceeds a certain threshold.
The passive components, including resistors and capacitors, are strategically placed to control the timing and frequency of the oscillation, as well as to ensure stable operation of the transistors. The circuit typically includes a feedback resistor that connects the collector of the first transistor to its base, which is essential for maintaining the oscillation. Additionally, a small capacitor may be used to filter out noise and stabilize the voltage levels in the circuit.
Overall, the two-transistor Joule Thief is a simple yet effective design that showcases the principles of inductive energy transfer and transistor operation, making it a popular project among electronics enthusiasts and hobbyists.I saw this Youtube video of a schematic of a two transistor Joule Thief by Sanjev21. I notice that this video has been removed. 🔗 External reference
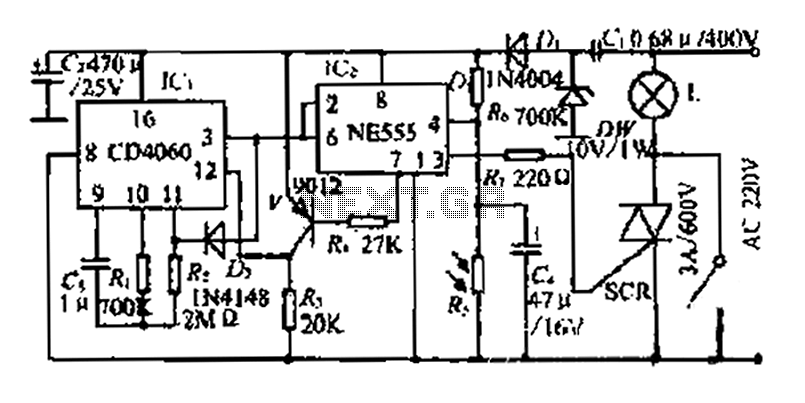
The two-transistor Joule Thief is a compact and efficient circuit designed to extract energy from low-voltage sources, such as depleted batteries. This circuit typically consists of two NPN transistors, a few passive components, and a transformer. The main purpose of the Joule Thief is to boost the voltage from a low-power source to a usable level, making it particularly useful for powering small electronic devices.
In the schematic, each transistor plays a crucial role in the oscillation process. The first transistor is responsible for initiating the oscillation by turning on and allowing current to flow through the primary winding of the transformer. This current generates a magnetic field, which induces a voltage in the secondary winding. As the magnetic field collapses, the induced voltage can be significantly higher than the original input voltage. The second transistor acts as a feedback mechanism that helps sustain the oscillation by providing additional current to the first transistor when the voltage at the base of the first transistor exceeds a certain threshold.
The passive components, including resistors and capacitors, are strategically placed to control the timing and frequency of the oscillation, as well as to ensure stable operation of the transistors. The circuit typically includes a feedback resistor that connects the collector of the first transistor to its base, which is essential for maintaining the oscillation. Additionally, a small capacitor may be used to filter out noise and stabilize the voltage levels in the circuit.
Overall, the two-transistor Joule Thief is a simple yet effective design that showcases the principles of inductive energy transfer and transistor operation, making it a popular project among electronics enthusiasts and hobbyists.I saw this Youtube video of a schematic of a two transistor Joule Thief by Sanjev21. I notice that this video has been removed. 🔗 External reference