1.5V LED FLasher Using 3 Transistors
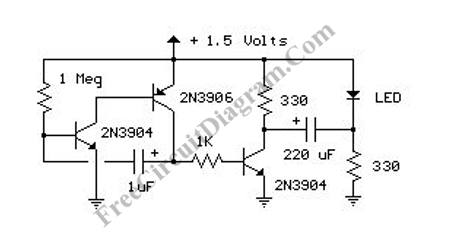
The LED flasher circuit operates by flashing an LED using only a 1.5-volt power supply. Typically, a power supply of more than 2 volts is required for an LED to function.
The LED flasher circuit designed for operation at 1.5 volts utilizes a simple yet effective configuration to enable the LED to flash. This circuit typically incorporates a 555 timer IC configured in astable mode, which generates a square wave output. The frequency of the flashing can be adjusted by varying the resistor and capacitor values connected to the timer.
In this configuration, the circuit includes a power source, usually a single AA battery, which provides the necessary 1.5 volts. The LED is connected to the output of the 555 timer, allowing it to turn on and off rapidly, creating a flashing effect. A resistor is placed in series with the LED to limit the current flowing through it, ensuring that the LED operates within its safe limits.
The use of a low voltage supply is advantageous for battery-operated devices, minimizing power consumption while still achieving the desired visual effect. The circuit can be further enhanced by adding a transistor to drive the LED if higher brightness is required, allowing for greater current flow without exceeding the output limits of the 555 timer.
Overall, this LED flasher circuit represents an efficient solution for applications requiring low power consumption while still providing a reliable flashing LED indicator.LED flasher circuit here will flash a LED using only 1.5 volts ?supply voltage. Normally, to make any LED lamp works, you need more than 2 volts power supply 🔗 External reference
The LED flasher circuit designed for operation at 1.5 volts utilizes a simple yet effective configuration to enable the LED to flash. This circuit typically incorporates a 555 timer IC configured in astable mode, which generates a square wave output. The frequency of the flashing can be adjusted by varying the resistor and capacitor values connected to the timer.
In this configuration, the circuit includes a power source, usually a single AA battery, which provides the necessary 1.5 volts. The LED is connected to the output of the 555 timer, allowing it to turn on and off rapidly, creating a flashing effect. A resistor is placed in series with the LED to limit the current flowing through it, ensuring that the LED operates within its safe limits.
The use of a low voltage supply is advantageous for battery-operated devices, minimizing power consumption while still achieving the desired visual effect. The circuit can be further enhanced by adding a transistor to drive the LED if higher brightness is required, allowing for greater current flow without exceeding the output limits of the 555 timer.
Overall, this LED flasher circuit represents an efficient solution for applications requiring low power consumption while still providing a reliable flashing LED indicator.LED flasher circuit here will flash a LED using only 1.5 volts ?supply voltage. Normally, to make any LED lamp works, you need more than 2 volts power supply 🔗 External reference