1 9V Variable Desktop Power Supply
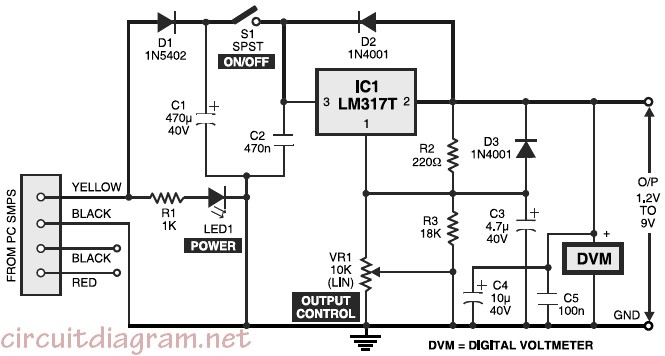
Variable desktop power supply that converts a high input voltage (12V) from the SMPS/PSU of a desktop computer into a small output voltage (1.25V to 9V).
The variable desktop power supply is designed to provide adjustable output voltages ranging from 1.25V to 9V, utilizing a high input voltage of 12V sourced from the switched-mode power supply (SMPS) or power supply unit (PSU) of a desktop computer. This device is particularly useful for powering various electronic components and circuits that require different operating voltages.
The core of the power supply typically consists of a buck converter circuit, which steps down the 12V input to the desired output voltage. The buck converter operates by switching a transistor on and off at a high frequency, controlling the energy transferred to an inductor. The average voltage across the inductor is regulated by adjusting the duty cycle of the switching signal, allowing for precise control over the output voltage.
Key components of the circuit include:
1. **Input Capacitor**: This capacitor filters the input voltage to ensure stability and reduce voltage ripple from the PSU.
2. **Switching Transistor**: A MOSFET or BJT is used as a switch to control the current flow through the inductor.
3. **Inductor**: This component stores energy when the transistor is on and releases it to the output when the transistor is off, effectively reducing the voltage.
4. **Diode**: A Schottky diode is typically used to provide a path for the inductor current when the switching transistor is off, ensuring efficient energy transfer.
5. **Output Capacitor**: This capacitor smooths the output voltage and reduces ripple, providing a stable voltage to the load.
6. **Feedback Network**: A voltage divider is often employed to provide feedback to the control circuit, enabling it to adjust the duty cycle based on the output voltage.
7. **Adjustable Resistor or Potentiometer**: This allows users to set the desired output voltage by varying the resistance in the feedback network.
The design can also incorporate additional features such as overcurrent protection, thermal shutdown, and short-circuit protection to enhance reliability and safety. The variable output capability makes this power supply suitable for a wide range of applications, from testing circuits to powering microcontrollers and sensors.
Overall, the variable desktop power supply is a versatile and essential tool in electronics development and testing, providing reliable and adjustable power for various electronic applications.Variable desktop power supply which will convert a high input voltage (12V) from the SMPS / PSU of a desktop computer into small output voltage (1.25 to 9. 🔗 External reference
The variable desktop power supply is designed to provide adjustable output voltages ranging from 1.25V to 9V, utilizing a high input voltage of 12V sourced from the switched-mode power supply (SMPS) or power supply unit (PSU) of a desktop computer. This device is particularly useful for powering various electronic components and circuits that require different operating voltages.
The core of the power supply typically consists of a buck converter circuit, which steps down the 12V input to the desired output voltage. The buck converter operates by switching a transistor on and off at a high frequency, controlling the energy transferred to an inductor. The average voltage across the inductor is regulated by adjusting the duty cycle of the switching signal, allowing for precise control over the output voltage.
Key components of the circuit include:
1. **Input Capacitor**: This capacitor filters the input voltage to ensure stability and reduce voltage ripple from the PSU.
2. **Switching Transistor**: A MOSFET or BJT is used as a switch to control the current flow through the inductor.
3. **Inductor**: This component stores energy when the transistor is on and releases it to the output when the transistor is off, effectively reducing the voltage.
4. **Diode**: A Schottky diode is typically used to provide a path for the inductor current when the switching transistor is off, ensuring efficient energy transfer.
5. **Output Capacitor**: This capacitor smooths the output voltage and reduces ripple, providing a stable voltage to the load.
6. **Feedback Network**: A voltage divider is often employed to provide feedback to the control circuit, enabling it to adjust the duty cycle based on the output voltage.
7. **Adjustable Resistor or Potentiometer**: This allows users to set the desired output voltage by varying the resistance in the feedback network.
The design can also incorporate additional features such as overcurrent protection, thermal shutdown, and short-circuit protection to enhance reliability and safety. The variable output capability makes this power supply suitable for a wide range of applications, from testing circuits to powering microcontrollers and sensors.
Overall, the variable desktop power supply is a versatile and essential tool in electronics development and testing, providing reliable and adjustable power for various electronic applications.Variable desktop power supply which will convert a high input voltage (12V) from the SMPS / PSU of a desktop computer into small output voltage (1.25 to 9. 🔗 External reference