100W Audio Amplifier
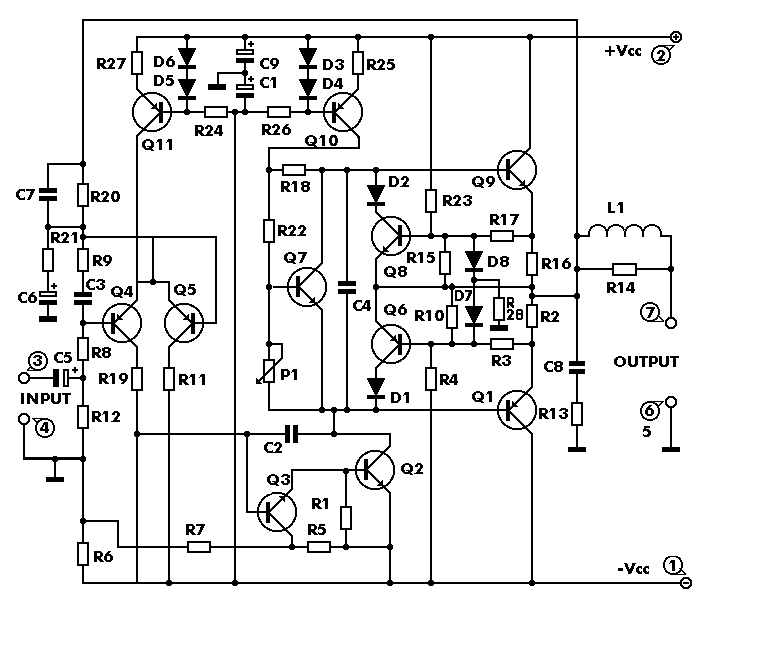
The circuit works from a symmetrical -40 VDC power supply and draws a maximum current of 2.6 A. The input circuit of the amplifier is a differential amplifier built around Q4 and Q5 that employ DC feedback thus preventing any DC voltage from appearing across the speaker with the usual destructive results. Q11 acts as a current source and ensures that the input stage draws a constant current of 1 mA. The signal which appears as a voltage drop across the resistor connected in series with the collector of Q4 is used to drive the DARLINGTON pair Q3, Q2 which together with the constant current source of 7 mA that is Q10, form the driver stage.
The described circuit is a high-fidelity audio amplifier that operates from a symmetrical -40 VDC power supply, capable of delivering a maximum output current of 2.6 A. The design incorporates a differential amplifier configuration utilizing transistors Q4 and Q5, which are crucial for maintaining signal integrity and ensuring that no DC offset is present at the output. This is particularly important as DC voltage across the speaker can lead to damage. The inclusion of DC feedback in this configuration stabilizes the circuit and enhances linearity.
Transistor Q11 functions as a constant current source, providing a steady biasing current of 1 mA to the input stage. This consistent current flow is essential for maintaining the performance of the differential amplifier, ensuring that it operates efficiently across varying signal conditions. The voltage drop generated across the resistor connected to the collector of Q4 is an important signal that is utilized to drive the subsequent driver stage.
The driver stage is composed of a Darlington pair formed by transistors Q3 and Q2. This configuration is advantageous for its high current gain, allowing the amplifier to drive larger loads with minimal input signal. The current source Q10, which provides a constant current of 7 mA to the driver stage, ensures that the Darlington pair operates effectively, maintaining the desired output characteristics while minimizing distortion.
Overall, this circuit design emphasizes stability, efficiency, and protection of the speaker, making it suitable for high-performance audio applications. The careful selection of components and their configuration ensures that the amplifier can deliver high-quality sound reproduction while safeguarding the connected audio equipment.The circuit works from a symmetrical 40 VDC power supply and draws a maximum current of 2.6 A. The input circuit of the amplifier is a differential amplifier built around Q4 and Q5 that employ DC feedback thus preventing any DC voltage from appearing across the speaker with the usual destructive results. Q11 acts as a current source and ensures that the input stage draws a constant current of 1 mA. The signal which appears as a voltage drop across the resistor connected in series with the collector of Q4 is used to drive the DARLINGTON pair Q3, Q2 which together with the constant current source of 7 mA that is Q10, form the driver stage. This stage 🔗 External reference
The described circuit is a high-fidelity audio amplifier that operates from a symmetrical -40 VDC power supply, capable of delivering a maximum output current of 2.6 A. The design incorporates a differential amplifier configuration utilizing transistors Q4 and Q5, which are crucial for maintaining signal integrity and ensuring that no DC offset is present at the output. This is particularly important as DC voltage across the speaker can lead to damage. The inclusion of DC feedback in this configuration stabilizes the circuit and enhances linearity.
Transistor Q11 functions as a constant current source, providing a steady biasing current of 1 mA to the input stage. This consistent current flow is essential for maintaining the performance of the differential amplifier, ensuring that it operates efficiently across varying signal conditions. The voltage drop generated across the resistor connected to the collector of Q4 is an important signal that is utilized to drive the subsequent driver stage.
The driver stage is composed of a Darlington pair formed by transistors Q3 and Q2. This configuration is advantageous for its high current gain, allowing the amplifier to drive larger loads with minimal input signal. The current source Q10, which provides a constant current of 7 mA to the driver stage, ensures that the Darlington pair operates effectively, maintaining the desired output characteristics while minimizing distortion.
Overall, this circuit design emphasizes stability, efficiency, and protection of the speaker, making it suitable for high-performance audio applications. The careful selection of components and their configuration ensures that the amplifier can deliver high-quality sound reproduction while safeguarding the connected audio equipment.The circuit works from a symmetrical 40 VDC power supply and draws a maximum current of 2.6 A. The input circuit of the amplifier is a differential amplifier built around Q4 and Q5 that employ DC feedback thus preventing any DC voltage from appearing across the speaker with the usual destructive results. Q11 acts as a current source and ensures that the input stage draws a constant current of 1 mA. The signal which appears as a voltage drop across the resistor connected in series with the collector of Q4 is used to drive the DARLINGTON pair Q3, Q2 which together with the constant current source of 7 mA that is Q10, form the driver stage. This stage 🔗 External reference