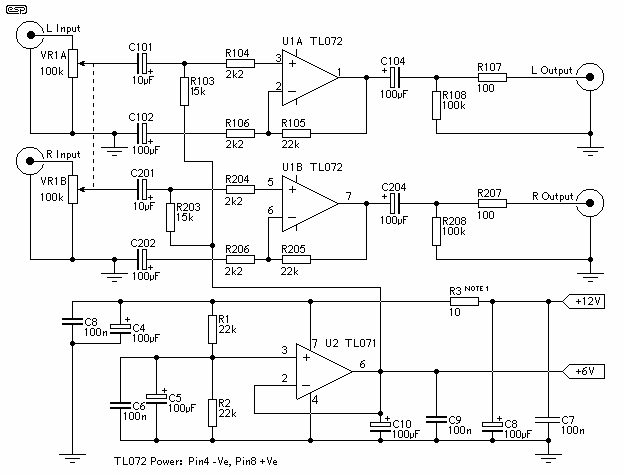
10W Class D Power Audio Amplifier with TDA7480
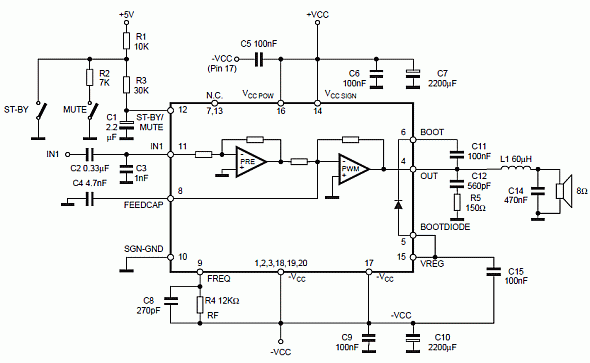
Class D audio power amplifier schematic diagram with TDA7480, capable of 10W output power at a load of 8Ω/4Ω and a total harmonic distortion of 10%. Requires a split-supply (max. ±20V).
The Class D audio power amplifier utilizing the TDA7480 is designed to deliver efficient audio amplification with a maximum output power of 10W, suitable for both 8Ω and 4Ω loads. This amplifier operates with a total harmonic distortion (THD) of 10%, which is a critical specification for maintaining audio fidelity in various applications, including home audio systems and portable devices.
The TDA7480 integrates a variety of features that enhance its performance, including built-in protection mechanisms against over-temperature and short-circuit conditions, ensuring reliable operation. The amplifier requires a split power supply, with a maximum voltage rating of ±20V, allowing for flexibility in system design and compatibility with various power sources.
In the schematic, the power stage of the amplifier is designed to efficiently switch the output transistors, minimizing power loss and enabling high-efficiency operation typical of Class D amplifiers. The input stage includes differential inputs to reduce noise and improve signal integrity. Feedback loops are implemented to stabilize gain and reduce distortion, contributing to the overall audio quality.
Additional components in the circuit may include filter capacitors to smooth the power supply and decoupling capacitors to reduce high-frequency noise. Input coupling capacitors are also utilized to block DC offsets from the audio source, ensuring that only the desired AC audio signal is amplified.
The layout of the circuit should be carefully considered to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ensure optimal thermal management. Proper grounding techniques and the placement of components can significantly impact the performance of the amplifier, making it essential to follow best practices in PCB design.
Overall, this Class D audio power amplifier schematic with the TDA7480 is a robust solution for high-efficiency audio amplification, providing a balance between power output, audio quality, and thermal performance.Class D audio power amplifier schematic diagram with TDA7480, capable of 10W output power at a load of 8w/4w and a total harmonic distorsion of 10%. Requires a split-supply (max. ±20V).. 🔗 External reference
The Class D audio power amplifier utilizing the TDA7480 is designed to deliver efficient audio amplification with a maximum output power of 10W, suitable for both 8Ω and 4Ω loads. This amplifier operates with a total harmonic distortion (THD) of 10%, which is a critical specification for maintaining audio fidelity in various applications, including home audio systems and portable devices.
The TDA7480 integrates a variety of features that enhance its performance, including built-in protection mechanisms against over-temperature and short-circuit conditions, ensuring reliable operation. The amplifier requires a split power supply, with a maximum voltage rating of ±20V, allowing for flexibility in system design and compatibility with various power sources.
In the schematic, the power stage of the amplifier is designed to efficiently switch the output transistors, minimizing power loss and enabling high-efficiency operation typical of Class D amplifiers. The input stage includes differential inputs to reduce noise and improve signal integrity. Feedback loops are implemented to stabilize gain and reduce distortion, contributing to the overall audio quality.
Additional components in the circuit may include filter capacitors to smooth the power supply and decoupling capacitors to reduce high-frequency noise. Input coupling capacitors are also utilized to block DC offsets from the audio source, ensuring that only the desired AC audio signal is amplified.
The layout of the circuit should be carefully considered to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ensure optimal thermal management. Proper grounding techniques and the placement of components can significantly impact the performance of the amplifier, making it essential to follow best practices in PCB design.
Overall, this Class D audio power amplifier schematic with the TDA7480 is a robust solution for high-efficiency audio amplification, providing a balance between power output, audio quality, and thermal performance.Class D audio power amplifier schematic diagram with TDA7480, capable of 10W output power at a load of 8w/4w and a total harmonic distorsion of 10%. Requires a split-supply (max. ±20V).. 🔗 External reference