12 Vdc - 120 Vac Inverter
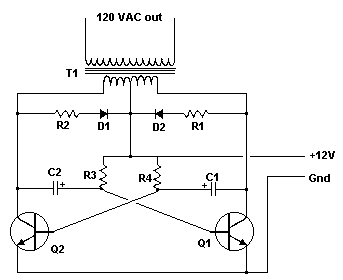
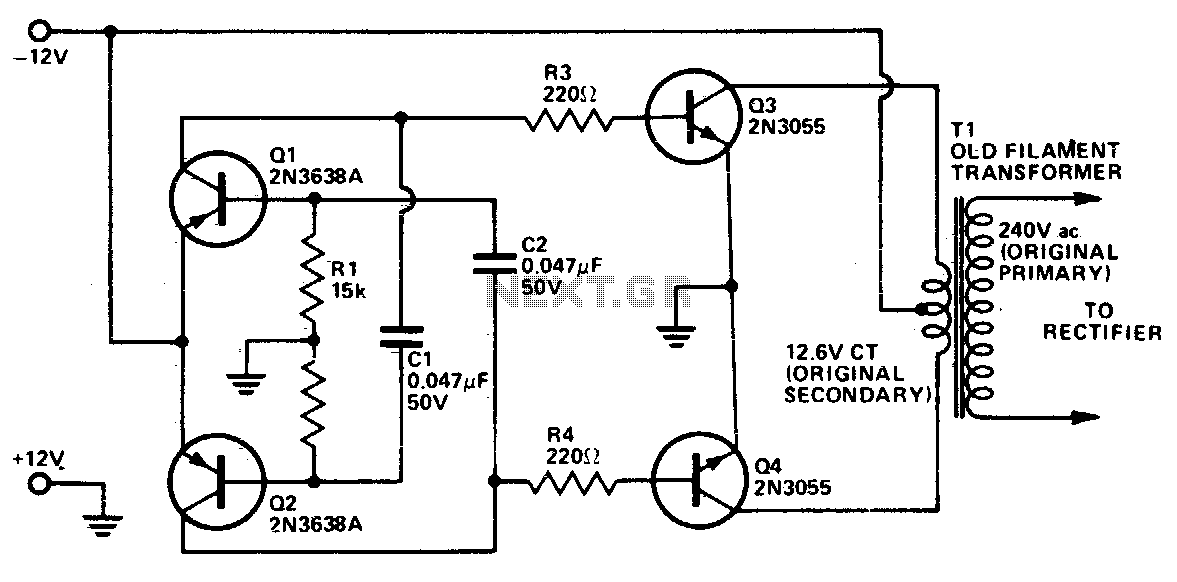
An Inverter is a device that converts 12 volts d.c to 120 volts a.c., which is what we use in our homes. This project will handle about 300 watts, which is perfect for lights, small T.V.s and radio equipment. This Inverter takes 12 volt d.c and steps it up to 120 volt a.c. The wattage depends on which transistors you use for Q1 and Q2, as well as the "Amp Rating" of the transformer you use for T1. This inverter can be constructed to supply anywhere from 1 to 1000 (1 KW) watts. If Q1, Q2 are 2N3055 NPN Transistors.
The inverter circuit described is a fundamental power electronics device designed to convert direct current (DC) from a 12V source into alternating current (AC) at a standard household voltage of 120V. The primary components of this inverter include two NPN transistors (Q1 and Q2), which serve as the switching elements, and a transformer (T1) that steps up the voltage from 12V to 120V.
The operation of the inverter is based on a push-pull configuration. When one transistor (Q1) is turned on, it allows current to flow through the primary winding of the transformer, inducing a magnetic field. As Q1 turns off, the other transistor (Q2) turns on, allowing current to flow in the opposite direction through the primary winding. This alternating action generates an alternating current in the secondary winding of the transformer, producing the desired 120V AC output.
The choice of transistors is critical in determining the wattage capacity of the inverter. The 2N3055 transistors are suitable for handling significant power levels, but their current ratings and thermal management must be considered to prevent overheating. The transformer (T1) must also be selected based on its amp rating, as it must be capable of handling the output power without saturating or overheating.
For applications requiring variable output power, the inverter circuit can be designed to accommodate different transistor types and transformer specifications, allowing for a range of output capacities from 1 watt to 1000 watts (1 kW). This flexibility makes the inverter suitable for various applications, including powering lights, small televisions, and radio equipment.
In conclusion, the described inverter circuit is a versatile and essential device for converting low-voltage DC power into usable AC power, with careful consideration given to component selection to ensure reliable and efficient operation.An Inverter is a device that converts 12 volts d.c to 120 volts a.c. , which is what we use in our homes. This project will handle about 300 watts, which is perfect for lights, small T.V.`s and radio equipment. This Inverter takes 12 volt d.c and steps it up to 120 volt a.c. The wattage depends on which transistors you use for Q1 and Q2, as well as the "Amp Rating" of the transformer you use for T1. This inverter can be constructed to supply anywhere from 1 to 1000 (1 KW) watts. If Q1, Q2 are 2N3055 NPN Transistors 🔗 External reference
The inverter circuit described is a fundamental power electronics device designed to convert direct current (DC) from a 12V source into alternating current (AC) at a standard household voltage of 120V. The primary components of this inverter include two NPN transistors (Q1 and Q2), which serve as the switching elements, and a transformer (T1) that steps up the voltage from 12V to 120V.
The operation of the inverter is based on a push-pull configuration. When one transistor (Q1) is turned on, it allows current to flow through the primary winding of the transformer, inducing a magnetic field. As Q1 turns off, the other transistor (Q2) turns on, allowing current to flow in the opposite direction through the primary winding. This alternating action generates an alternating current in the secondary winding of the transformer, producing the desired 120V AC output.
The choice of transistors is critical in determining the wattage capacity of the inverter. The 2N3055 transistors are suitable for handling significant power levels, but their current ratings and thermal management must be considered to prevent overheating. The transformer (T1) must also be selected based on its amp rating, as it must be capable of handling the output power without saturating or overheating.
For applications requiring variable output power, the inverter circuit can be designed to accommodate different transistor types and transformer specifications, allowing for a range of output capacities from 1 watt to 1000 watts (1 kW). This flexibility makes the inverter suitable for various applications, including powering lights, small televisions, and radio equipment.
In conclusion, the described inverter circuit is a versatile and essential device for converting low-voltage DC power into usable AC power, with careful consideration given to component selection to ensure reliable and efficient operation.An Inverter is a device that converts 12 volts d.c to 120 volts a.c. , which is what we use in our homes. This project will handle about 300 watts, which is perfect for lights, small T.V.`s and radio equipment. This Inverter takes 12 volt d.c and steps it up to 120 volt a.c. The wattage depends on which transistors you use for Q1 and Q2, as well as the "Amp Rating" of the transformer you use for T1. This inverter can be constructed to supply anywhere from 1 to 1000 (1 KW) watts. If Q1, Q2 are 2N3055 NPN Transistors 🔗 External reference