12 vdc to 240 vac inverter
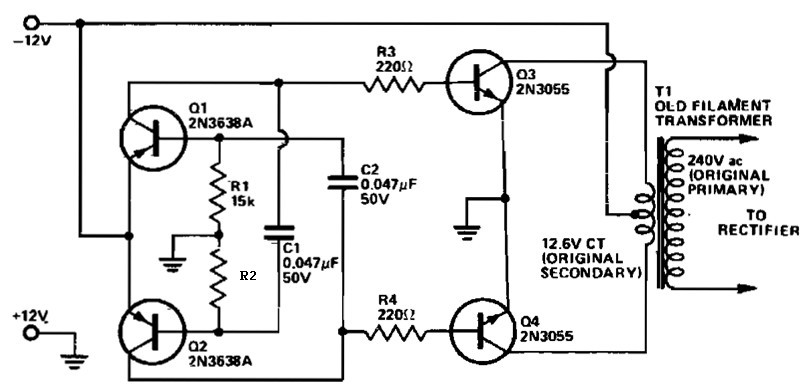
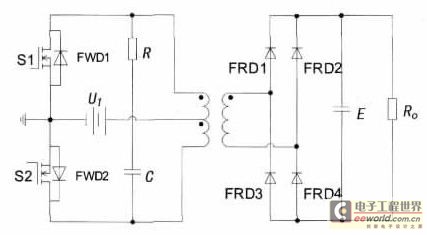
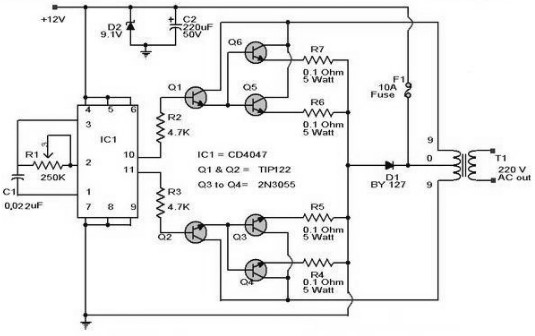
This 12 VDC to 240 VAC inverter circuit does not utilize specialized components, such as the toroidal transformer commonly found in many inverter circuits.
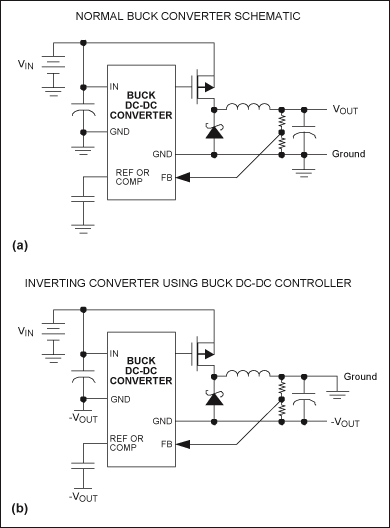
The inverter circuit described is designed to convert a 12 VDC input into a 240 VAC output without relying on specialized components like toroidal transformers. Instead, it may employ a simpler architecture, possibly utilizing a standard transformer or a switching method to achieve the necessary voltage conversion.
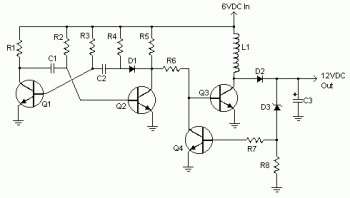
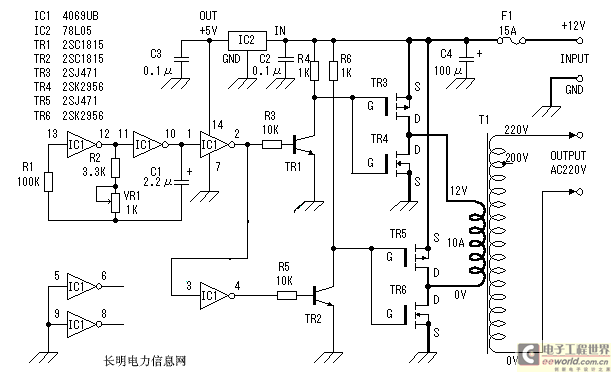
The circuit typically consists of a power stage, which could include MOSFETs or IGBTs for efficient switching, and a control circuit to manage the operation of these switches. The control circuit may generate a pulse-width modulation (PWM) signal to regulate the output voltage and maintain a stable AC waveform.
To ensure proper operation, the design must include protective elements such as fuses or circuit breakers to prevent overcurrent conditions. Additionally, filtering components, such as capacitors and inductors, may be necessary to smooth the output waveform and reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI).
The output stage may also incorporate feedback mechanisms to monitor the output voltage and adjust the PWM signal accordingly, ensuring that the inverter maintains the desired output voltage under varying load conditions.
Overall, this inverter circuit represents a practical solution for applications requiring AC power from a DC source, leveraging standard components while maintaining efficiency and reliability.This 12 VDC to 240 VAC Inverter circuit are not using special components such as the torodial transformer found in many inverters circuit.. 🔗 External reference
The inverter circuit described is designed to convert a 12 VDC input into a 240 VAC output without relying on specialized components like toroidal transformers. Instead, it may employ a simpler architecture, possibly utilizing a standard transformer or a switching method to achieve the necessary voltage conversion.
The circuit typically consists of a power stage, which could include MOSFETs or IGBTs for efficient switching, and a control circuit to manage the operation of these switches. The control circuit may generate a pulse-width modulation (PWM) signal to regulate the output voltage and maintain a stable AC waveform.
To ensure proper operation, the design must include protective elements such as fuses or circuit breakers to prevent overcurrent conditions. Additionally, filtering components, such as capacitors and inductors, may be necessary to smooth the output waveform and reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI).
The output stage may also incorporate feedback mechanisms to monitor the output voltage and adjust the PWM signal accordingly, ensuring that the inverter maintains the desired output voltage under varying load conditions.
Overall, this inverter circuit represents a practical solution for applications requiring AC power from a DC source, leveraging standard components while maintaining efficiency and reliability.This 12 VDC to 240 VAC Inverter circuit are not using special components such as the torodial transformer found in many inverters circuit.. 🔗 External reference