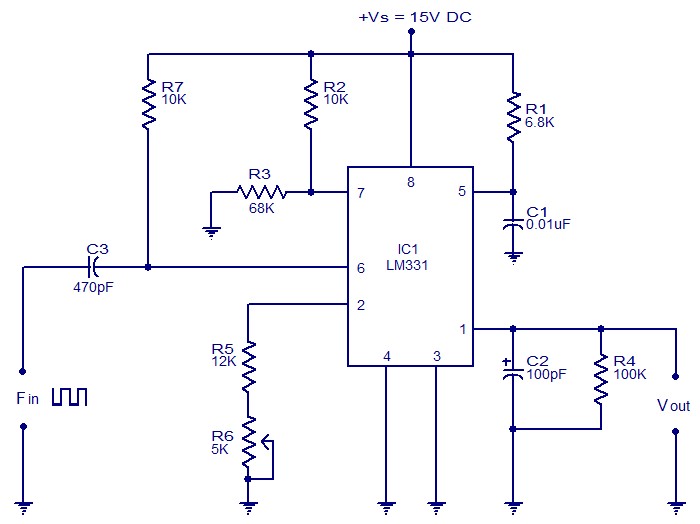
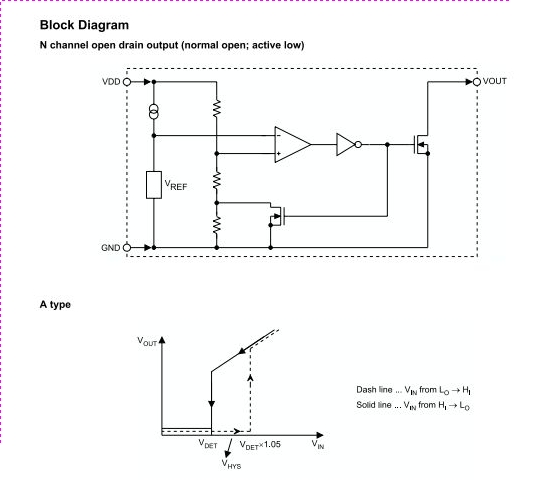
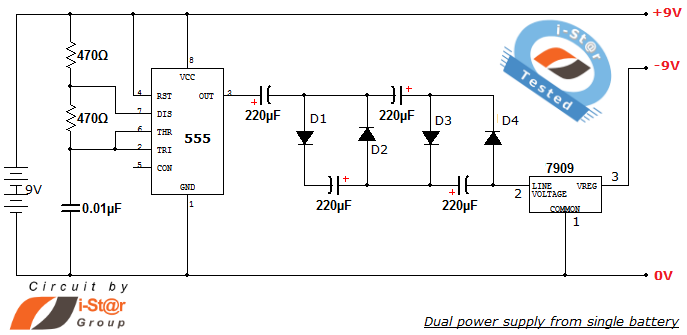
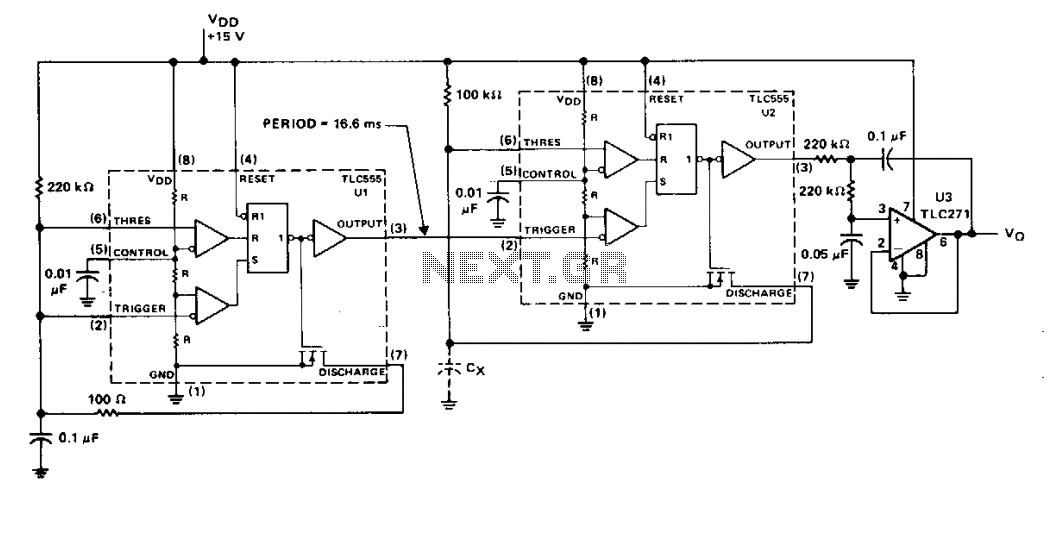
Making a Voltage Inverter from a Buck (Step-Down) DC-DC Converter
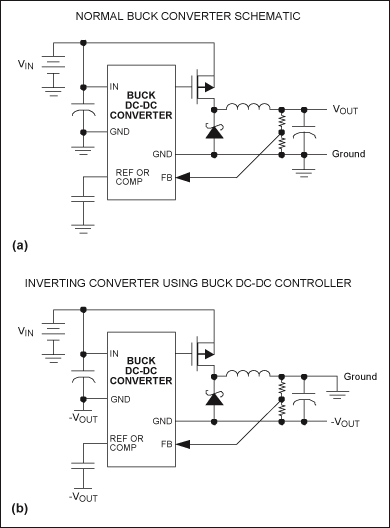
Any step-down DC-DC converter can be utilized as an inverter without modifications to the operating schematic. The only differences between the standard step-down application and the inverting operation are the labels of the connection points. The step-down VOUT is...
A step-down DC-DC converter, commonly referred to as a buck converter, is designed to convert a higher input voltage to a lower output voltage efficiently. In its standard application, the converter regulates the output voltage (VOUT) to a desired level, which is lower than the input voltage (VIN). However, this same topology can be employed in an inverting configuration, where the output voltage is of opposite polarity to the input voltage.
In this inverting operation, the connections at the converter's terminals are simply relabeled. The input terminal, traditionally associated with the positive voltage, is now connected to the negative voltage source, while the output terminal, which typically delivers a positive voltage, is now designated to output a negative voltage. This allows for the generation of a negative voltage rail from a positive supply, which can be particularly useful in applications requiring dual power supplies.
The fundamental operation of the buck converter remains unchanged, utilizing a switching element (typically a MOSFET), an inductor, a diode, and output capacitors to regulate voltage. The control mechanism, often based on pulse-width modulation (PWM), adjusts the duty cycle of the switching element to maintain the desired output voltage level, regardless of whether it is positive or negative.
In summary, the step-down DC-DC converter's versatility allows it to function as an inverter through simple reconfiguration of its connection labels, while retaining its core operational principles. This adaptability makes it a valuable component in various electronic applications requiring voltage inversion.Any step-down DC-DC converter can be used as an inverter with no changes to the operating schematic. The only differences between the normal step-down application and inverting operation are the labels of the connection points. The step-down VOUT is.. 🔗 External reference
A step-down DC-DC converter, commonly referred to as a buck converter, is designed to convert a higher input voltage to a lower output voltage efficiently. In its standard application, the converter regulates the output voltage (VOUT) to a desired level, which is lower than the input voltage (VIN). However, this same topology can be employed in an inverting configuration, where the output voltage is of opposite polarity to the input voltage.
In this inverting operation, the connections at the converter's terminals are simply relabeled. The input terminal, traditionally associated with the positive voltage, is now connected to the negative voltage source, while the output terminal, which typically delivers a positive voltage, is now designated to output a negative voltage. This allows for the generation of a negative voltage rail from a positive supply, which can be particularly useful in applications requiring dual power supplies.
The fundamental operation of the buck converter remains unchanged, utilizing a switching element (typically a MOSFET), an inductor, a diode, and output capacitors to regulate voltage. The control mechanism, often based on pulse-width modulation (PWM), adjusts the duty cycle of the switching element to maintain the desired output voltage level, regardless of whether it is positive or negative.
In summary, the step-down DC-DC converter's versatility allows it to function as an inverter through simple reconfiguration of its connection labels, while retaining its core operational principles. This adaptability makes it a valuable component in various electronic applications requiring voltage inversion.Any step-down DC-DC converter can be used as an inverter with no changes to the operating schematic. The only differences between the normal step-down application and inverting operation are the labels of the connection points. The step-down VOUT is.. 🔗 External reference