6vdc to 12vdc converter circuit
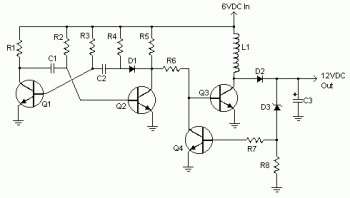
Various values of D3 can be utilized to achieve different output voltages ranging from approximately 0.6V to around 30V. It is important to note that at elevated voltages, the circuit's performance may diminish, potentially resulting in lower current output. Additionally, a larger capacitor C3 may be required for higher voltages and/or increased current demands.
The described circuit utilizes a diode (D3) to regulate output voltage levels effectively. By selecting diodes with different forward voltage drops, the circuit can be tailored to provide a specific output voltage, which is crucial in applications requiring precise voltage regulation. The range of output voltages from 0.6V to 30V indicates versatility, allowing the circuit to be used in various electronic applications, from low-power devices to more substantial systems.
However, as the output voltage increases, the performance of the circuit may decline due to factors such as increased resistance and reduced efficiency. The diode's characteristics, including its forward voltage drop and reverse recovery time, play a significant role in this performance. Therefore, careful selection of D3 is essential for maintaining optimal functionality across the desired voltage range.
Furthermore, the capacitor C3 serves a vital role in stabilizing the output voltage. At higher output voltages or when higher currents are required, a larger capacitor may be necessary to maintain voltage stability and minimize ripple. The capacitance value must be chosen based on the load requirements and the desired transient response of the circuit. A larger capacitance can help absorb fluctuations in current demand, ensuring a steady voltage output under varying load conditions.
In summary, the circuit's design allows for flexibility in output voltage through the selection of D3, but considerations regarding performance at higher voltages and the sizing of C3 are critical for achieving the desired operational characteristics. Proper analysis and component selection will yield a reliable voltage regulation solution suitable for a broad spectrum of electronic applications.Different values of D3 can be used to get different output voltages from about 0. 6V to around 30V. Note that at higher voltages the circuit might not perform as well and may not produce as much current. You may also need to use a larger C3 for higher voltages and/or higher currents. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit utilizes a diode (D3) to regulate output voltage levels effectively. By selecting diodes with different forward voltage drops, the circuit can be tailored to provide a specific output voltage, which is crucial in applications requiring precise voltage regulation. The range of output voltages from 0.6V to 30V indicates versatility, allowing the circuit to be used in various electronic applications, from low-power devices to more substantial systems.
However, as the output voltage increases, the performance of the circuit may decline due to factors such as increased resistance and reduced efficiency. The diode's characteristics, including its forward voltage drop and reverse recovery time, play a significant role in this performance. Therefore, careful selection of D3 is essential for maintaining optimal functionality across the desired voltage range.
Furthermore, the capacitor C3 serves a vital role in stabilizing the output voltage. At higher output voltages or when higher currents are required, a larger capacitor may be necessary to maintain voltage stability and minimize ripple. The capacitance value must be chosen based on the load requirements and the desired transient response of the circuit. A larger capacitance can help absorb fluctuations in current demand, ensuring a steady voltage output under varying load conditions.
In summary, the circuit's design allows for flexibility in output voltage through the selection of D3, but considerations regarding performance at higher voltages and the sizing of C3 are critical for achieving the desired operational characteristics. Proper analysis and component selection will yield a reliable voltage regulation solution suitable for a broad spectrum of electronic applications.Different values of D3 can be used to get different output voltages from about 0. 6V to around 30V. Note that at higher voltages the circuit might not perform as well and may not produce as much current. You may also need to use a larger C3 for higher voltages and/or higher currents. 🔗 External reference