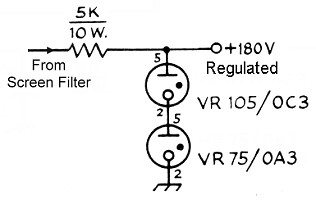
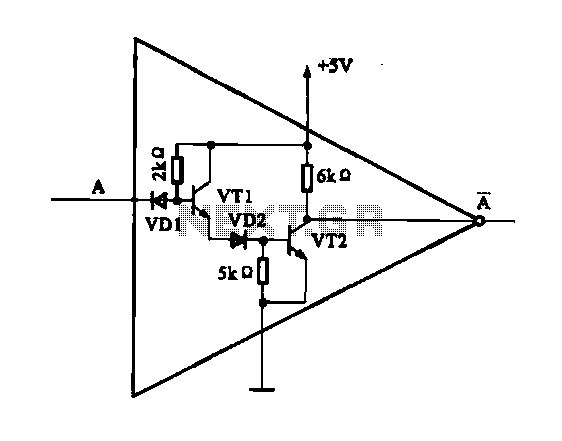
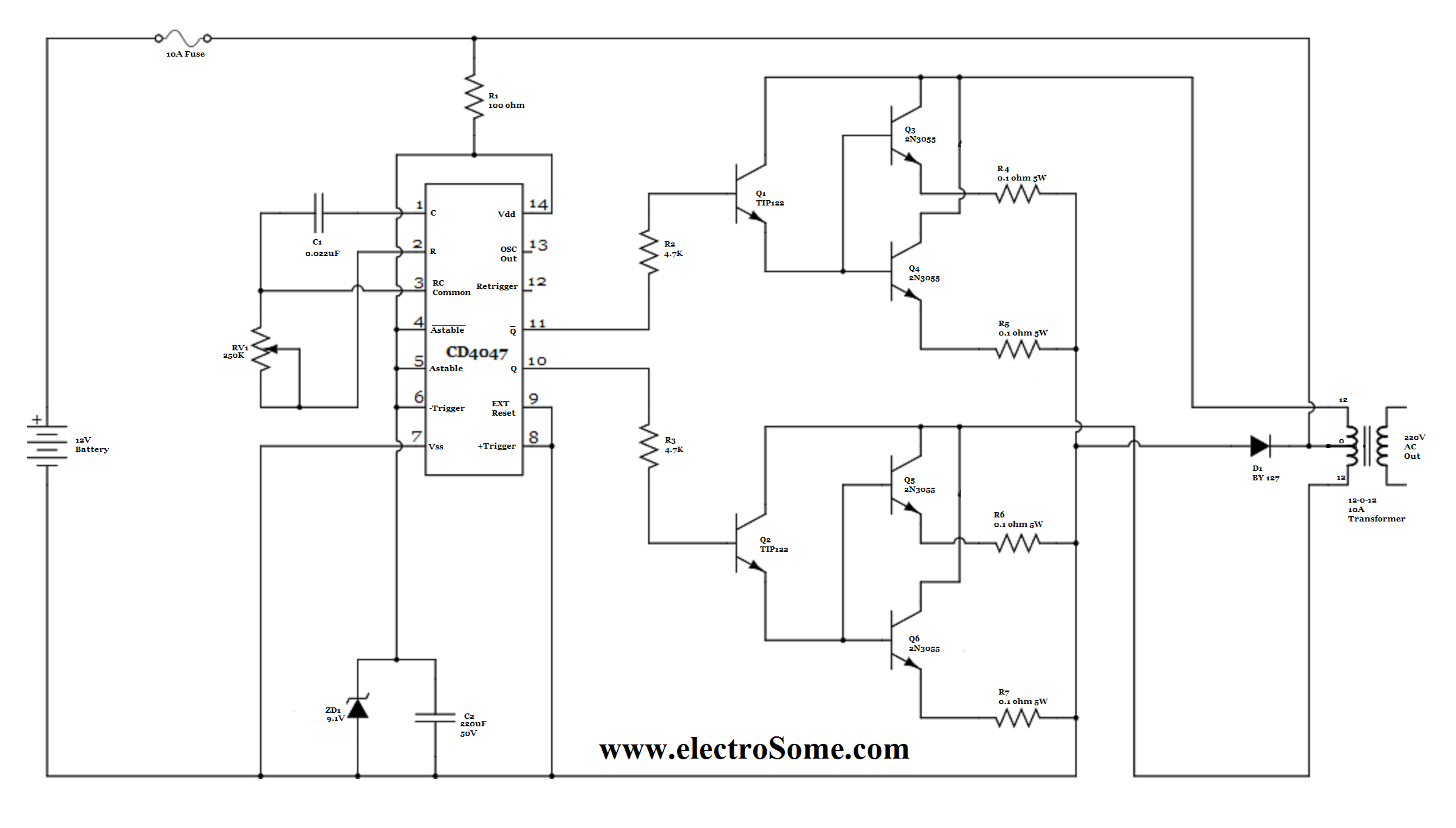
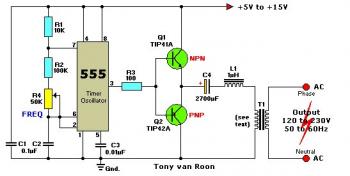
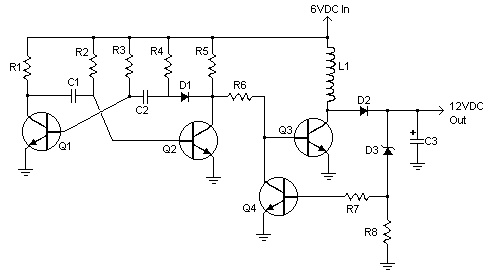
12v regulated inverter supply
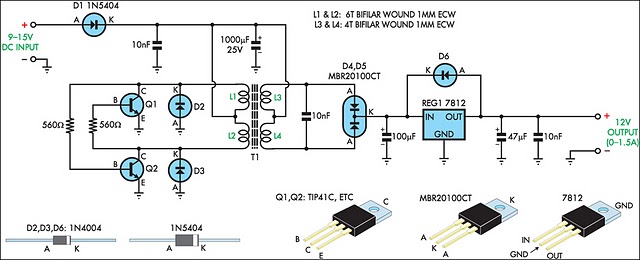
When operating 12V electronic devices from lead-acid battery banks, the voltage supplied to the appliance can fluctuate significantly, ranging from below 11V when the batteries are discharged to over 14V during the charging process. Many appliances are not capable of withstanding such wide voltage variations and may either perform inadequately or sustain damage.
To address the voltage fluctuations encountered when using lead-acid battery banks for 12V electronic devices, a voltage regulation circuit is essential. This circuit can be designed using a linear voltage regulator or a switching regulator, depending on the efficiency and heat dissipation requirements of the application.
A linear voltage regulator, such as the LM7812, can provide a stable output voltage of 12V. It operates by maintaining a constant output voltage despite variations in input voltage and load current. However, linear regulators are less efficient, particularly when there is a large difference between input and output voltage, as they dissipate the excess voltage as heat. Therefore, adequate heat sinking must be implemented to prevent thermal shutdown.
In contrast, a switching regulator, such as a buck converter, is more efficient for applications where the input voltage can be significantly higher than the desired output voltage. A buck converter steps down the voltage through a high-frequency switching process, allowing for greater efficiency and reduced heat generation. This is particularly advantageous when the battery voltage exceeds 14V during charging.
To implement such a circuit, the following components are typically included:
- A voltage regulator IC (either linear or switching type).
- Input and output capacitors to stabilize the voltage and filter noise.
- Inductors and diodes (for switching regulators) to manage energy transfer and rectify the output.
- Additional protection components such as fuses and surge protectors to safeguard against over-voltage and short-circuit conditions.
Incorporating a battery management system (BMS) can further enhance the reliability of the setup. The BMS monitors the state of charge, temperature, and health of the battery, ensuring that the batteries are not over-discharged or overcharged, which could lead to performance degradation or failure.
Overall, implementing a robust voltage regulation system will ensure that 12V electronic devices receive a stable and safe operating voltage, thereby enhancing performance and longevity.When running 12V electronic devices from lead-acid battery banks, the voltage to the appliance can vary from below 11V with discharged batteries, to well above 14V during charging. Many appliances will not tolerate such a wide fluctuation and may perform poorly or be damaged.. 🔗 External reference
To address the voltage fluctuations encountered when using lead-acid battery banks for 12V electronic devices, a voltage regulation circuit is essential. This circuit can be designed using a linear voltage regulator or a switching regulator, depending on the efficiency and heat dissipation requirements of the application.
A linear voltage regulator, such as the LM7812, can provide a stable output voltage of 12V. It operates by maintaining a constant output voltage despite variations in input voltage and load current. However, linear regulators are less efficient, particularly when there is a large difference between input and output voltage, as they dissipate the excess voltage as heat. Therefore, adequate heat sinking must be implemented to prevent thermal shutdown.
In contrast, a switching regulator, such as a buck converter, is more efficient for applications where the input voltage can be significantly higher than the desired output voltage. A buck converter steps down the voltage through a high-frequency switching process, allowing for greater efficiency and reduced heat generation. This is particularly advantageous when the battery voltage exceeds 14V during charging.
To implement such a circuit, the following components are typically included:
- A voltage regulator IC (either linear or switching type).
- Input and output capacitors to stabilize the voltage and filter noise.
- Inductors and diodes (for switching regulators) to manage energy transfer and rectify the output.
- Additional protection components such as fuses and surge protectors to safeguard against over-voltage and short-circuit conditions.
Incorporating a battery management system (BMS) can further enhance the reliability of the setup. The BMS monitors the state of charge, temperature, and health of the battery, ensuring that the batteries are not over-discharged or overcharged, which could lead to performance degradation or failure.
Overall, implementing a robust voltage regulation system will ensure that 12V electronic devices receive a stable and safe operating voltage, thereby enhancing performance and longevity.When running 12V electronic devices from lead-acid battery banks, the voltage to the appliance can vary from below 11V with discharged batteries, to well above 14V during charging. Many appliances will not tolerate such a wide fluctuation and may perform poorly or be damaged.. 🔗 External reference