12V to 6V Converter
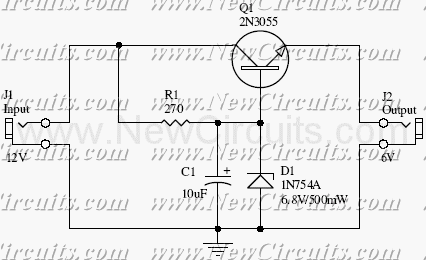
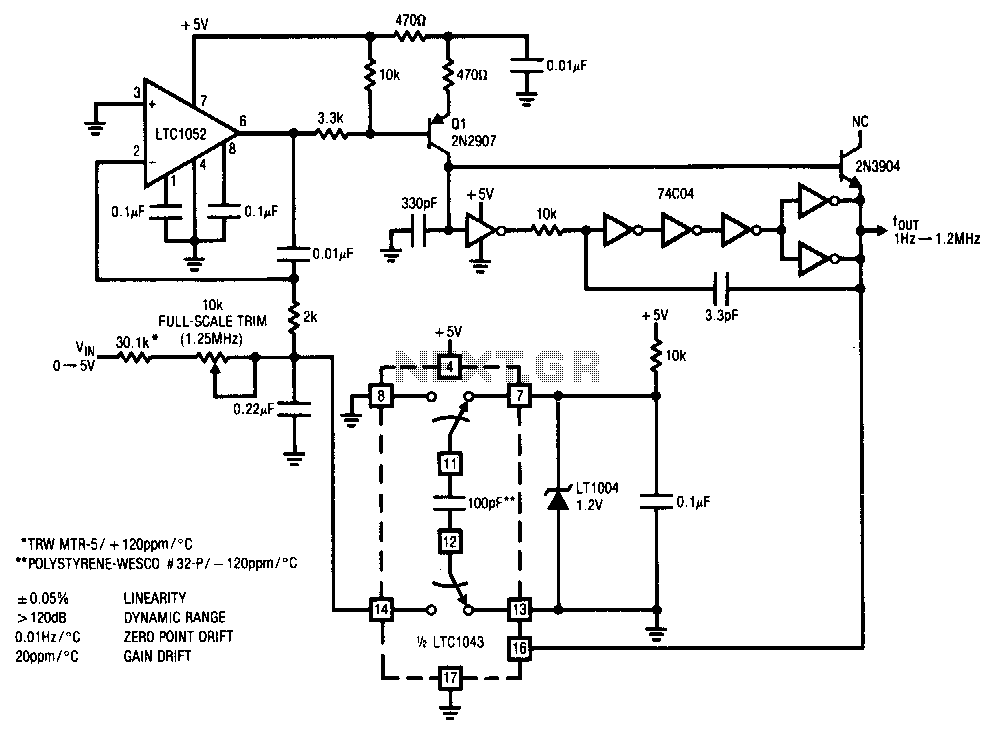
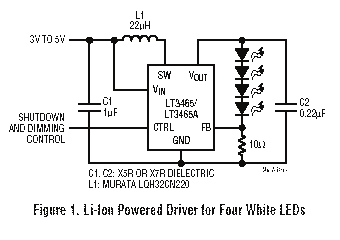
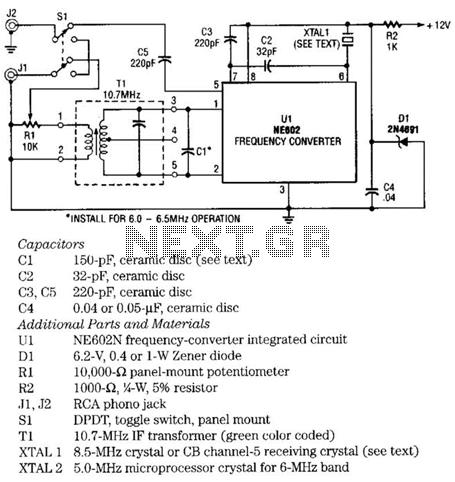
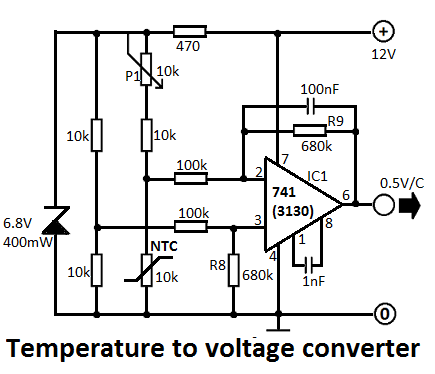
This small but useful circuit is a DC voltage converter for using 6V devices with car battery voltage. The maximum output current is dependent if the T1 is covered with a proper heat sink or not. You can use the circuit to drive devices that they sink maximum 0.5A current without any heat-sink and 5A with a large heat-sink.
The circuit described functions as a DC voltage converter, specifically designed to step down the higher voltage of a car battery (typically around 12V to 14.4V) to a stable 6V output suitable for powering devices that operate at this lower voltage. The core component of the circuit is a voltage regulator, often represented as T1 in the description.
To ensure optimal performance, it is critical to manage the thermal characteristics of the regulator. When T1 is equipped with an appropriate heat sink, it can handle a significantly higher output current of up to 5A. Without a heat sink, the maximum output current is limited to 0.5A due to thermal constraints, which could lead to overheating and potential damage to the regulator.
The circuit typically includes input and output capacitors to filter out voltage spikes and maintain stability. The input capacitor smooths the incoming voltage from the car battery, while the output capacitor ensures a steady voltage supply to the load. Additional components such as diodes may be included to prevent reverse polarity and protect the circuit from potential damage.
This voltage converter circuit can be utilized in various applications where 6V devices need to be powered from a car battery, such as powering LED lights, small motors, or other electronic devices designed for 6V operation. Proper design considerations, including the selection of T1 and the sizing of the heat sink, are essential to ensure reliable operation and longevity of the circuit.This small but useful circuit is a DC voltage convertor for using 6V devices with car battery voltage. The maximum output current is dependent if the T1 is covered with a proper heat sink or not. You can use the circuit to drive devices that they sink maximum 0.5A current without any heat-sink and 5A with a large heat-sink.
🔗 External reference
The circuit described functions as a DC voltage converter, specifically designed to step down the higher voltage of a car battery (typically around 12V to 14.4V) to a stable 6V output suitable for powering devices that operate at this lower voltage. The core component of the circuit is a voltage regulator, often represented as T1 in the description.
To ensure optimal performance, it is critical to manage the thermal characteristics of the regulator. When T1 is equipped with an appropriate heat sink, it can handle a significantly higher output current of up to 5A. Without a heat sink, the maximum output current is limited to 0.5A due to thermal constraints, which could lead to overheating and potential damage to the regulator.
The circuit typically includes input and output capacitors to filter out voltage spikes and maintain stability. The input capacitor smooths the incoming voltage from the car battery, while the output capacitor ensures a steady voltage supply to the load. Additional components such as diodes may be included to prevent reverse polarity and protect the circuit from potential damage.
This voltage converter circuit can be utilized in various applications where 6V devices need to be powered from a car battery, such as powering LED lights, small motors, or other electronic devices designed for 6V operation. Proper design considerations, including the selection of T1 and the sizing of the heat sink, are essential to ensure reliable operation and longevity of the circuit.This small but useful circuit is a DC voltage convertor for using 6V devices with car battery voltage. The maximum output current is dependent if the T1 is covered with a proper heat sink or not. You can use the circuit to drive devices that they sink maximum 0.5A current without any heat-sink and 5A with a large heat-sink.
🔗 External reference