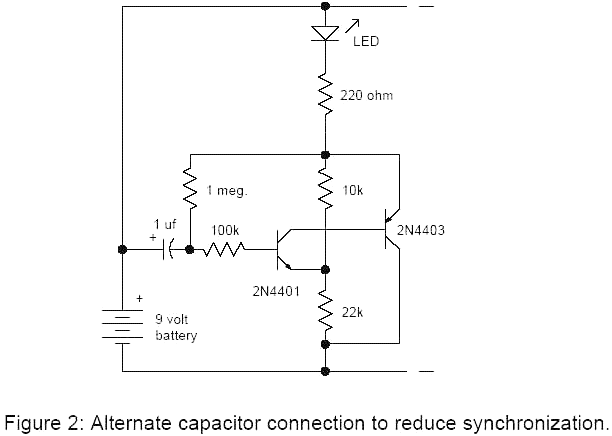
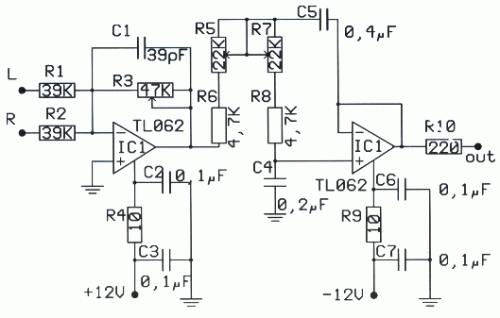
175MHz high-frequency amplifier circuit composed by a field effect transistor
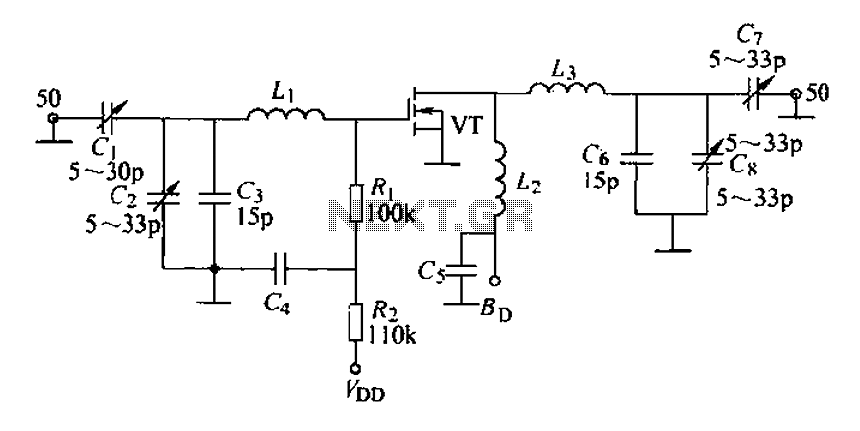
A 175 MHz high-frequency amplifier circuit utilizing a field-effect transistor (FET) is presented. The field-effect transistor used is the 3D04H, along with its associated components and parameters.
The 175 MHz high-frequency amplifier circuit is designed to amplify signals in the specified frequency range, making it suitable for applications in communication systems, RF signal processing, and other high-frequency applications. The core component of this circuit is the 3D04H field-effect transistor, which is known for its high gain and low noise characteristics at high frequencies.
The circuit typically consists of several key components surrounding the FET, including resistors, capacitors, and possibly inductors, which are configured to optimize the amplifier's performance. The input signal is fed into the gate of the FET, where it is amplified due to the transistor's ability to control the output current based on the input voltage.
Biasing resistors are essential for setting the operating point of the FET, ensuring that it operates in the appropriate region of its transfer characteristics for linear amplification. Coupling capacitors may be used at the input and output stages to block DC components while allowing the AC signal to pass through, thus preventing any DC biasing from affecting subsequent stages in the circuit.
Feedback components may also be included to stabilize gain and improve bandwidth. The layout of the circuit should minimize parasitic capacitances and inductances that can adversely affect high-frequency performance. Proper grounding and power supply decoupling are critical to reduce noise and ensure stable operation.
Overall, the design of this 175 MHz high-frequency amplifier circuit emphasizes the importance of component selection, layout, and biasing techniques to achieve effective amplification of high-frequency signals.175MHz high-frequency amplifier circuit by a field effect transistor shown in Fig. Field effect transistor VT is 3D04H, components, and parameters,
The 175 MHz high-frequency amplifier circuit is designed to amplify signals in the specified frequency range, making it suitable for applications in communication systems, RF signal processing, and other high-frequency applications. The core component of this circuit is the 3D04H field-effect transistor, which is known for its high gain and low noise characteristics at high frequencies.
The circuit typically consists of several key components surrounding the FET, including resistors, capacitors, and possibly inductors, which are configured to optimize the amplifier's performance. The input signal is fed into the gate of the FET, where it is amplified due to the transistor's ability to control the output current based on the input voltage.
Biasing resistors are essential for setting the operating point of the FET, ensuring that it operates in the appropriate region of its transfer characteristics for linear amplification. Coupling capacitors may be used at the input and output stages to block DC components while allowing the AC signal to pass through, thus preventing any DC biasing from affecting subsequent stages in the circuit.
Feedback components may also be included to stabilize gain and improve bandwidth. The layout of the circuit should minimize parasitic capacitances and inductances that can adversely affect high-frequency performance. Proper grounding and power supply decoupling are critical to reduce noise and ensure stable operation.
Overall, the design of this 175 MHz high-frequency amplifier circuit emphasizes the importance of component selection, layout, and biasing techniques to achieve effective amplification of high-frequency signals.175MHz high-frequency amplifier circuit by a field effect transistor shown in Fig. Field effect transistor VT is 3D04H, components, and parameters,