200mA 12V Op Current Gain Stage
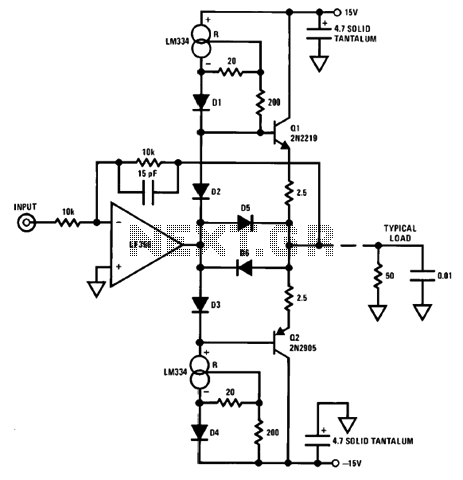
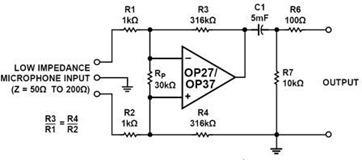
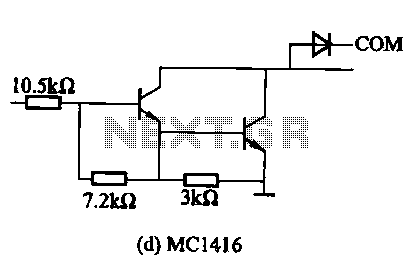
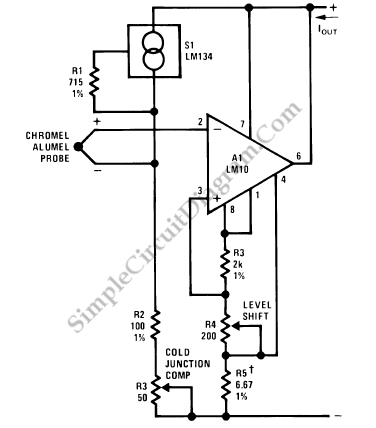
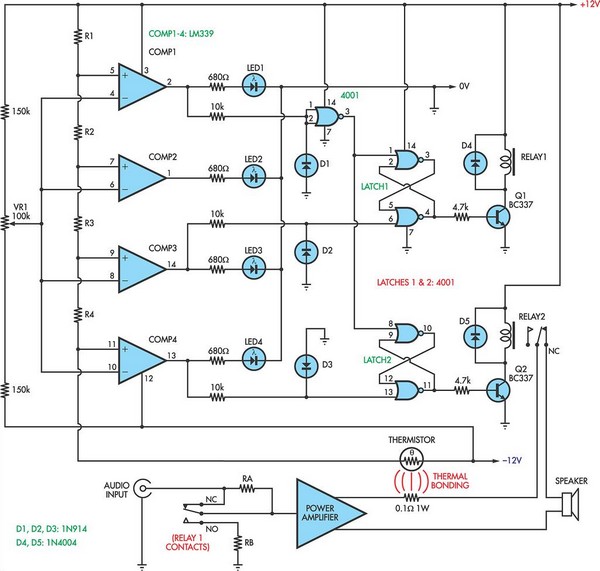
An output booster is required to achieve the necessary current or voltage gain. A significant output is often needed in conjunction with the output power limitations of most integrated circuit (IC) processors. The following figure presents a circuit diagram of a typical current gain stage for designing booster stages that achieve power gain while maintaining good dynamic performance.
An output booster circuit is essential in applications where the signal needs to be amplified to meet specific current or voltage requirements. This circuit typically consists of a transistor-based configuration, which can be either a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) or a field-effect transistor (FET), depending on the desired characteristics and performance.
The fundamental purpose of the output booster is to enhance the output power while ensuring that the dynamic response of the system remains optimal. This is particularly important in scenarios where the load demands exceed the capabilities of the driving IC. The design includes feedback mechanisms to stabilize the gain and reduce distortion, which is crucial for maintaining signal integrity.
In a typical current gain stage, the input signal is fed into the base (or gate) of the transistor, which controls the flow of current from the collector (or drain) to the emitter (or source). The configuration can be set up in common emitter (or common source) mode to provide significant voltage gain, or in common collector (or common drain) mode to deliver high current gain with low output impedance.
The circuit may also incorporate additional components such as resistors for biasing, capacitors for coupling and bypassing, and inductors for filtering, which collectively aid in achieving the desired frequency response and stability. Careful selection of these components is necessary to optimize performance for specific applications, ensuring that the booster can handle the required power levels without introducing excessive noise or distortion.
Overall, the design of an output booster circuit is a critical aspect of electronic system design, particularly in high-performance applications where power efficiency and signal fidelity are paramount.An output booster is needed when you want to achieve the needed current/voltage gain. Great output commonly need in accociation with the the output power limitation of mostly IC processing. The following figure shows you circuit diagram of the typical current gain stage if you want to design a booster stages which achieve power gain while maintaining good dynamic performance.
The design of. 🔗 External reference
An output booster circuit is essential in applications where the signal needs to be amplified to meet specific current or voltage requirements. This circuit typically consists of a transistor-based configuration, which can be either a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) or a field-effect transistor (FET), depending on the desired characteristics and performance.
The fundamental purpose of the output booster is to enhance the output power while ensuring that the dynamic response of the system remains optimal. This is particularly important in scenarios where the load demands exceed the capabilities of the driving IC. The design includes feedback mechanisms to stabilize the gain and reduce distortion, which is crucial for maintaining signal integrity.
In a typical current gain stage, the input signal is fed into the base (or gate) of the transistor, which controls the flow of current from the collector (or drain) to the emitter (or source). The configuration can be set up in common emitter (or common source) mode to provide significant voltage gain, or in common collector (or common drain) mode to deliver high current gain with low output impedance.
The circuit may also incorporate additional components such as resistors for biasing, capacitors for coupling and bypassing, and inductors for filtering, which collectively aid in achieving the desired frequency response and stability. Careful selection of these components is necessary to optimize performance for specific applications, ensuring that the booster can handle the required power levels without introducing excessive noise or distortion.
Overall, the design of an output booster circuit is a critical aspect of electronic system design, particularly in high-performance applications where power efficiency and signal fidelity are paramount.An output booster is needed when you want to achieve the needed current/voltage gain. Great output commonly need in accociation with the the output power limitation of mostly IC processing. The following figure shows you circuit diagram of the typical current gain stage if you want to design a booster stages which achieve power gain while maintaining good dynamic performance.
The design of. 🔗 External reference