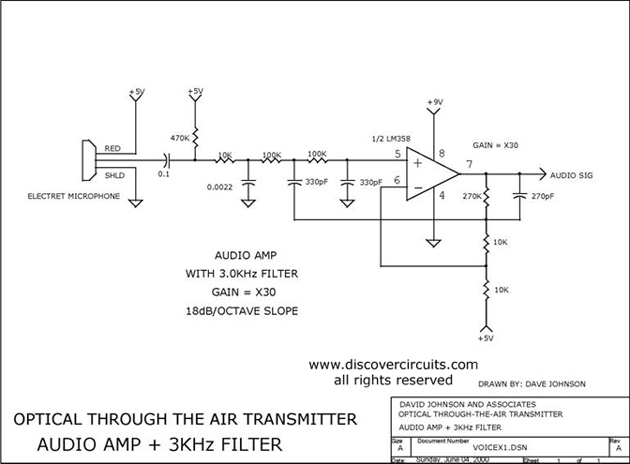
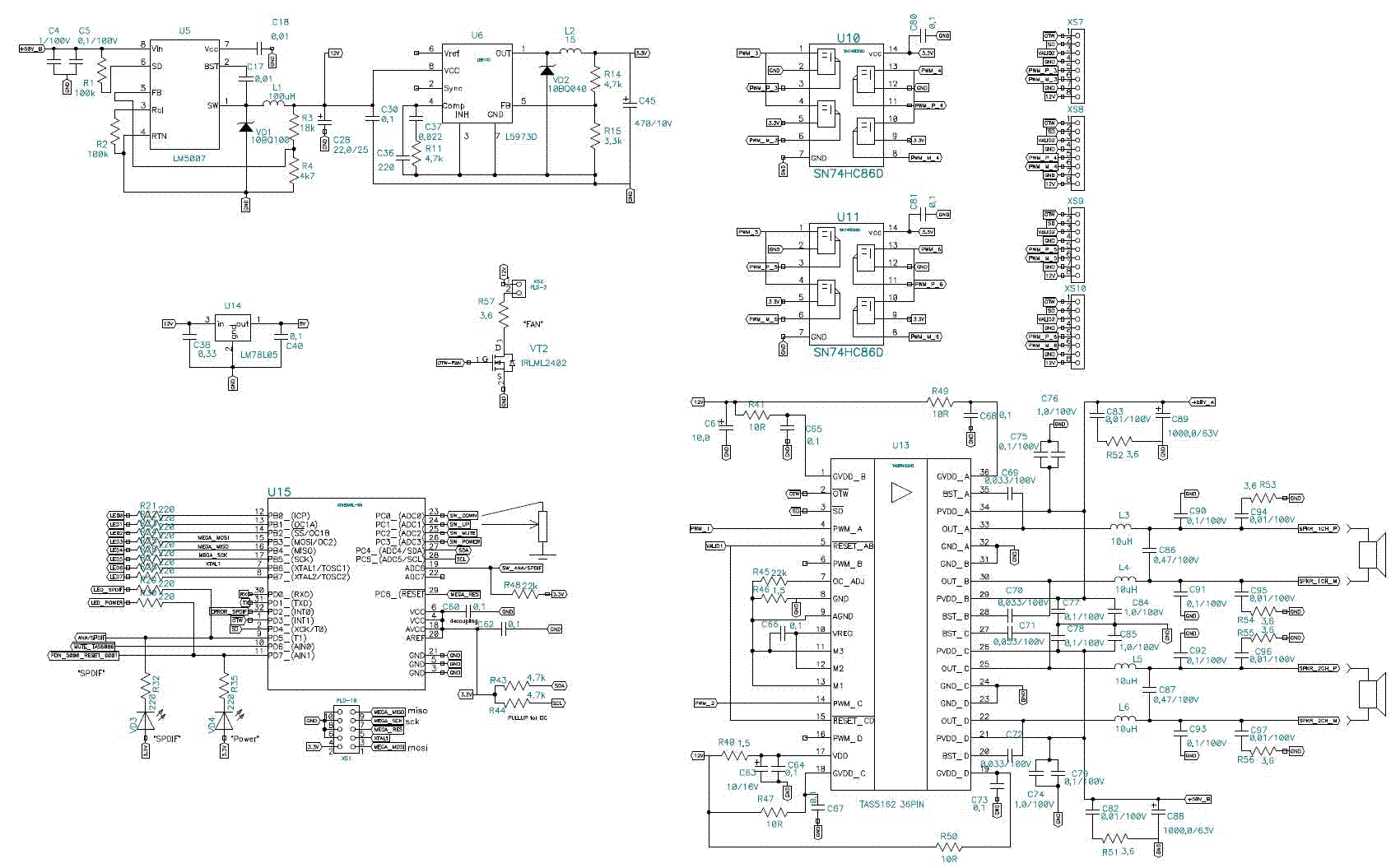
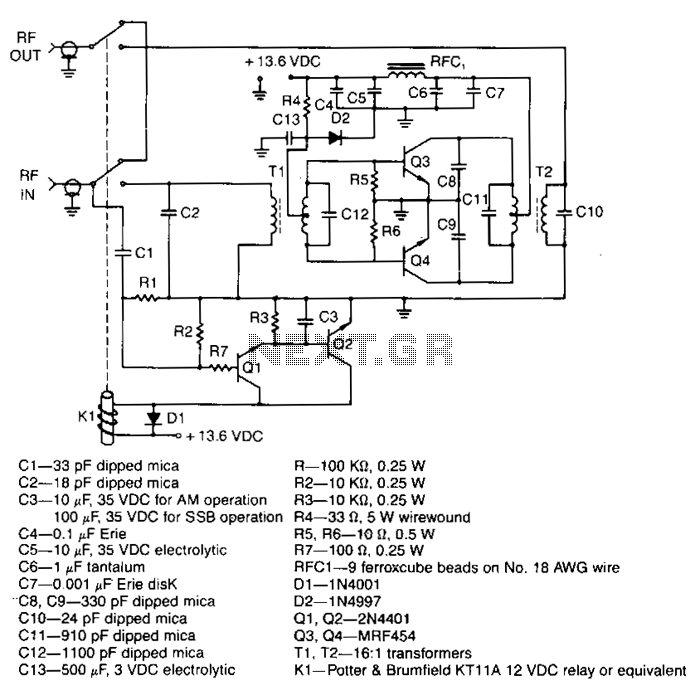
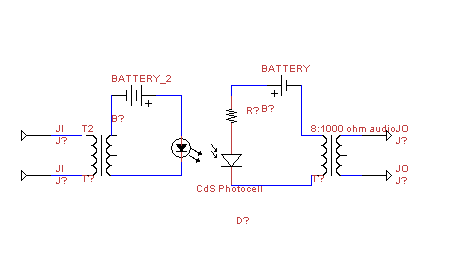
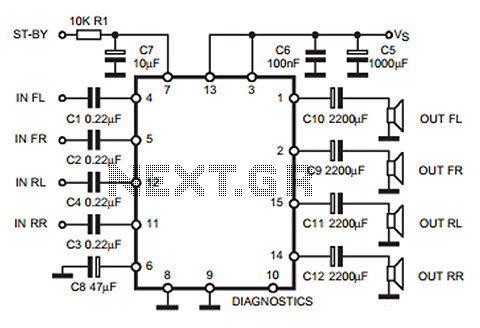
22 Watt Stereo audio Amplifier
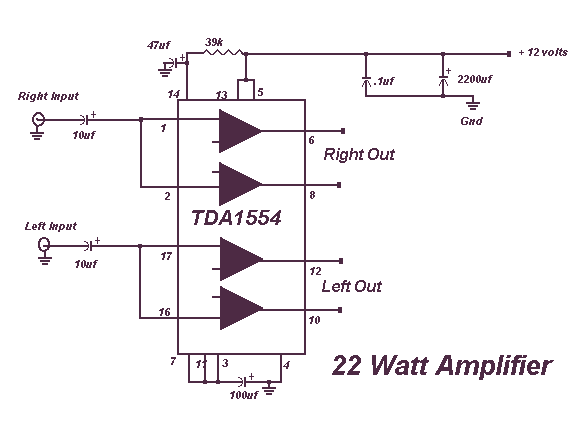
This circuit is very basic to build and puts out great power for your car or home. Keep all leads as short as possible.
This circuit is designed to deliver substantial power output suitable for automotive or residential applications. The fundamental architecture typically involves a power supply, switching components, and output stage configured to handle the required load.
The power supply section may consist of a transformer or a DC power source, which is responsible for converting the input voltage to the desired output level. A rectifier circuit, composed of diodes, is often employed to convert AC to DC if necessary.
Switching components, such as transistors or MOSFETs, are utilized to control the flow of current through the circuit. These components should be chosen based on their current and voltage ratings to ensure they can handle the load without overheating or failing.
The output stage may include capacitors for filtering to smooth out voltage fluctuations and provide a stable output. Inductors might also be incorporated to reduce noise and improve performance.
To achieve optimal performance, it is crucial to minimize lead lengths between components. Short leads reduce resistance and inductance, which can adversely affect circuit efficiency and performance. Proper layout and grounding techniques should be employed to further enhance the circuit's reliability and functionality.
Overall, this circuit serves as a versatile solution for power amplification in various applications, ensuring effective energy delivery for both automotive and home use.This circuit is very basic to build and puts out great power for your car or home. Keep all leads as short as possible. 🔗 External reference
This circuit is designed to deliver substantial power output suitable for automotive or residential applications. The fundamental architecture typically involves a power supply, switching components, and output stage configured to handle the required load.
The power supply section may consist of a transformer or a DC power source, which is responsible for converting the input voltage to the desired output level. A rectifier circuit, composed of diodes, is often employed to convert AC to DC if necessary.
Switching components, such as transistors or MOSFETs, are utilized to control the flow of current through the circuit. These components should be chosen based on their current and voltage ratings to ensure they can handle the load without overheating or failing.
The output stage may include capacitors for filtering to smooth out voltage fluctuations and provide a stable output. Inductors might also be incorporated to reduce noise and improve performance.
To achieve optimal performance, it is crucial to minimize lead lengths between components. Short leads reduce resistance and inductance, which can adversely affect circuit efficiency and performance. Proper layout and grounding techniques should be employed to further enhance the circuit's reliability and functionality.
Overall, this circuit serves as a versatile solution for power amplification in various applications, ensuring effective energy delivery for both automotive and home use.This circuit is very basic to build and puts out great power for your car or home. Keep all leads as short as possible. 🔗 External reference