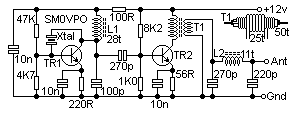
250mW audio amplifier
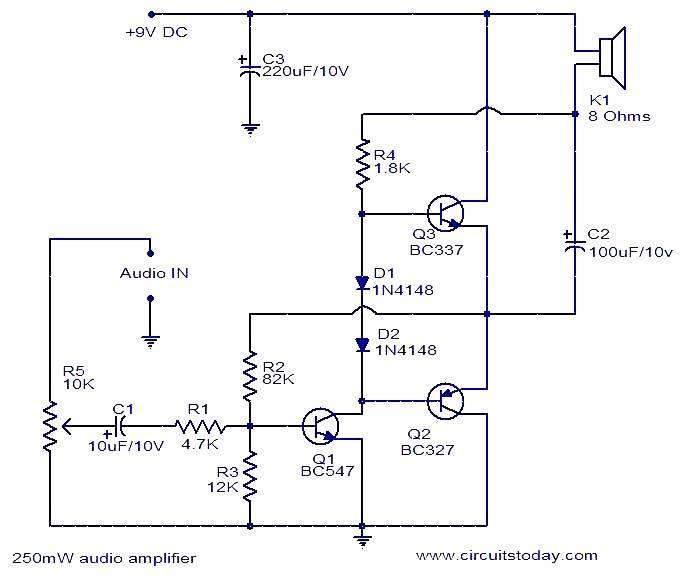
This is a simple three-transistor audio amplifier circuit capable of delivering 250 mW to an 8-ohm speaker. Complementary transistors BC337 and BC227 (Q3 and Q2) are utilized as the output pair, while transistor Q1 (BC547) functions as the preamplifier. The potentiometer R5 serves as a volume control. Capacitor C1 decouples the DC from the audio source, and resistor R2 enhances the amplifier's stability. This amplifier is particularly suitable for use in small radio sets and as a preamplifier in high-power audio amplifiers.
The three-transistor audio amplifier circuit is designed to enhance audio signals for various applications, particularly in compact electronic devices. The circuit employs a configuration where the BC547 transistor (Q1) acts as a preamplifier, boosting the weak audio signals received from the audio source. The output stage consists of complementary transistors BC337 (Q3) and BC227 (Q2), which are configured to drive an 8-ohm speaker effectively, delivering a power output of 250 mW.
The use of a potentiometer (R5) allows for adjustable volume control, enabling users to fine-tune the audio output to their preference. Capacitor C1 plays a crucial role in filtering out any DC offset from the audio input, ensuring that only the desired audio signal is amplified. This is essential for maintaining audio fidelity and preventing distortion.
Resistor R2 contributes to the overall stability of the amplifier circuit, which is vital for consistent performance and reliability. The design is particularly advantageous for small radio sets, where space is limited, yet high-quality audio output is desired. Additionally, this amplifier can serve as an effective preamplifier stage in larger, high-power audio amplifiers, enhancing the versatility of the circuit in various audio applications.Here is a very simple three transistor audio amplifier circuit that can deliver 250mW to a 8Ohm speaker. Complementary transistors BC337 and BC227 (Q3 and Q2) are used as the output pair. Transistor Q1 (BC 547) acts as the preamplifier. POT R5 can be used as a volume control. Capacitor C1 decouples the DC from the audio source. Resistor R2 ensures better stability for the amplifier. This amplifier is very suitable for application in small radio sets and as a preamplifier in high power audio amplifiers. 🔗 External reference
The three-transistor audio amplifier circuit is designed to enhance audio signals for various applications, particularly in compact electronic devices. The circuit employs a configuration where the BC547 transistor (Q1) acts as a preamplifier, boosting the weak audio signals received from the audio source. The output stage consists of complementary transistors BC337 (Q3) and BC227 (Q2), which are configured to drive an 8-ohm speaker effectively, delivering a power output of 250 mW.
The use of a potentiometer (R5) allows for adjustable volume control, enabling users to fine-tune the audio output to their preference. Capacitor C1 plays a crucial role in filtering out any DC offset from the audio input, ensuring that only the desired audio signal is amplified. This is essential for maintaining audio fidelity and preventing distortion.
Resistor R2 contributes to the overall stability of the amplifier circuit, which is vital for consistent performance and reliability. The design is particularly advantageous for small radio sets, where space is limited, yet high-quality audio output is desired. Additionally, this amplifier can serve as an effective preamplifier stage in larger, high-power audio amplifiers, enhancing the versatility of the circuit in various audio applications.Here is a very simple three transistor audio amplifier circuit that can deliver 250mW to a 8Ohm speaker. Complementary transistors BC337 and BC227 (Q3 and Q2) are used as the output pair. Transistor Q1 (BC 547) acts as the preamplifier. POT R5 can be used as a volume control. Capacitor C1 decouples the DC from the audio source. Resistor R2 ensures better stability for the amplifier. This amplifier is very suitable for application in small radio sets and as a preamplifier in high power audio amplifiers. 🔗 External reference