2Mhz Frequency Counter Circuit
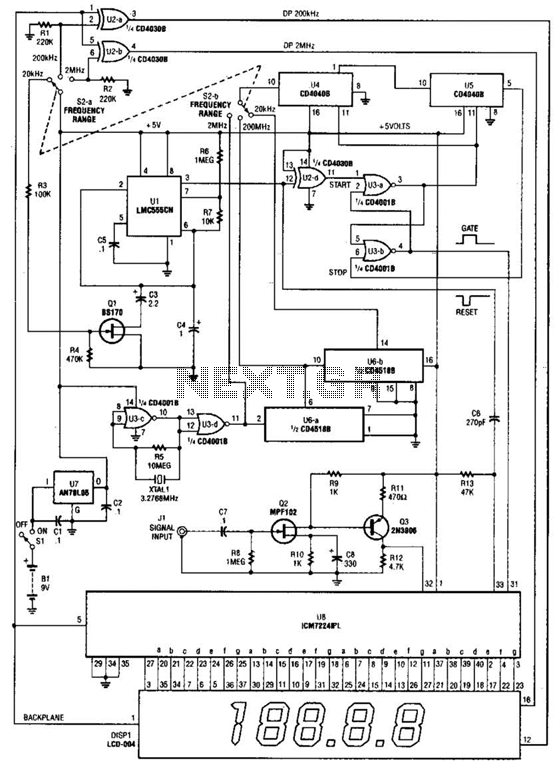
This is a schematic and block diagram of a 2-MHz frequency counter. It utilizes an LSI counter/display driver, an LCD readout, and several logic chips for timebase and timing pulse circuitry. Q2 and Q3 serve as a signal (input) amplifier. The circuit includes a crystal oscillator built around U3-c and XTAL1, which delivers the primary timing reference signal. This signal is then divided twice to generate two additional timing references, providing three selectable timing references for the circuitry. The ICM7224IPL is an integrated circuit that encompasses the counter and display driver to operate the LCD-004 display.
The 2-MHz frequency counter circuit is designed to accurately measure and display frequency signals up to 2 MHz. The core of the design is the ICM7224IPL, which integrates both the counter functionality and the display driver, facilitating a streamlined architecture that reduces component count and complexity. The LCD-004 display is utilized for visual output, allowing users to easily read the frequency measurements.
The signal amplification stage is critical for ensuring the input signal is adequately processed. Transistors Q2 and Q3 are configured as a differential amplifier to enhance the input signal's amplitude, improving the overall sensitivity of the frequency counter. This is particularly important in applications where the input signal may be weak or subject to noise.
The crystal oscillator, consisting of U3-c and XTAL1, serves as the timing backbone of the circuit. It generates a stable frequency reference that is essential for accurate counting. The crystal's frequency stability ensures that the measurements taken by the counter are precise and reliable. The oscillator output is then divided by two stages, creating multiple timing references. This feature allows for flexibility in measurement, as users can select among three different timing references according to their specific requirements.
The logic chips incorporated into the circuit are responsible for managing the timing pulse circuitry, coordinating the operation of the counter, and ensuring that the display driver receives the correct signals to present the frequency reading. The design emphasizes modularity, enabling easy upgrades or modifications to accommodate future enhancements or changes in application needs.
Overall, this frequency counter schematic represents a well-thought-out design that combines essential components to achieve accurate frequency measurement and display, making it suitable for a variety of electronic applications. This is a schematic and block diagram of a 2-MHz frequency counter. It uses and LSI counter/display driver, LCD readout, and a few logic chips for timebase and timing pulse circuitry. Q2 and Q3 form a signal (input) amplifier. The circuit contains a crystal oscillator built around U3- c and XTAL1, which provides the primary timing-reference signal.
That signal is then divided twice to provide two additional timing references, giving the circuitry three selectable timing references. The ICM7224IPL is an integrated circuit that consists of the counter and display driver to drive the LCD-004 display.
The 2-MHz frequency counter circuit is designed to accurately measure and display frequency signals up to 2 MHz. The core of the design is the ICM7224IPL, which integrates both the counter functionality and the display driver, facilitating a streamlined architecture that reduces component count and complexity. The LCD-004 display is utilized for visual output, allowing users to easily read the frequency measurements.
The signal amplification stage is critical for ensuring the input signal is adequately processed. Transistors Q2 and Q3 are configured as a differential amplifier to enhance the input signal's amplitude, improving the overall sensitivity of the frequency counter. This is particularly important in applications where the input signal may be weak or subject to noise.
The crystal oscillator, consisting of U3-c and XTAL1, serves as the timing backbone of the circuit. It generates a stable frequency reference that is essential for accurate counting. The crystal's frequency stability ensures that the measurements taken by the counter are precise and reliable. The oscillator output is then divided by two stages, creating multiple timing references. This feature allows for flexibility in measurement, as users can select among three different timing references according to their specific requirements.
The logic chips incorporated into the circuit are responsible for managing the timing pulse circuitry, coordinating the operation of the counter, and ensuring that the display driver receives the correct signals to present the frequency reading. The design emphasizes modularity, enabling easy upgrades or modifications to accommodate future enhancements or changes in application needs.
Overall, this frequency counter schematic represents a well-thought-out design that combines essential components to achieve accurate frequency measurement and display, making it suitable for a variety of electronic applications. This is a schematic and block diagram of a 2-MHz frequency counter. It uses and LSI counter/display driver, LCD readout, and a few logic chips for timebase and timing pulse circuitry. Q2 and Q3 form a signal (input) amplifier. The circuit contains a crystal oscillator built around U3- c and XTAL1, which provides the primary timing-reference signal.
That signal is then divided twice to provide two additional timing references, giving the circuitry three selectable timing references. The ICM7224IPL is an integrated circuit that consists of the counter and display driver to drive the LCD-004 display.