2N4401 NPN General Purpose Amplifier
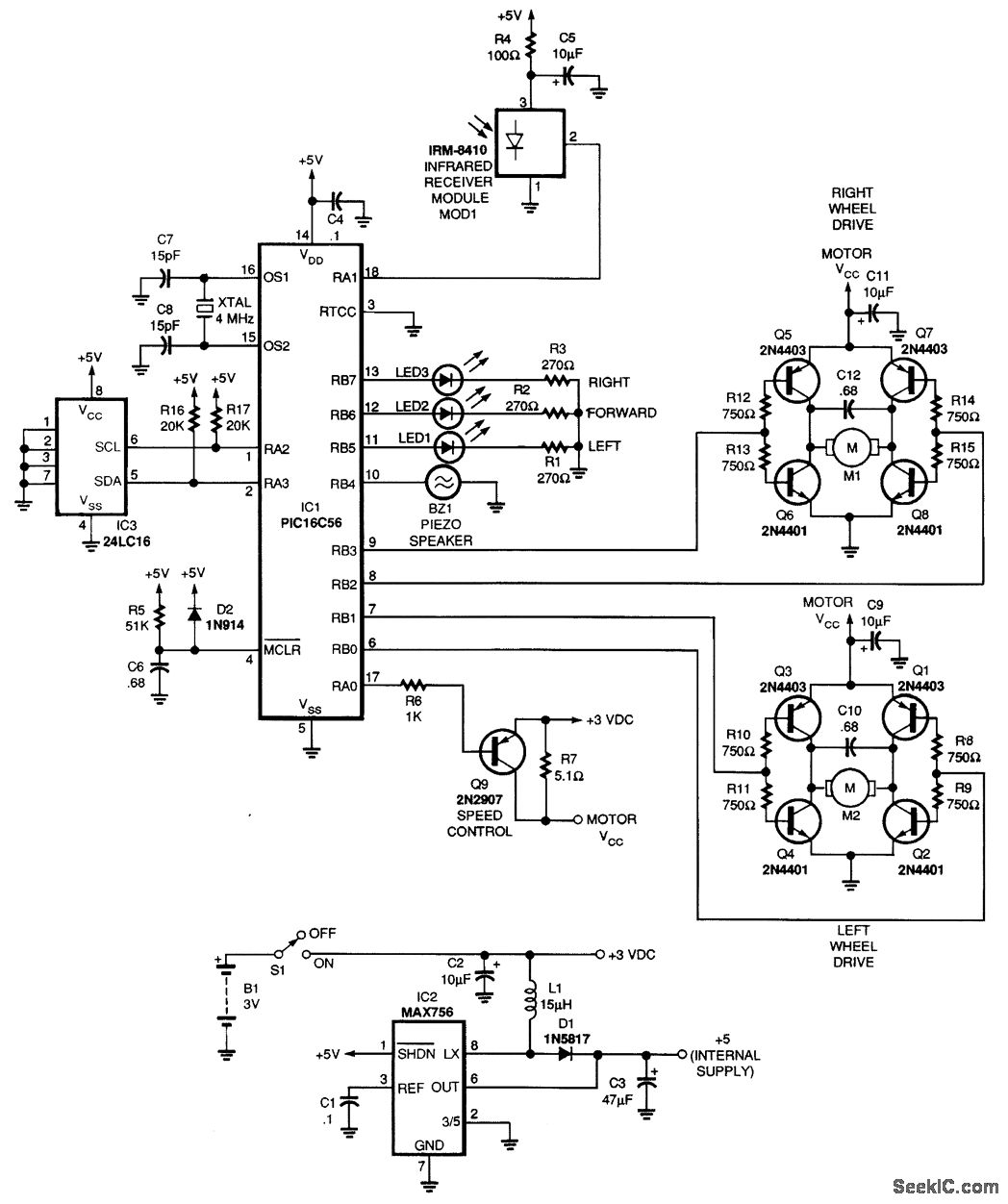
This article describes the Flip-Flop Flashers and Buzzers circuit utilizing the 2N4401 transistor. The content is straightforward and provides valuable insights. Components mentioned in this article can enhance the reader's understanding. For instance, the article includes information on where to find and purchase components such as the 2N4401 transistor. Additionally, it covers Audio Amplifier Circuits that also use the 2N4401.
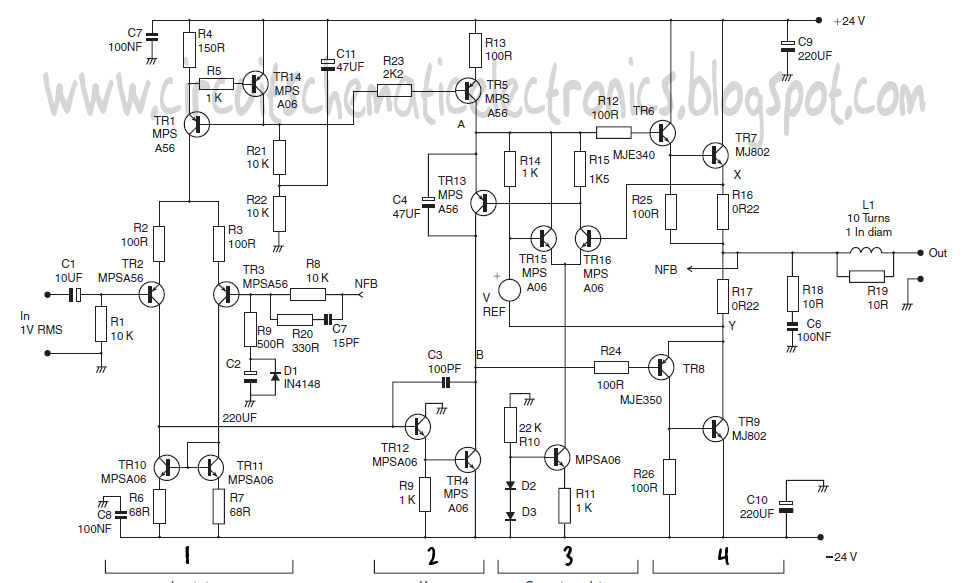
The Flip-Flop Flashers and Buzzers circuit using the 2N4401 is designed to create alternating signals that can be used for visual or auditory indications. The 2N4401 is an NPN bipolar junction transistor commonly employed for switching and amplification purposes. In this circuit, the transistor operates in a flip-flop configuration, allowing it to toggle between two states, thus producing a flashing effect or driving a buzzer.
The circuit typically consists of a few key components: resistors, capacitors, and the 2N4401 transistor. A pair of resistors is used to set the biasing conditions for the transistor, ensuring it operates within the desired range. Capacitors are utilized to create timing delays, which determine the frequency of the flashing or buzzing output. The values of these components can be adjusted to modify the performance characteristics of the circuit.
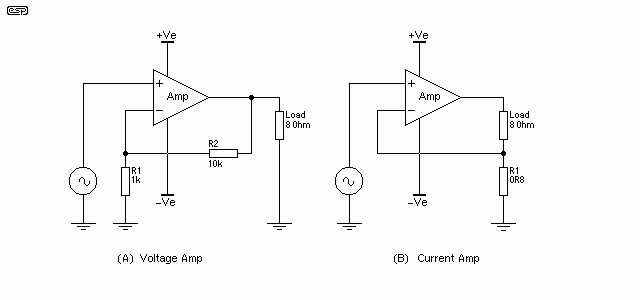
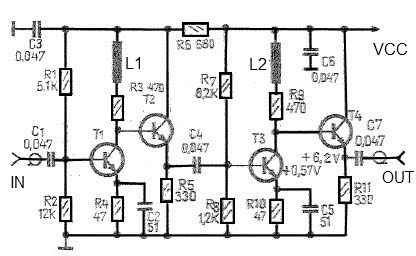
For the audio amplifier circuit, the 2N4401 functions similarly, amplifying audio signals for better sound output. The circuit may include additional components such as potentiometers for volume control and coupling capacitors to block DC components while allowing AC audio signals to pass through.
When assembling these circuits, it is crucial to follow proper electronic assembly techniques, ensuring all connections are secure and components are oriented correctly. The schematic diagram will illustrate the arrangement of components and their interconnections, providing a clear guide for construction.
In summary, the Flip-Flop Flashers and Buzzers circuit, along with the Audio Amplifier Circuits using the 2N4401, exemplifies the versatility of this transistor in various applications. Understanding the operation and configuration of these circuits can significantly enhance one's proficiency in electronics.This article describes the Flip-Flop Flashers, Buzzers CIRCUIT (2N4401). The content is very simple, very helpful. Components in this article can help you understand better understanding of this article. For example, in this article, you can go to find and buy these components: 2N4401. Flip-Flop Fla. This article describes the Audio Amplifier Circ uits (2N4401). The content is very simple, very helpful. Components in this article can help you understand better understanding of this article. For example, in this article, you can go to find and buy these components: 2N4401. Audio Amplifier Circuits. 🔗 External reference
The Flip-Flop Flashers and Buzzers circuit using the 2N4401 is designed to create alternating signals that can be used for visual or auditory indications. The 2N4401 is an NPN bipolar junction transistor commonly employed for switching and amplification purposes. In this circuit, the transistor operates in a flip-flop configuration, allowing it to toggle between two states, thus producing a flashing effect or driving a buzzer.
The circuit typically consists of a few key components: resistors, capacitors, and the 2N4401 transistor. A pair of resistors is used to set the biasing conditions for the transistor, ensuring it operates within the desired range. Capacitors are utilized to create timing delays, which determine the frequency of the flashing or buzzing output. The values of these components can be adjusted to modify the performance characteristics of the circuit.
For the audio amplifier circuit, the 2N4401 functions similarly, amplifying audio signals for better sound output. The circuit may include additional components such as potentiometers for volume control and coupling capacitors to block DC components while allowing AC audio signals to pass through.
When assembling these circuits, it is crucial to follow proper electronic assembly techniques, ensuring all connections are secure and components are oriented correctly. The schematic diagram will illustrate the arrangement of components and their interconnections, providing a clear guide for construction.
In summary, the Flip-Flop Flashers and Buzzers circuit, along with the Audio Amplifier Circuits using the 2N4401, exemplifies the versatility of this transistor in various applications. Understanding the operation and configuration of these circuits can significantly enhance one's proficiency in electronics.This article describes the Flip-Flop Flashers, Buzzers CIRCUIT (2N4401). The content is very simple, very helpful. Components in this article can help you understand better understanding of this article. For example, in this article, you can go to find and buy these components: 2N4401. Flip-Flop Fla. This article describes the Audio Amplifier Circ uits (2N4401). The content is very simple, very helpful. Components in this article can help you understand better understanding of this article. For example, in this article, you can go to find and buy these components: 2N4401. Audio Amplifier Circuits. 🔗 External reference