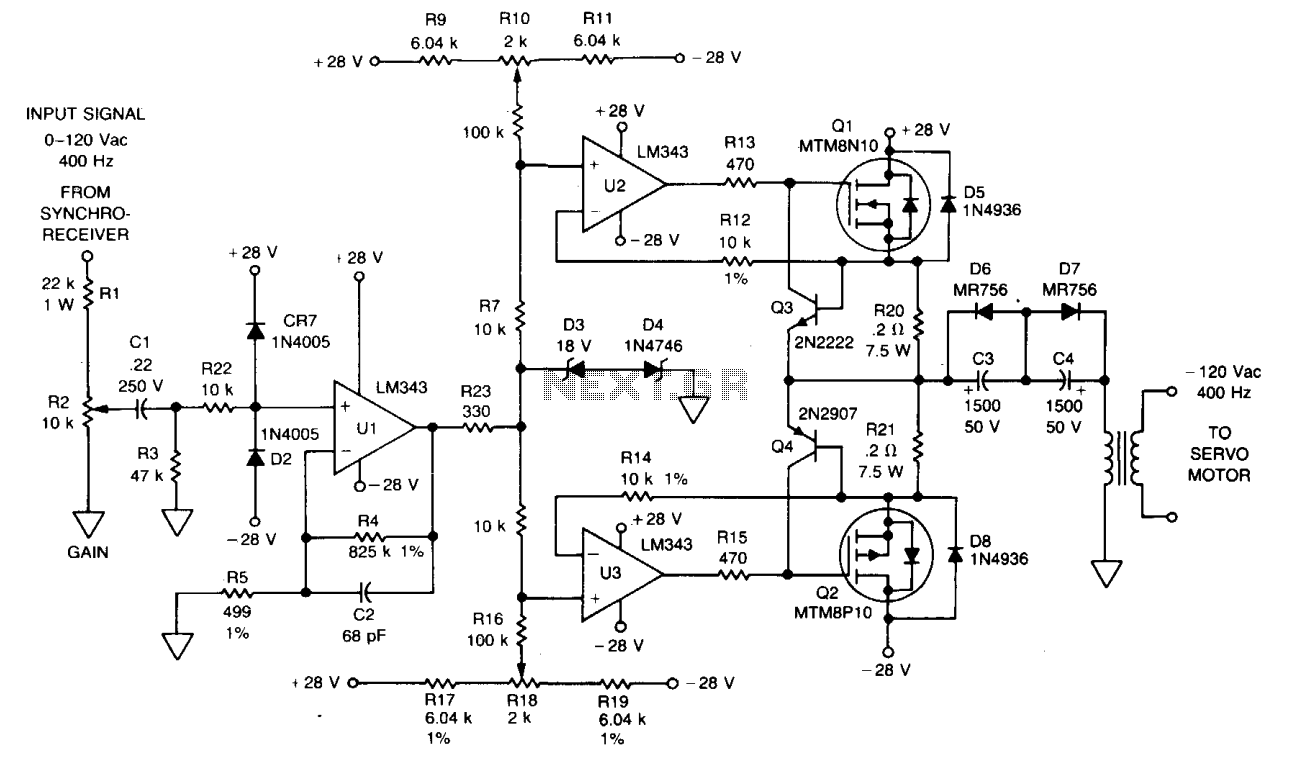
Pre mic audio amplifier with ic LM386

This circuit amplifies sound signals from a condenser microphone to drive a small-sized loudspeaker. The key component is a pre-amplifier using a single transistor to increase the sound signal power before it is sent to an amplifier, specifically the integrated circuit LM386, which drives the loudspeaker. The circuit operates with a 9V power supply. The microphone (MIC1) captures sound signals, which are then amplified by the transistor (Q1). The amplified signal exits through the collector pin (C) and is coupled through capacitor C2. The variable resistor (VR1) adjusts the sound level before feeding into the input of IC1. The LM386 (IC1) is a 1-watt integrated circuit with pin 3 as the input. Capacitor C3 filters out noise from the input signal, grounding it. The amplified output is sent to pin 5, where capacitors C5 and resistor R5 further filter the signal before it is transmitted to the loudspeaker. Capacitor C6 enhances low-frequency sound quality before the audio reaches the loudspeaker.
The circuit serves as a basic audio amplification system designed for applications requiring sound signal enhancement from a microphone. The condenser microphone (MIC1) is responsible for converting acoustic signals into electrical signals. The transistor (Q1) acts as a pre-amplifier, providing initial gain to the weak microphone signal. The collector pin (C) of the transistor outputs the amplified signal, which is then coupled through capacitor C2 to block any DC offset while allowing the AC audio signal to pass.
The variable resistor (VR1) is crucial for adjusting the gain and ensuring that the audio output level is suitable for the application, preventing distortion or clipping of the audio signal. The LM386 integrated circuit is known for its low voltage operation and high efficiency in audio applications. With pin 3 designated as the input, the LM386 receives the amplified signal, while capacitor C3 serves to filter out any high-frequency noise that might interfere with the audio quality.
The output from the LM386 at pin 5 is further processed through capacitor C5 and resistor R5, which work together to eliminate any residual noise and ensure a clean audio signal is sent to the loudspeaker. Capacitor C6 is included to improve the low-frequency response of the audio output, enhancing the overall sound quality before it reaches the loudspeaker.
This circuit is suitable for various applications, including portable audio devices, small public address systems, and other scenarios where compact size and efficient power usage are essential. The use of the LM386 allows for a straightforward design, making it accessible for hobbyists and professionals alike.This circuit be signal sound expansion from condenser microphone give with small-sized loudspeaker. It compose the importance is part pre mic use transistor just one enlarge sound signal gives the power goes up change come to a part amplifier with the integrated circuit LM386 utter go out give aloudspeaker. When feed9V power supplyreach the circui t. The MIC1 and Q1 which be part pre mic, by mic will take sound signal has come in then deliver Q1 enlarge a signal has power size goes up to go out the way collector pin (C) change C2 coupling signal. Then deliver with VR1 for fine signal sound level gives with Input of IC1. Which IC1 numberLM386be theintegrated circuit amplifies1 watt size has pin 3 are input and have C3 will eradicate source noise with input signal discharge down ground.
When amplify finished will export come to the way output pin 5 by have C5 and R5 eradicate a signal takes to stir go out sound signal will have that to change go to still. The C6 coupling signal and enhance sound quality of low frequency improve. Before reach a loudspeaker makes a noise to come out. 🔗 External reference
The circuit serves as a basic audio amplification system designed for applications requiring sound signal enhancement from a microphone. The condenser microphone (MIC1) is responsible for converting acoustic signals into electrical signals. The transistor (Q1) acts as a pre-amplifier, providing initial gain to the weak microphone signal. The collector pin (C) of the transistor outputs the amplified signal, which is then coupled through capacitor C2 to block any DC offset while allowing the AC audio signal to pass.
The variable resistor (VR1) is crucial for adjusting the gain and ensuring that the audio output level is suitable for the application, preventing distortion or clipping of the audio signal. The LM386 integrated circuit is known for its low voltage operation and high efficiency in audio applications. With pin 3 designated as the input, the LM386 receives the amplified signal, while capacitor C3 serves to filter out any high-frequency noise that might interfere with the audio quality.
The output from the LM386 at pin 5 is further processed through capacitor C5 and resistor R5, which work together to eliminate any residual noise and ensure a clean audio signal is sent to the loudspeaker. Capacitor C6 is included to improve the low-frequency response of the audio output, enhancing the overall sound quality before it reaches the loudspeaker.
This circuit is suitable for various applications, including portable audio devices, small public address systems, and other scenarios where compact size and efficient power usage are essential. The use of the LM386 allows for a straightforward design, making it accessible for hobbyists and professionals alike.This circuit be signal sound expansion from condenser microphone give with small-sized loudspeaker. It compose the importance is part pre mic use transistor just one enlarge sound signal gives the power goes up change come to a part amplifier with the integrated circuit LM386 utter go out give aloudspeaker. When feed9V power supplyreach the circui t. The MIC1 and Q1 which be part pre mic, by mic will take sound signal has come in then deliver Q1 enlarge a signal has power size goes up to go out the way collector pin (C) change C2 coupling signal. Then deliver with VR1 for fine signal sound level gives with Input of IC1. Which IC1 numberLM386be theintegrated circuit amplifies1 watt size has pin 3 are input and have C3 will eradicate source noise with input signal discharge down ground.
When amplify finished will export come to the way output pin 5 by have C5 and R5 eradicate a signal takes to stir go out sound signal will have that to change go to still. The C6 coupling signal and enhance sound quality of low frequency improve. Before reach a loudspeaker makes a noise to come out. 🔗 External reference