4 ~ 20mA transmitter circuit diagram TMP35 temperature
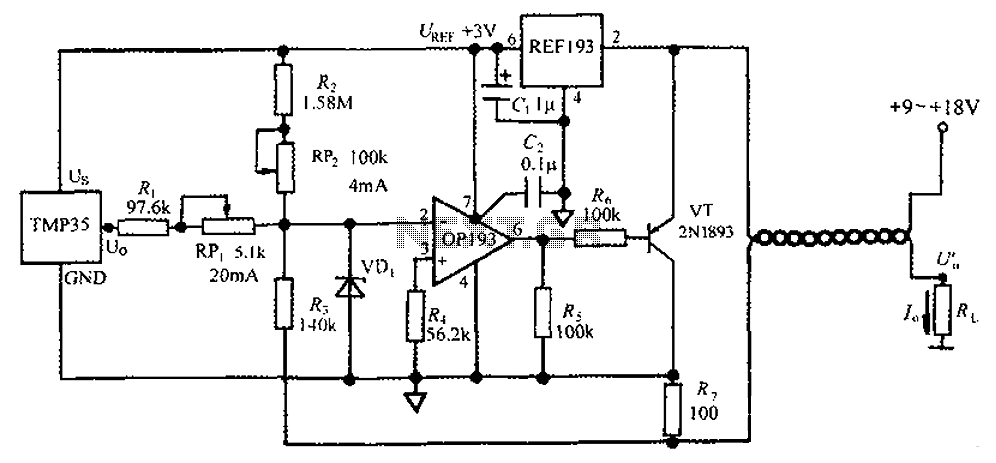
The circuit consists of a TMP35 temperature transmitter that converts a voltage signal output from the TMP35 into a standard 4 to 20 mA current signal. This configuration is suitable for use in automated instrumentation and industrial temperature control systems. The 4 mA output represents the zero-scale value, while the 20 mA output indicates the full-scale value. The REF193 serves as a 3V reference voltage source, and the OP193 is utilized as an operational amplifier. Calibration is facilitated by the inclusion of two potentiometers, RP1 and RP2, which allow for independent adjustments of zero and full-scale values. A Schottky diode, VD1, is incorporated to prevent increases in the open-loop voltage of the OP193. The recommended power supply voltage for this circuit ranges from +9V to +18V.
The transmitter's output current can be expressed as a function of the input voltage from the TMP35 sensor, which is a linear temperature sensor providing a voltage output proportional to the temperature. The TMP35 outputs a voltage of 10 mV per degree Celsius, allowing for a direct correlation between temperature and output current. The operational amplifier (OP193) amplifies this voltage signal to the required level, while the REF193 provides a stable reference voltage for accurate current regulation.
The circuit design features two adjustable potentiometers, RP1 and RP2, which are critical for fine-tuning the zero and full-scale outputs. Adjusting RP1 alters the zero-scale output, ensuring that at a specific temperature (usually at the lower end of the temperature range), the output current is precisely set to 4 mA. Similarly, RP2 is used to adjust the full-scale output, ensuring that at the maximum temperature (the upper limit of the intended measurement range), the output current reaches 20 mA.
The inclusion of the Schottky diode (VD1) is significant as it protects the operational amplifier from potential damage due to excessive voltage levels that could occur in an open-loop condition. This diode allows for fast switching and low forward voltage drop, making it an ideal choice for this application.
The power supply requirements of +9V to +18V ensure that the circuit operates efficiently while providing sufficient headroom for the operational amplifier and other components. Overall, this TMP35 temperature transmitter circuit is designed to provide a reliable and accurate method for temperature measurement and control in various industrial applications, leveraging the 4 to 20 mA current loop standard widely used in process control systems.4 ~ 20mA constituted by a TMP35 temperature transmitter circuit as shown in FIG. This circuit can be a voltage signal TMP35 output is converted into a standard 4 ~ 20mA current signal, for the use of automated instrumentation, industrial temperature control. Here is 4mA as zero-scale value, 20mA full-scale value. REF193 is 3V reference voltage source, OP193 operational amplifier. RP1, RP2, respectively, and full scale calibration potentiometer zero, both can be adjusted independently of each other. VD1 Schottky diode, which prevents OP193 open loop voltage increases. Preferably the power supply voltage + 9 ~ + 18V. Transmitter output current expression is:
The transmitter's output current can be expressed as a function of the input voltage from the TMP35 sensor, which is a linear temperature sensor providing a voltage output proportional to the temperature. The TMP35 outputs a voltage of 10 mV per degree Celsius, allowing for a direct correlation between temperature and output current. The operational amplifier (OP193) amplifies this voltage signal to the required level, while the REF193 provides a stable reference voltage for accurate current regulation.
The circuit design features two adjustable potentiometers, RP1 and RP2, which are critical for fine-tuning the zero and full-scale outputs. Adjusting RP1 alters the zero-scale output, ensuring that at a specific temperature (usually at the lower end of the temperature range), the output current is precisely set to 4 mA. Similarly, RP2 is used to adjust the full-scale output, ensuring that at the maximum temperature (the upper limit of the intended measurement range), the output current reaches 20 mA.
The inclusion of the Schottky diode (VD1) is significant as it protects the operational amplifier from potential damage due to excessive voltage levels that could occur in an open-loop condition. This diode allows for fast switching and low forward voltage drop, making it an ideal choice for this application.
The power supply requirements of +9V to +18V ensure that the circuit operates efficiently while providing sufficient headroom for the operational amplifier and other components. Overall, this TMP35 temperature transmitter circuit is designed to provide a reliable and accurate method for temperature measurement and control in various industrial applications, leveraging the 4 to 20 mA current loop standard widely used in process control systems.4 ~ 20mA constituted by a TMP35 temperature transmitter circuit as shown in FIG. This circuit can be a voltage signal TMP35 output is converted into a standard 4 ~ 20mA current signal, for the use of automated instrumentation, industrial temperature control. Here is 4mA as zero-scale value, 20mA full-scale value. REF193 is 3V reference voltage source, OP193 operational amplifier. RP1, RP2, respectively, and full scale calibration potentiometer zero, both can be adjusted independently of each other. VD1 Schottky diode, which prevents OP193 open loop voltage increases. Preferably the power supply voltage + 9 ~ + 18V. Transmitter output current expression is: