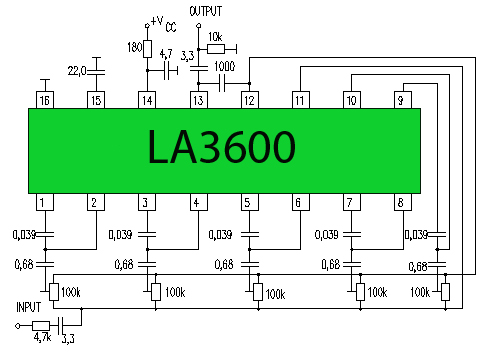
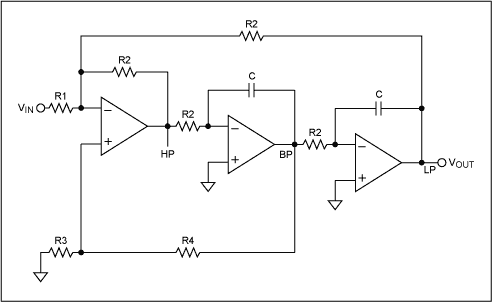
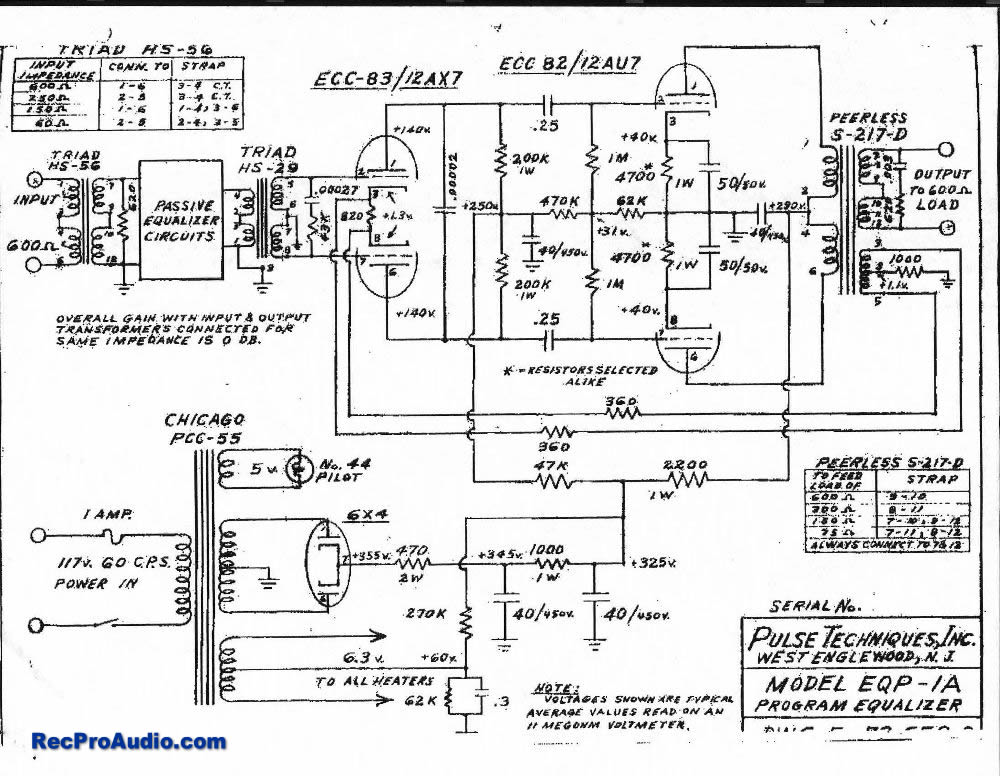
5 Band Graphic Equalizer
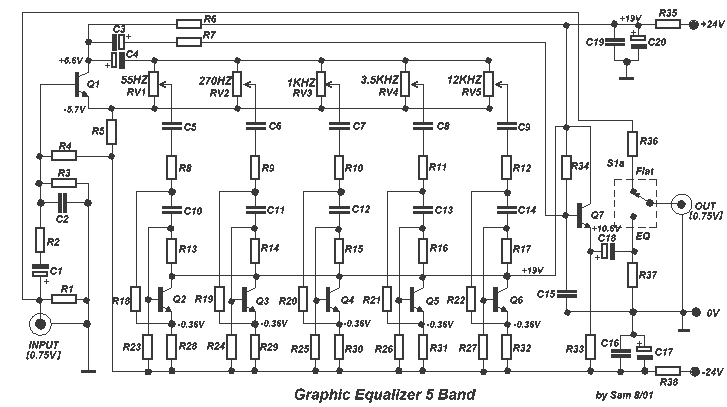
Another unit of graphic EQ with five bands. The basic difference with the other circuits is that instead of an IC, a transistor is used and the power supply goes up to +/- 24V DC, ensuring low distortion and larger overload margins. With switch S1, we can isolate the EQ in or out of operation, allowing the musical signal to pass without any alteration.
Additional Content: This graphic EQ unit is designed with a focus on high performance and versatility. It features five bands, providing a wide range of sound modification possibilities. Instead of using an integrated circuit (IC), this unit utilizes a transistor, which can often provide better performance in terms of speed and power consumption.
The power supply of this unit is designed to handle up to +/- 24V DC. This high voltage range ensures low distortion in the output signal, making it ideal for applications that require clean and clear sound reproduction. Additionally, this high voltage range provides larger overload margins, which means the unit can handle higher input signals without the risk of damage.
One key feature of this unit is switch S1. This switch allows the user to isolate the EQ either in or out of operation. When the EQ is isolated, it allows the musical signal to pass through the unit without any alteration. This feature provides flexibility in how the unit is used, as it can either modify the sound signal or simply let it pass through unaltered.
In conclusion, this graphic EQ unit is a high-performance device designed with versatility and durability in mind. Its unique design features, such as the use of a transistor instead of an IC and a high voltage power supply, ensure it delivers low distortion and can handle a wide range of input signals. With the ability to isolate the EQ, this unit can be used in a variety of audio applications.Another one unit of graphic EQ. five bands. The basic difference with the other circuits is, that I use instead of IC, transistor and the power supply, go up in +/- 24V DC, ensuring low distortion and bigger margins of overloading. With switch S1, we can isolate the EQ. inside or except operation, leaving the musical signal to pass without no alteration. 🔗 External reference
Additional Content: This graphic EQ unit is designed with a focus on high performance and versatility. It features five bands, providing a wide range of sound modification possibilities. Instead of using an integrated circuit (IC), this unit utilizes a transistor, which can often provide better performance in terms of speed and power consumption.
The power supply of this unit is designed to handle up to +/- 24V DC. This high voltage range ensures low distortion in the output signal, making it ideal for applications that require clean and clear sound reproduction. Additionally, this high voltage range provides larger overload margins, which means the unit can handle higher input signals without the risk of damage.
One key feature of this unit is switch S1. This switch allows the user to isolate the EQ either in or out of operation. When the EQ is isolated, it allows the musical signal to pass through the unit without any alteration. This feature provides flexibility in how the unit is used, as it can either modify the sound signal or simply let it pass through unaltered.
In conclusion, this graphic EQ unit is a high-performance device designed with versatility and durability in mind. Its unique design features, such as the use of a transistor instead of an IC and a high voltage power supply, ensure it delivers low distortion and can handle a wide range of input signals. With the ability to isolate the EQ, this unit can be used in a variety of audio applications.Another one unit of graphic EQ. five bands. The basic difference with the other circuits is, that I use instead of IC, transistor and the power supply, go up in +/- 24V DC, ensuring low distortion and bigger margins of overloading. With switch S1, we can isolate the EQ. inside or except operation, leaving the musical signal to pass without no alteration. 🔗 External reference