555 timer circuit temperature sensor temperature
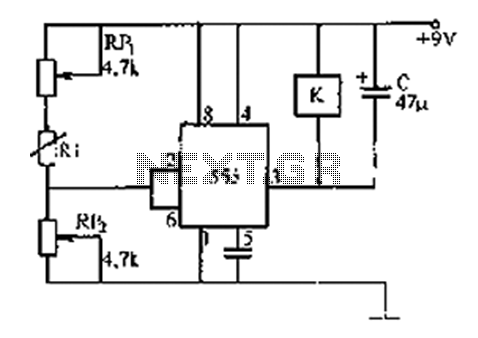
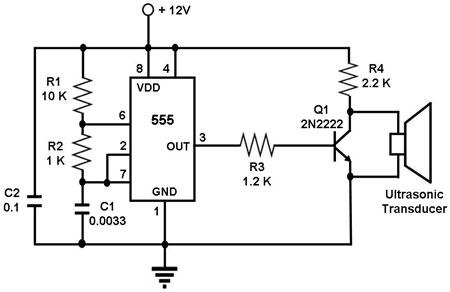
The 555 timer integrates both analog and digital functions within a scaled integrated device. Typically manufactured using a bipolar process, it is designated as the 555 timer, while the CMOS version is referred to as the 7555. In addition to the single timer, there are corresponding dual timers, namely the 556 and 7556. The 555 timer operates over a wide supply voltage range of 4.5V to 16V, whereas the 7555 can function between 3V and 18V. The output drive current is approximately 200mA, allowing compatibility with CMOS analog circuits or TTL levels. This device is cost-effective and exhibits reliable performance, requiring only a few external resistors and capacitors to implement various functions such as multivibrators, Schmitt triggers, single-shot pulse generation, and conversion circuits.
The 555 timer is a versatile integrated circuit that serves multiple applications in timing, pulse generation, and oscillation. Its architecture consists of two voltage comparators, a flip-flop, a discharge transistor, and a resistor divider network. The device can be configured in three primary modes: astable, monostable, and bistable.
In astable mode, the 555 timer functions as an oscillator, generating a continuous square wave output. This configuration is achieved by connecting two resistors and a capacitor to the timing pins, allowing the circuit to oscillate between high and low states. The frequency and duty cycle of the output waveform can be adjusted by varying the values of the resistors and capacitor.
In monostable mode, the 555 timer acts as a one-shot pulse generator. A trigger input causes the output to transition to a high state for a specified duration, determined by an external resistor and capacitor. This mode is useful for applications requiring a single pulse output in response to an input signal.
In bistable mode, the 555 timer operates as a flip-flop, providing a stable output that can be toggled between high and low states using two separate trigger inputs. This configuration is ideal for applications such as toggle switches or memory storage.
The device's wide supply voltage range and output current capability make it suitable for driving various loads, including LEDs, small motors, and other components in electronic circuits. The 555 timer's simplicity, combined with its reliability and low cost, has made it a popular choice in both hobbyist and professional electronics projects. With minimal external components, it can be integrated into complex systems, providing essential timing and control functions across a diverse array of applications.555 timer is a combination of analog and digital functions in scale integrated devices. Usually made with bipolar process called 555, with the CMOS process is referred to 7555, in addition to single timer, there are corresponding dual timer 556/7556 Wide supply voltage range 555 timer can be 4.5V ~ 16V work, 7555 can work 3 ~ 18V, output drive current of about 200mA, so its output can be, CMOS analog circuits or compatible with TTL level in at. Low cost, reliable performance, requires only a few external resistors, capacitors, you can achieve multivibrator, Schmitt trigger, and a single-shot pulse generation and conversion circuits, etc.
The 555 timer is a versatile integrated circuit that serves multiple applications in timing, pulse generation, and oscillation. Its architecture consists of two voltage comparators, a flip-flop, a discharge transistor, and a resistor divider network. The device can be configured in three primary modes: astable, monostable, and bistable.
In astable mode, the 555 timer functions as an oscillator, generating a continuous square wave output. This configuration is achieved by connecting two resistors and a capacitor to the timing pins, allowing the circuit to oscillate between high and low states. The frequency and duty cycle of the output waveform can be adjusted by varying the values of the resistors and capacitor.
In monostable mode, the 555 timer acts as a one-shot pulse generator. A trigger input causes the output to transition to a high state for a specified duration, determined by an external resistor and capacitor. This mode is useful for applications requiring a single pulse output in response to an input signal.
In bistable mode, the 555 timer operates as a flip-flop, providing a stable output that can be toggled between high and low states using two separate trigger inputs. This configuration is ideal for applications such as toggle switches or memory storage.
The device's wide supply voltage range and output current capability make it suitable for driving various loads, including LEDs, small motors, and other components in electronic circuits. The 555 timer's simplicity, combined with its reliability and low cost, has made it a popular choice in both hobbyist and professional electronics projects. With minimal external components, it can be integrated into complex systems, providing essential timing and control functions across a diverse array of applications.555 timer is a combination of analog and digital functions in scale integrated devices. Usually made with bipolar process called 555, with the CMOS process is referred to 7555, in addition to single timer, there are corresponding dual timer 556/7556 Wide supply voltage range 555 timer can be 4.5V ~ 16V work, 7555 can work 3 ~ 18V, output drive current of about 200mA, so its output can be, CMOS analog circuits or compatible with TTL level in at. Low cost, reliable performance, requires only a few external resistors, capacitors, you can achieve multivibrator, Schmitt trigger, and a single-shot pulse generation and conversion circuits, etc.