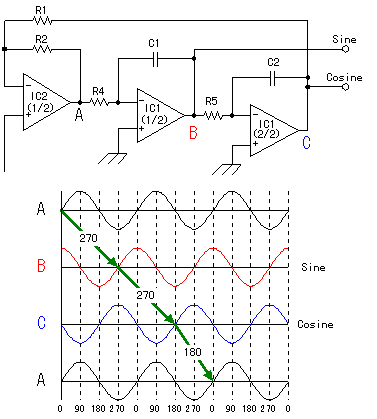
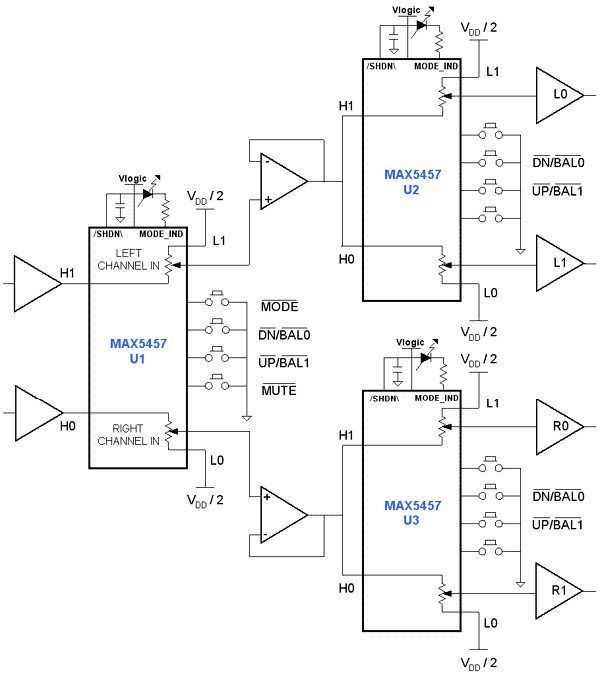
Wien Bridge Oscillator Circuit
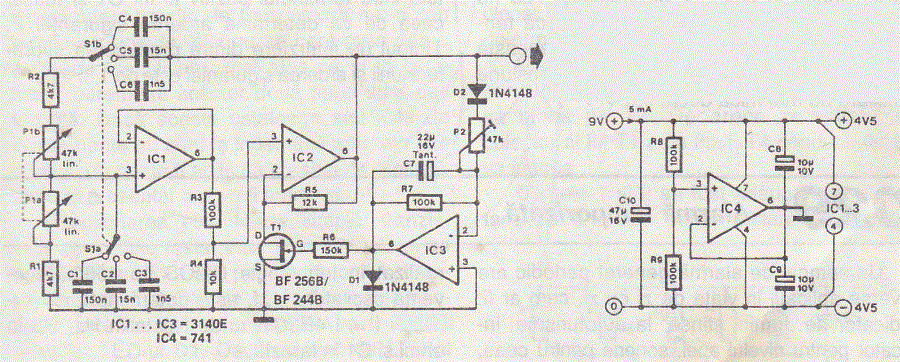
This Wien bridge oscillator is straightforward and, like all Wien oscillators, exhibits low distortion. The resonance frequency can be easily adjusted.
The Wien bridge oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that generates sine waves. It is based on the principle of a bridge circuit, which includes resistors and capacitors arranged in a specific configuration. The circuit typically consists of two resistors and two capacitors, configured to form a feedback loop that allows for the generation of oscillations.
The fundamental frequency of oscillation is determined by the values of the resistors and capacitors used in the circuit. By adjusting these component values, the resonance frequency can be altered, allowing for a wide range of output frequencies. This adjustability is a significant advantage, making the Wien bridge oscillator suitable for various applications in audio and signal processing.
To maintain oscillation, the circuit often includes an automatic gain control mechanism. This is typically achieved using a thermistor or a light-dependent resistor (LDR) in the feedback path, which helps stabilize the amplitude of the output signal. As the output amplitude increases, the resistance of the controlling element changes, reducing the gain and preventing distortion.
The output of the Wien bridge oscillator is a clean, sinusoidal waveform, which is advantageous for applications requiring low distortion, such as audio signal generation or testing. The design of the circuit allows for easy implementation on a breadboard or PCB, making it accessible for both educational purposes and practical applications in electronic design.
Overall, the Wien bridge oscillator is a valuable circuit in electronics, known for its simplicity and effectiveness in generating stable sine wave signals.THis Wien bridge oscillator is very simple and as every wien oscillator has low distorsion and the resonance frequency can be easily adjusted. This frequen.. 🔗 External reference
The Wien bridge oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that generates sine waves. It is based on the principle of a bridge circuit, which includes resistors and capacitors arranged in a specific configuration. The circuit typically consists of two resistors and two capacitors, configured to form a feedback loop that allows for the generation of oscillations.
The fundamental frequency of oscillation is determined by the values of the resistors and capacitors used in the circuit. By adjusting these component values, the resonance frequency can be altered, allowing for a wide range of output frequencies. This adjustability is a significant advantage, making the Wien bridge oscillator suitable for various applications in audio and signal processing.
To maintain oscillation, the circuit often includes an automatic gain control mechanism. This is typically achieved using a thermistor or a light-dependent resistor (LDR) in the feedback path, which helps stabilize the amplitude of the output signal. As the output amplitude increases, the resistance of the controlling element changes, reducing the gain and preventing distortion.
The output of the Wien bridge oscillator is a clean, sinusoidal waveform, which is advantageous for applications requiring low distortion, such as audio signal generation or testing. The design of the circuit allows for easy implementation on a breadboard or PCB, making it accessible for both educational purposes and practical applications in electronic design.
Overall, the Wien bridge oscillator is a valuable circuit in electronics, known for its simplicity and effectiveness in generating stable sine wave signals.THis Wien bridge oscillator is very simple and as every wien oscillator has low distorsion and the resonance frequency can be easily adjusted. This frequen.. 🔗 External reference