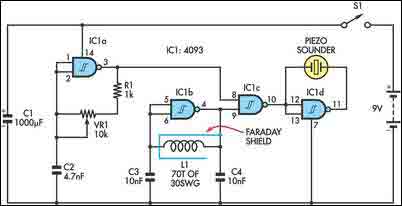
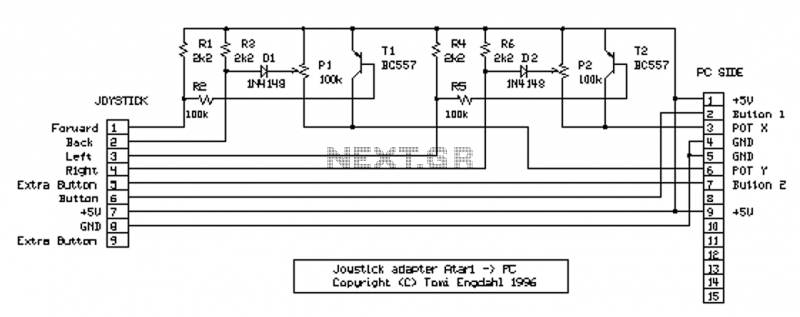
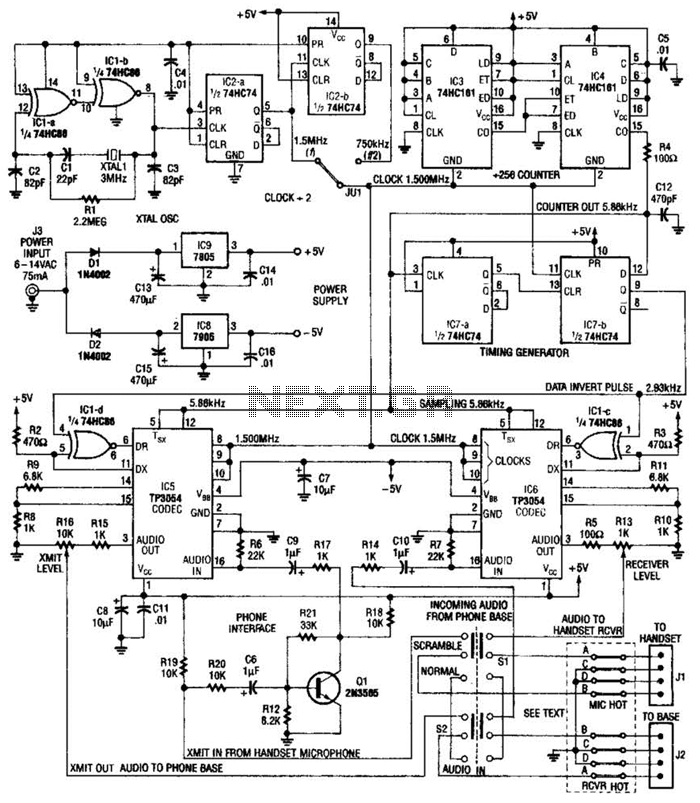
555 Touch-sensitive switch circuit diagram
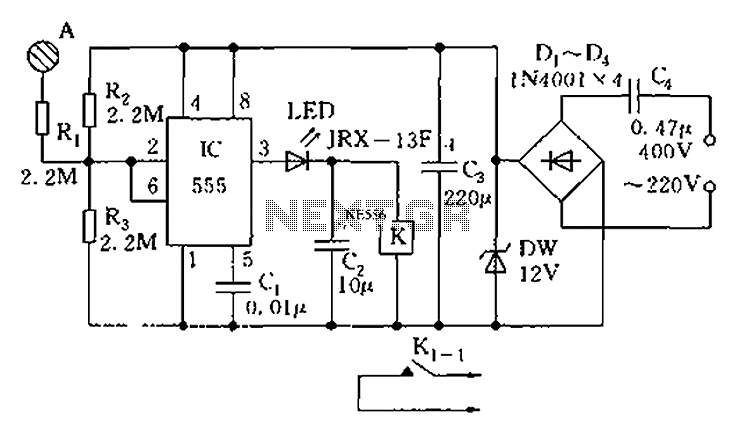
The touch sensor switch circuit diagram features a step-down rectifier circuit, a 555 timer, and flip-flops. When a hand touches the metal sheet A, the sensor signal activates the internal comparator of the 555 timer, setting the output to K, which closes contact K1-1. If a further trigger occurs at A, K is released, and K1-1 is disconnected.
The touch sensor switch circuit operates on the principle of capacitive sensing, where the presence of a hand near the metal sheet alters the capacitance, triggering the circuit's response. The step-down rectifier circuit is responsible for converting the AC voltage to a lower DC voltage suitable for the operation of the 555 timer and other components. The 555 timer, configured in a monostable or astable mode, serves as the core of the timing mechanism, generating a pulse when activated.
Upon the initial touch of the hand to the metal sheet A, the capacitance change is detected, sending a signal to the internal comparator within the 555 timer. This comparator assesses the voltage levels and, upon detecting the touch, sets the output state to K. This action energizes the relay or switch associated with contact K1-1, effectively closing the circuit and allowing current to flow to the connected load.
If the hand remains in contact with the metal sheet, the circuit remains in this activated state. However, if a second trigger occurs—such as the removal of the hand or a subsequent touch—the circuit resets, and the output at K is released, opening contact K1-1 and disconnecting the load. This functionality allows for a simple yet effective method of controlling devices with a non-mechanical touch interface, enhancing user interaction without the need for physical switches.
The inclusion of flip-flops in the circuit design adds a layer of stability and control, enabling the circuit to maintain its state until a defined condition is met, preventing accidental activation or deactivation. Proper component selection, including capacitors and resistors, is crucial for ensuring the sensitivity and responsiveness of the touch sensor switch circuit. As shown in FIG touch sensor switch circuit diagram The circuit consists of step-down rectifier circuit 555 and flip-flops. When the hand touches the metal sheet A, sensor sign al causes the internal comparator flip 555 is set, K pull, contact K1-1 closed; if more trigger at A, then K release, K1-1 disconnected.
The touch sensor switch circuit operates on the principle of capacitive sensing, where the presence of a hand near the metal sheet alters the capacitance, triggering the circuit's response. The step-down rectifier circuit is responsible for converting the AC voltage to a lower DC voltage suitable for the operation of the 555 timer and other components. The 555 timer, configured in a monostable or astable mode, serves as the core of the timing mechanism, generating a pulse when activated.
Upon the initial touch of the hand to the metal sheet A, the capacitance change is detected, sending a signal to the internal comparator within the 555 timer. This comparator assesses the voltage levels and, upon detecting the touch, sets the output state to K. This action energizes the relay or switch associated with contact K1-1, effectively closing the circuit and allowing current to flow to the connected load.
If the hand remains in contact with the metal sheet, the circuit remains in this activated state. However, if a second trigger occurs—such as the removal of the hand or a subsequent touch—the circuit resets, and the output at K is released, opening contact K1-1 and disconnecting the load. This functionality allows for a simple yet effective method of controlling devices with a non-mechanical touch interface, enhancing user interaction without the need for physical switches.
The inclusion of flip-flops in the circuit design adds a layer of stability and control, enabling the circuit to maintain its state until a defined condition is met, preventing accidental activation or deactivation. Proper component selection, including capacitors and resistors, is crucial for ensuring the sensitivity and responsiveness of the touch sensor switch circuit. As shown in FIG touch sensor switch circuit diagram The circuit consists of step-down rectifier circuit 555 and flip-flops. When the hand touches the metal sheet A, sensor sign al causes the internal comparator flip 555 is set, K pull, contact K1-1 closed; if more trigger at A, then K release, K1-1 disconnected.