5V Regulated Power SupplyCircuit
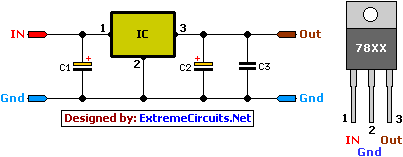
This circuit is a compact +5V power supply that is beneficial for digital electronics experimentation. Inexpensive wall transformers with variable output voltage can be found at electronics shops and supermarkets. While these transformers are readily available, their voltage regulation is often inadequate, making them less suitable for digital circuit experiments unless improved regulation is implemented. The following circuit addresses this issue. It provides a +5V output with a current capacity of approximately 150 mA, which can be increased to 1 A with adequate cooling for the 7805 regulator chip. The circuit includes overload and thermal protection. It is essential that the capacitors used have a sufficiently high voltage rating to safely accommodate the input voltage supplied to the circuit. The circuit can be easily assembled on a piece of veroboard. For different voltage outputs, the circuit can be modified by replacing the 7805 chip with another regulator from the 78xx family, where the last digits in the chip code indicate the output voltage. It is crucial to ensure that the input voltage is at least 3V higher than the regulator output voltage for optimal performance.
This circuit functions as a reliable +5V power supply, ideal for digital electronics projects. The core of the circuit is the 7805 voltage regulator, which maintains a stable output voltage of +5V. The input voltage to the regulator should be sourced from a wall transformer that is capable of delivering a voltage higher than +5V, typically in the range of +8V to +12V, to ensure proper regulation. The regulator can supply up to 1A of current with sufficient heat dissipation, which is achieved through the use of a heat sink.
The circuit should include a pair of capacitors at the input and output of the regulator. A 0.33 µF capacitor is recommended at the input to filter out high-frequency noise, while a 0.1 µF capacitor at the output helps stabilize the output voltage. Additionally, a larger electrolytic capacitor, typically in the range of 10 µF to 100 µF, can be placed at the output to provide better transient response and further smooth the output voltage.
Thermal protection is an essential feature of this circuit, as the 7805 regulator can become hot under load. It is advisable to include a thermal cutoff switch or a fuse in the circuit to prevent overheating. Overload protection can be implemented using a simple current-limiting resistor or a more sophisticated solution involving a PTC resettable fuse.
For users requiring different output voltages, the circuit can be easily adapted by swapping the 7805 with other regulators from the 78xx series, such as the 7812 for +12V or the 7809 for +9V. Each variant has a specific output voltage indicated by the last two digits of its part number. When modifying the circuit for different output voltages, it is crucial to recalculate the input voltage requirements based on the new output voltage to maintain proper operation and ensure that the input voltage remains at least 3V above the desired output voltage.
Overall, this circuit design provides a straightforward and effective solution for powering digital electronics, ensuring stable voltage and current while offering flexibility for various applications.This circuit is a small +5V power supply, which is useful when experimenting with digital electronics. Small inexpensive wall tranformers with variable output voltage are available from any electronics shop and supermarket.
Those transformers are easily available, but usually their voltage regulation is very poor, which makes then not very usable for digital circuit experimenter unless a better regulation can be achieved in some way. The following circuit is the answer to the problem. This circuit can give +5V output at about 150 mA current, but it can be increased to 1 A when good cooling is added to 7805 regulator chip. The circuit has overload and thermal protection. The capacitors must have enough high voltage rating to safely handle the input voltage feed to circuit.
The circuit is very easy to build for example into a piece of veroboard. If you need other voltages than +5V, you can modify the circuit by replacing the 7805 chips with another regulator with different output voltage from regulator 78xx chip family. The last numbers in the the chip code tells the output voltage. Remember that the input voltage muts be at least 3V greater than regulator output voltage ot otherwise the regulator does not work well.
🔗 External reference
This circuit functions as a reliable +5V power supply, ideal for digital electronics projects. The core of the circuit is the 7805 voltage regulator, which maintains a stable output voltage of +5V. The input voltage to the regulator should be sourced from a wall transformer that is capable of delivering a voltage higher than +5V, typically in the range of +8V to +12V, to ensure proper regulation. The regulator can supply up to 1A of current with sufficient heat dissipation, which is achieved through the use of a heat sink.
The circuit should include a pair of capacitors at the input and output of the regulator. A 0.33 µF capacitor is recommended at the input to filter out high-frequency noise, while a 0.1 µF capacitor at the output helps stabilize the output voltage. Additionally, a larger electrolytic capacitor, typically in the range of 10 µF to 100 µF, can be placed at the output to provide better transient response and further smooth the output voltage.
Thermal protection is an essential feature of this circuit, as the 7805 regulator can become hot under load. It is advisable to include a thermal cutoff switch or a fuse in the circuit to prevent overheating. Overload protection can be implemented using a simple current-limiting resistor or a more sophisticated solution involving a PTC resettable fuse.
For users requiring different output voltages, the circuit can be easily adapted by swapping the 7805 with other regulators from the 78xx series, such as the 7812 for +12V or the 7809 for +9V. Each variant has a specific output voltage indicated by the last two digits of its part number. When modifying the circuit for different output voltages, it is crucial to recalculate the input voltage requirements based on the new output voltage to maintain proper operation and ensure that the input voltage remains at least 3V above the desired output voltage.
Overall, this circuit design provides a straightforward and effective solution for powering digital electronics, ensuring stable voltage and current while offering flexibility for various applications.This circuit is a small +5V power supply, which is useful when experimenting with digital electronics. Small inexpensive wall tranformers with variable output voltage are available from any electronics shop and supermarket.
Those transformers are easily available, but usually their voltage regulation is very poor, which makes then not very usable for digital circuit experimenter unless a better regulation can be achieved in some way. The following circuit is the answer to the problem. This circuit can give +5V output at about 150 mA current, but it can be increased to 1 A when good cooling is added to 7805 regulator chip. The circuit has overload and thermal protection. The capacitors must have enough high voltage rating to safely handle the input voltage feed to circuit.
The circuit is very easy to build for example into a piece of veroboard. If you need other voltages than +5V, you can modify the circuit by replacing the 7805 chips with another regulator with different output voltage from regulator 78xx chip family. The last numbers in the the chip code tells the output voltage. Remember that the input voltage muts be at least 3V greater than regulator output voltage ot otherwise the regulator does not work well.
🔗 External reference