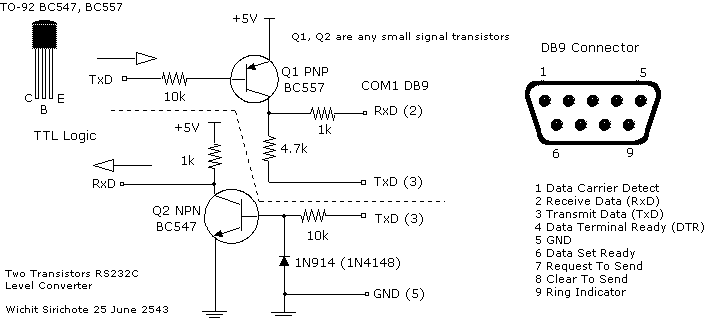
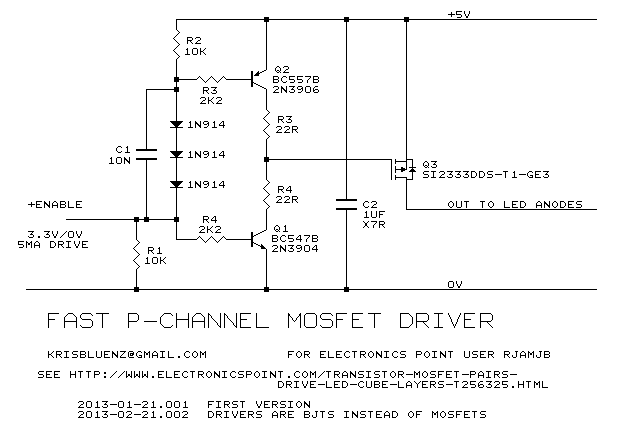
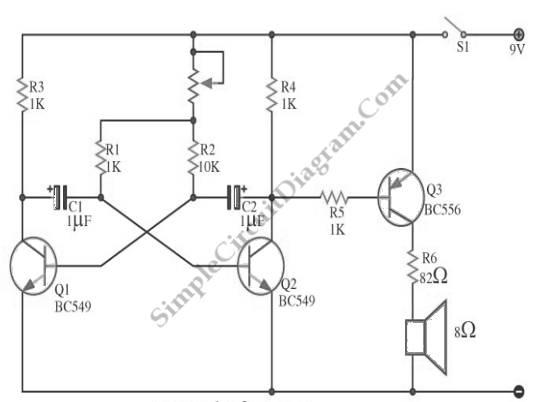
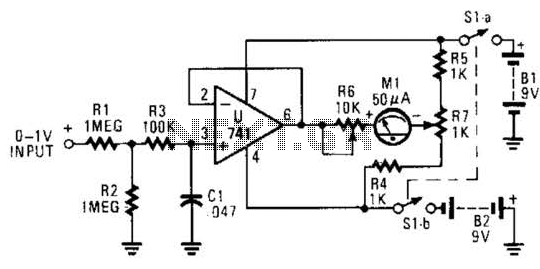
6 Transistor Tildens H-Bridge

This diagram illustrates the 6 transistor Tilden H-bridge circuit. Although it is not as old as the original basic H-bridge, it has a long history and serves as the foundation for many BEAM driver circuits. Bruce Robinson provides an explanation of this circuit.
The 6 transistor Tilden H-bridge circuit is a specific configuration used for driving DC motors, enabling control over the motor’s direction and speed. This circuit employs six bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) arranged in a bridge configuration, allowing for both forward and reverse motor operation. The transistors are typically arranged in pairs, with each pair controlling the current flow through the motor in opposite directions.
In this configuration, two transistors are turned on to allow current to flow in one direction, while the other two transistors are turned off. To reverse the direction of the motor, the opposite pair of transistors is activated. The use of BJTs in this circuit allows for efficient switching and control, making it suitable for various applications, including robotics and automation.
The circuit is often used in BEAM robotics, where simple, efficient motor control is essential. The Tilden H-bridge's design minimizes component count while maintaining functionality, making it an attractive choice for hobbyists and engineers alike. Bruce Robinson’s explanation of the circuit provides valuable insights into its operation, highlighting the importance of proper transistor selection and biasing to ensure reliable performance.
In summary, the 6 transistor Tilden H-bridge circuit is a versatile and foundational design in the realm of DC motor control, with applications extending into various fields of electronics and robotics. Its historical significance and practical utility continue to influence modern circuit design.This diagram is certainly the 6 transistor Tilden H-bridge circuit; while not as old as the original basic H-bridge, this goes way back, and will be the basis for a lot of BEAM driver circuits. Bruce Robinson explaination about this circuit.. 🔗 External reference
The 6 transistor Tilden H-bridge circuit is a specific configuration used for driving DC motors, enabling control over the motor’s direction and speed. This circuit employs six bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) arranged in a bridge configuration, allowing for both forward and reverse motor operation. The transistors are typically arranged in pairs, with each pair controlling the current flow through the motor in opposite directions.
In this configuration, two transistors are turned on to allow current to flow in one direction, while the other two transistors are turned off. To reverse the direction of the motor, the opposite pair of transistors is activated. The use of BJTs in this circuit allows for efficient switching and control, making it suitable for various applications, including robotics and automation.
The circuit is often used in BEAM robotics, where simple, efficient motor control is essential. The Tilden H-bridge's design minimizes component count while maintaining functionality, making it an attractive choice for hobbyists and engineers alike. Bruce Robinson’s explanation of the circuit provides valuable insights into its operation, highlighting the importance of proper transistor selection and biasing to ensure reliable performance.
In summary, the 6 transistor Tilden H-bridge circuit is a versatile and foundational design in the realm of DC motor control, with applications extending into various fields of electronics and robotics. Its historical significance and practical utility continue to influence modern circuit design.This diagram is certainly the 6 transistor Tilden H-bridge circuit; while not as old as the original basic H-bridge, this goes way back, and will be the basis for a lot of BEAM driver circuits. Bruce Robinson explaination about this circuit.. 🔗 External reference