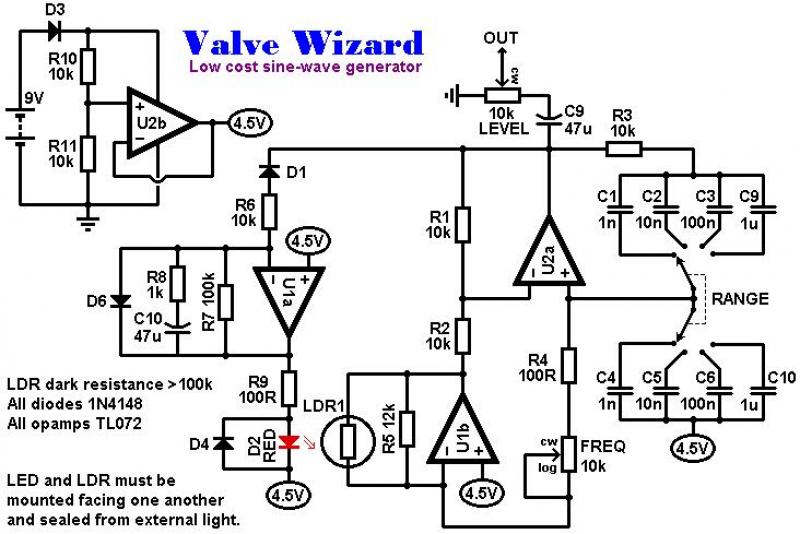
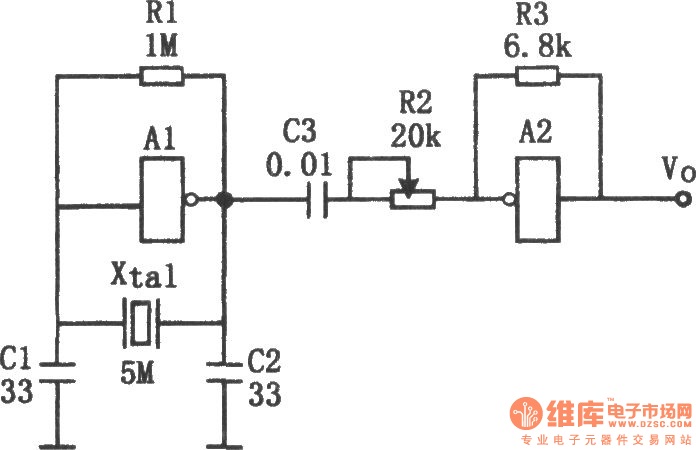
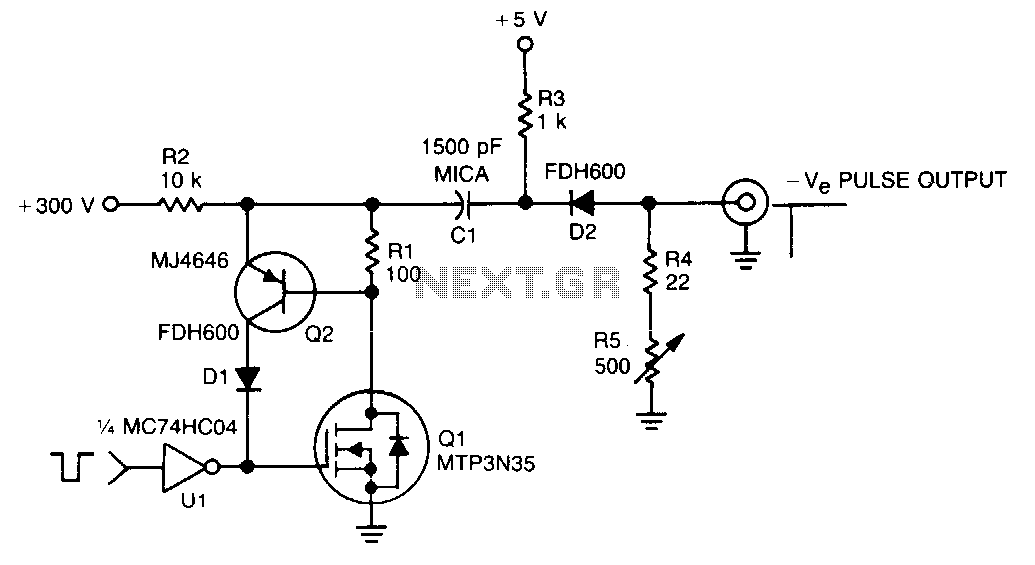
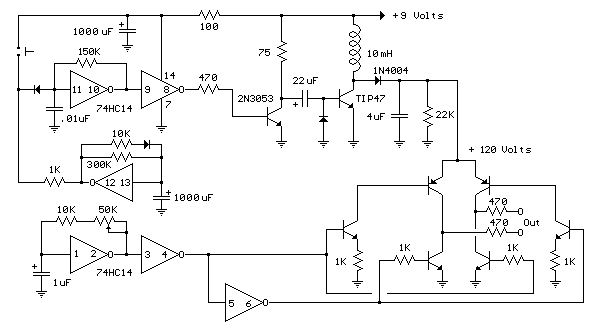
60Hz pulse generator
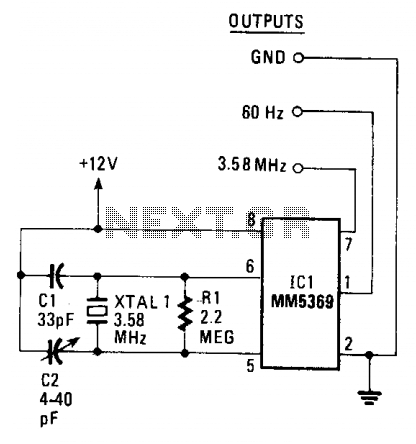
The circuit generates a clean, stable square wave and operates within a voltage range of 6 to 15 volts. The integrated circuit (IC) and color-burst crystal utilized are commonly found in television receivers. The output frequency of 3.58 MHz serves as a useful marker signal for shortwave bands.
The circuit design features a square wave oscillator that leverages a color-burst crystal, typically resonating at 3.58 MHz, which is a standard frequency used in television broadcasting. This frequency is particularly advantageous for applications in shortwave radio, where it can be employed as a reference signal or marker for tuning purposes.
Power supply considerations are crucial, as the circuit is designed to function effectively between 6 to 15 volts. This flexibility allows it to be integrated into various electronic systems without the need for extensive modifications. The IC used in the circuit is selected for its reliability and performance in generating stable oscillations, ensuring that the output remains consistent even with variations in supply voltage.
The output square wave can be utilized in multiple applications beyond shortwave radio, including signal processing and synchronization tasks in digital circuits. The clean nature of the square wave minimizes distortion, making it suitable for interfacing with other electronic components or systems.
Overall, this circuit serves as a versatile tool for generating a precise frequency signal, with applications across various fields of electronics, particularly in radio communications and television technology.The circuit provides a clean, stable square wave and it will operate on anywhere from 6 to 15 volts. The IC and color-burst crystal are the kind used in TV receivers. The 3.58 MHz output makes a handy marker signal for shortwave bands.
The circuit design features a square wave oscillator that leverages a color-burst crystal, typically resonating at 3.58 MHz, which is a standard frequency used in television broadcasting. This frequency is particularly advantageous for applications in shortwave radio, where it can be employed as a reference signal or marker for tuning purposes.
Power supply considerations are crucial, as the circuit is designed to function effectively between 6 to 15 volts. This flexibility allows it to be integrated into various electronic systems without the need for extensive modifications. The IC used in the circuit is selected for its reliability and performance in generating stable oscillations, ensuring that the output remains consistent even with variations in supply voltage.
The output square wave can be utilized in multiple applications beyond shortwave radio, including signal processing and synchronization tasks in digital circuits. The clean nature of the square wave minimizes distortion, making it suitable for interfacing with other electronic components or systems.
Overall, this circuit serves as a versatile tool for generating a precise frequency signal, with applications across various fields of electronics, particularly in radio communications and television technology.The circuit provides a clean, stable square wave and it will operate on anywhere from 6 to 15 volts. The IC and color-burst crystal are the kind used in TV receivers. The 3.58 MHz output makes a handy marker signal for shortwave bands.