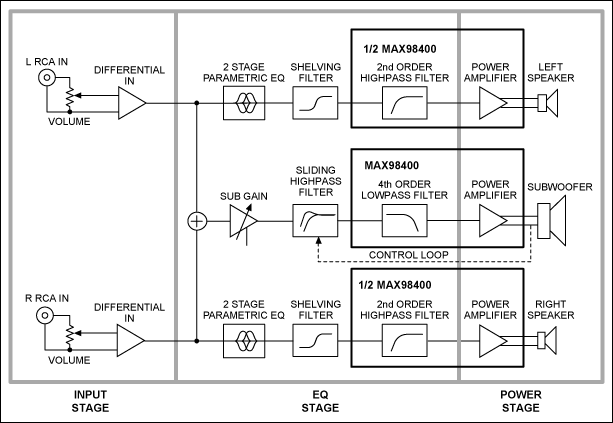
80 milliwatt Improved 3 Transistor Audio Amp
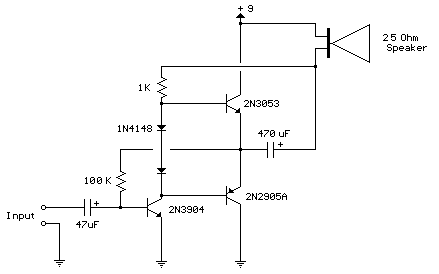
This circuit is similar to the previous one but utilizes positive feedback to increase the amplitude to the speaker. It was adapted from a small 5-transistor radio that employs a 25-ohm speaker. In the prior circuit, the load resistor for the driver transistor is connected directly to the positive supply, which presents a disadvantage. As the output becomes more positive, the voltage drop across the 470-ohm resistor diminishes, leading to a reduction in the base current supplied to the top NPN transistor. Consequently, the output cannot reach the positive supply voltage, as there would be no voltage across the 470-ohm resistor and no base current for the NPN transistor. This circuit addresses the issue to some extent, allowing for a larger voltage swing and potentially more output power, although the exact amount would require extensive testing. The output is still limited to a few volts when using small transistors, as the peak current will not exceed approximately 100 mA into a 25-ohm load. However, it represents an improvement over the previous circuit. In this configuration, the 1K load resistor is connected to the speaker, so when the output goes negative, the voltage across the 1K resistor decreases, assisting in turning off the top NPN transistor. Conversely, when the output is positive, the charge on the 470 µF capacitor helps turn on the top NPN transistor. The original radio circuit utilized a 300-ohm resistor at the location of the two diodes, but this design replaces the resistor with diodes to ensure the amplifier operates at lower voltages with reduced distortion. The transistors identified as 2N3053 and 2N2905 were selected from the previous circuit but can be substituted with smaller types. Any small transistor capable of handling 100 mA or more current may be used. While the 2N3904 or 2N3906 transistors are slightly on the smaller side, they may still function adequately at low volumes. The two diodes produce a relatively stable bias voltage as the battery depletes, which helps minimize crossover distortion. It is essential to maintain an idle current of approximately 10 to 20 milliamps with no signal, ensuring that the output transistors do not overheat under load. This circuit is compatible with a standard 8-ohm speaker, although the output power may be somewhat reduced. To optimize performance, it is recommended to select a resistor in place of the 100K resistor to set the output voltage at half the supply voltage (4.5 volts). This resistor can range from 50K to 700K, depending on the gain of the transistor used where the 3904 is indicated.
The described circuit employs a positive feedback mechanism to enhance the output amplitude, making it suitable for driving small speakers in low-power applications. The configuration is particularly effective for audio amplification in compact devices such as radios. The use of a 25-ohm speaker indicates that the circuit is designed for low-impedance loads, which can be beneficial in portable applications where efficiency and power conservation are essential.
The circuit's design incorporates a 1K load resistor connected to the speaker, which plays a pivotal role in the feedback loop. As the output signal fluctuates, the interaction between the speaker and the load resistor allows for improved transistor switching, enhancing the overall performance of the amplifier. The inclusion of a 470 µF capacitor is critical for stabilizing the voltage across the transistors during operation, ensuring that the circuit can handle dynamic audio signals without significant distortion.
The choice of transistors, such as the 2N3053 and 2N2905, provides flexibility in the design, allowing for various alternatives based on availability and performance requirements. It is advisable to consider the thermal characteristics of the selected transistors to prevent overheating, especially under continuous load conditions. The circuit's idle current specification ensures that the transistors operate within their safe limits, maintaining reliable performance over time.
For further optimization, careful selection of the feedback resistor is crucial. This resistor influences the gain of the amplifier and the overall output voltage swing. By adjusting this component, designers can tailor the circuit to specific applications, ensuring that it meets the desired performance criteria while minimizing distortion and maximizing efficiency.
Overall, this circuit represents a practical solution for low-power audio amplification, combining effective feedback mechanisms with component flexibility to achieve satisfactory performance in small electronic devices.This circuit is similar to the one above but uses positive feedback to get a little more amplitude to the speaker. I copied it from a small 5 transistor radio that uses a 25 ohm speaker. In the circuit above, the load resistor for the driver transistor is tied directly to the + supply. This has a disadvantage in that as the output moves positive, the drop across the 470 ohm resistor decreases which reduces the base current to the top NPN transistor. Thus the output cannot move all the way to the + supply because there wouldn`t be any voltage across the 470 resistor and no base current to the NPN transistor.
This circuit corrects the problem somewhat and allows a larger voltage swing and probably more output power, but I don`t know how much without doing a lot of testing. The output still won`t move more than a couple volts using small transistors since the peak current won`t be more than 100mA or so into a 25 ohm load.
But it`s an improvement over the other circuit above. In this circuit, the 1K load resistor is tied to the speaker so that as the output moves negative, the voltage on the 1K resistor is reduced, which aids in turning off the top NPN transistor. When the output moves positive, the charge on the 470uF capacitor aids in turning on the top NPN transistor.
The original circuit in the radio used a 300 ohm resistor where the 2 diodes are shown but I changed the resistor to 2 diodes so the amp would operate on lower voltages with less distortion. The transistors shown 2n3053 and 2n2905 are just parts I used for the other circuit above and could be smaller types.
Most any small transistors can be used, but they should be capable of 100mA or more current. A 2N3904 or 2N3906 are probably a little small, but would work at low volume. The 2 diodes generate a fairly constant bias voltage as the battery drains and reduces crossover distortion. But you should take care to insure the idle current is around 10 to 20 milliamps with no signal and the output transistors do not get hot under load.
The circuit should work with a regular 8 ohm speaker, but the output power may be somewhat less. To optimize the operation, select a resistor where the 100K is shown to set the output voltage at 1/2 the supply voltage (4. 5 volts). This resistor might be anything from 50K to 700K depending on the gain of the transistor used where the 3904 is shown.
🔗 External reference
The described circuit employs a positive feedback mechanism to enhance the output amplitude, making it suitable for driving small speakers in low-power applications. The configuration is particularly effective for audio amplification in compact devices such as radios. The use of a 25-ohm speaker indicates that the circuit is designed for low-impedance loads, which can be beneficial in portable applications where efficiency and power conservation are essential.
The circuit's design incorporates a 1K load resistor connected to the speaker, which plays a pivotal role in the feedback loop. As the output signal fluctuates, the interaction between the speaker and the load resistor allows for improved transistor switching, enhancing the overall performance of the amplifier. The inclusion of a 470 µF capacitor is critical for stabilizing the voltage across the transistors during operation, ensuring that the circuit can handle dynamic audio signals without significant distortion.
The choice of transistors, such as the 2N3053 and 2N2905, provides flexibility in the design, allowing for various alternatives based on availability and performance requirements. It is advisable to consider the thermal characteristics of the selected transistors to prevent overheating, especially under continuous load conditions. The circuit's idle current specification ensures that the transistors operate within their safe limits, maintaining reliable performance over time.
For further optimization, careful selection of the feedback resistor is crucial. This resistor influences the gain of the amplifier and the overall output voltage swing. By adjusting this component, designers can tailor the circuit to specific applications, ensuring that it meets the desired performance criteria while minimizing distortion and maximizing efficiency.
Overall, this circuit represents a practical solution for low-power audio amplification, combining effective feedback mechanisms with component flexibility to achieve satisfactory performance in small electronic devices.This circuit is similar to the one above but uses positive feedback to get a little more amplitude to the speaker. I copied it from a small 5 transistor radio that uses a 25 ohm speaker. In the circuit above, the load resistor for the driver transistor is tied directly to the + supply. This has a disadvantage in that as the output moves positive, the drop across the 470 ohm resistor decreases which reduces the base current to the top NPN transistor. Thus the output cannot move all the way to the + supply because there wouldn`t be any voltage across the 470 resistor and no base current to the NPN transistor.
This circuit corrects the problem somewhat and allows a larger voltage swing and probably more output power, but I don`t know how much without doing a lot of testing. The output still won`t move more than a couple volts using small transistors since the peak current won`t be more than 100mA or so into a 25 ohm load.
But it`s an improvement over the other circuit above. In this circuit, the 1K load resistor is tied to the speaker so that as the output moves negative, the voltage on the 1K resistor is reduced, which aids in turning off the top NPN transistor. When the output moves positive, the charge on the 470uF capacitor aids in turning on the top NPN transistor.
The original circuit in the radio used a 300 ohm resistor where the 2 diodes are shown but I changed the resistor to 2 diodes so the amp would operate on lower voltages with less distortion. The transistors shown 2n3053 and 2n2905 are just parts I used for the other circuit above and could be smaller types.
Most any small transistors can be used, but they should be capable of 100mA or more current. A 2N3904 or 2N3906 are probably a little small, but would work at low volume. The 2 diodes generate a fairly constant bias voltage as the battery drains and reduces crossover distortion. But you should take care to insure the idle current is around 10 to 20 milliamps with no signal and the output transistors do not get hot under load.
The circuit should work with a regular 8 ohm speaker, but the output power may be somewhat less. To optimize the operation, select a resistor where the 100K is shown to set the output voltage at 1/2 the supply voltage (4. 5 volts). This resistor might be anything from 50K to 700K depending on the gain of the transistor used where the 3904 is shown.
🔗 External reference