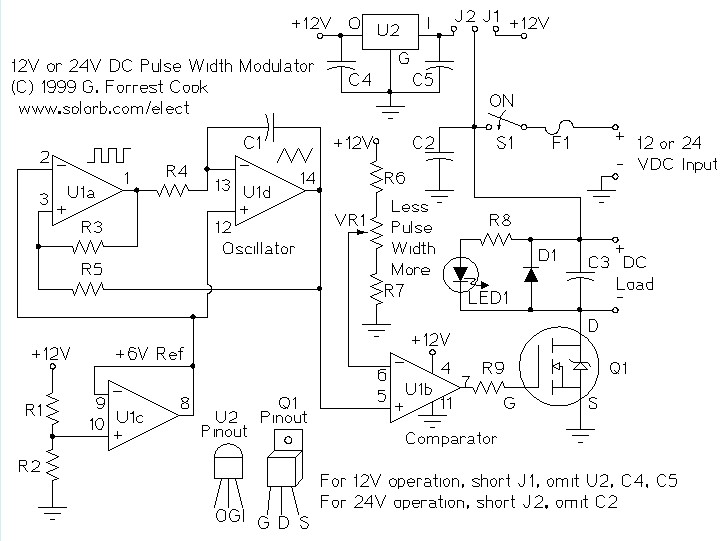
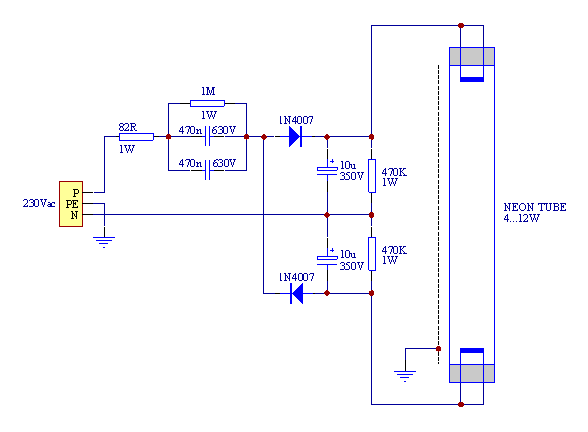
How Compact Fluorescent Lamps Work and How to Dim Them
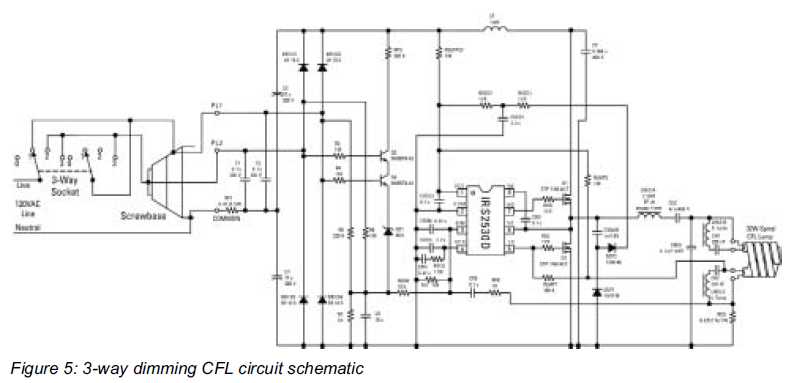
The dimming function introduces a new range of applications for compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs). Compact fluorescent lamps are rapidly replacing incandescent light bulbs due to their energy efficiency and longevity.
The integration of dimming capabilities into compact fluorescent lamps significantly enhances their versatility and usability in various lighting scenarios. Traditional incandescent bulbs have long provided dimming options, allowing users to adjust light intensity based on their needs. The advancement in CFL technology now allows for similar functionality, leading to a broader range of applications in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
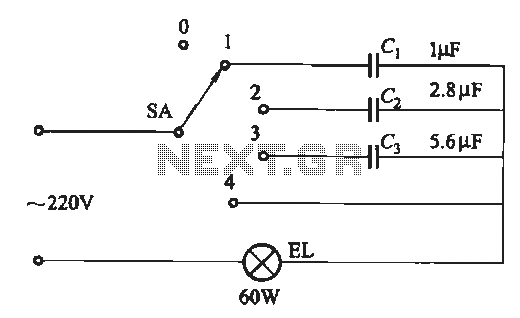
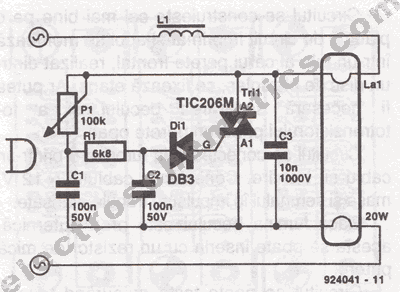
When implementing a dimming function in CFLs, it is essential to utilize a compatible dimmer switch designed specifically for CFLs. Standard dimmer switches designed for incandescent bulbs may not operate effectively with CFLs, potentially leading to flickering, buzzing, or reduced lifespan of the lamp. Specialized dimmers are engineered to accommodate the electrical characteristics of CFLs, ensuring smooth dimming performance and improved energy efficiency.
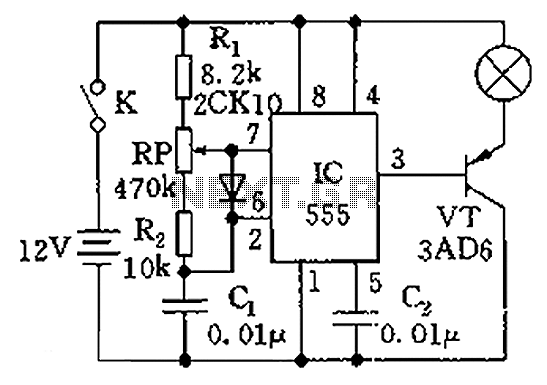
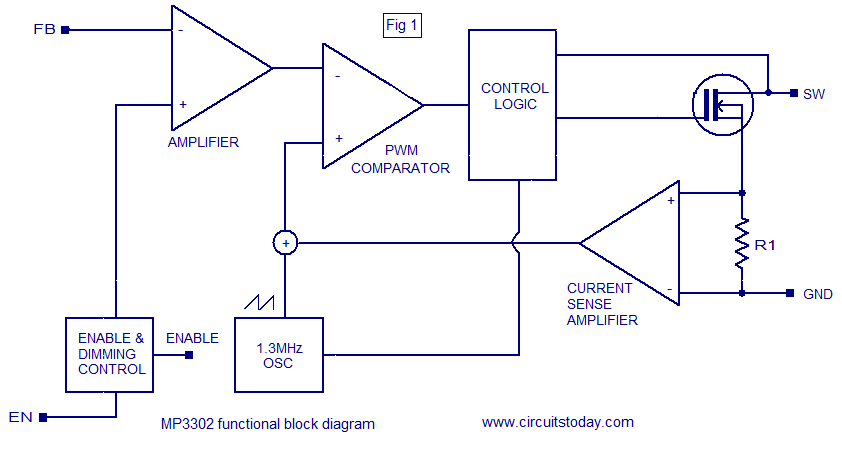
The circuit design for a dimmable CFL typically includes an electronic ballast that regulates the current and voltage supplied to the lamp. This ballast must be able to handle the varying power levels required during the dimming process. Additionally, the circuit may incorporate a microcontroller to manage the dimming levels, providing precise control over light output. This setup also allows for integration with smart home systems, enabling remote control and automation of lighting based on user preferences.
In summary, the dimming function in compact fluorescent lamps not only enhances their application range but also requires careful consideration of circuit design and compatibility with dimmer switches to ensure optimal performance and user satisfaction.Dimming function opens up a completely new family of CFL applications Compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs) are replacing incandescent light bulbs at a rapid rate due to their.. 🔗 External reference
The integration of dimming capabilities into compact fluorescent lamps significantly enhances their versatility and usability in various lighting scenarios. Traditional incandescent bulbs have long provided dimming options, allowing users to adjust light intensity based on their needs. The advancement in CFL technology now allows for similar functionality, leading to a broader range of applications in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
When implementing a dimming function in CFLs, it is essential to utilize a compatible dimmer switch designed specifically for CFLs. Standard dimmer switches designed for incandescent bulbs may not operate effectively with CFLs, potentially leading to flickering, buzzing, or reduced lifespan of the lamp. Specialized dimmers are engineered to accommodate the electrical characteristics of CFLs, ensuring smooth dimming performance and improved energy efficiency.
The circuit design for a dimmable CFL typically includes an electronic ballast that regulates the current and voltage supplied to the lamp. This ballast must be able to handle the varying power levels required during the dimming process. Additionally, the circuit may incorporate a microcontroller to manage the dimming levels, providing precise control over light output. This setup also allows for integration with smart home systems, enabling remote control and automation of lighting based on user preferences.
In summary, the dimming function in compact fluorescent lamps not only enhances their application range but also requires careful consideration of circuit design and compatibility with dimmer switches to ensure optimal performance and user satisfaction.Dimming function opens up a completely new family of CFL applications Compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs) are replacing incandescent light bulbs at a rapid rate due to their.. 🔗 External reference