8W + 8W tube amplifier circuit
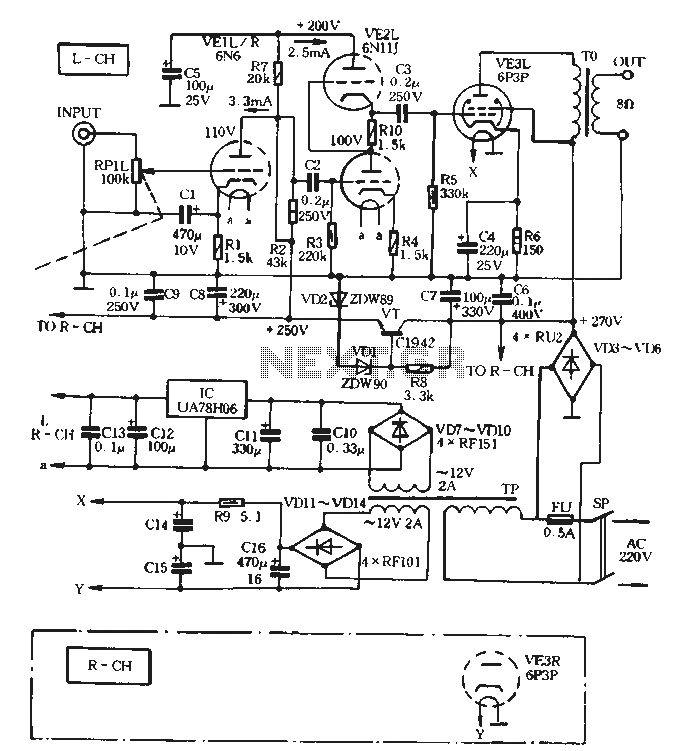
The VE1 preamplifier utilizes a low muscle, low resistance double triode 6N6 configuration, with separate halves for the left and right audio channels. The design operates within the CPI framework. It promotes the use of high-level VE2 household low resistance tubes EN11J, which contribute to low distortion throughout the audio path, employing a consensus and wide SRPP (Shunt Regulated Push-Pull) configuration. The final amplifier circuit, VE3, is directly powered by an AC 220V city grid through a VD3 to VD6 bridge rectifier. Capacitors C6 and C7 filter the rectified output to provide a +270V power supply for the 6P3P tube's screen grid. The +270V supply is regulated by VT and VD11, producing a stable +250V power supply for the anode of the VE1 preamplifier. Additionally, a secondary filter consisting of resistor R7 and capacitor C5 generates a +200V voltage for the SRPP circuits. This configuration allows for a simplified power supply transformer, reducing both size and weight while lowering production costs. The design also addresses the common mode rejection ratio (CMRR) effects associated with single-ended amplifiers, necessitating a more robust power supply. The anode power supply features dual capacitor filtering, while filament current is supplied by a combination of front-end and push IC (VA78H06) regulators. Another AC 12V, 2A winding is rectified by VD to VD14, with capacitors C14 to C16 filtering the output to generate approximately 2.4V for the two-channel amplifier tube filament power supply, using the "voice of the" finished product specifications (5; OVA ~ 12V x 21220V).
The VE1 preamplifier circuit is designed to provide high-quality audio amplification with minimal distortion. The use of a double triode 6N6 allows for effective signal processing in both audio channels, ensuring that stereo sound remains balanced and clear. The SRPP configuration is particularly beneficial for enhancing linearity and reducing harmonic distortion, making it suitable for high-fidelity audio applications.
The power supply architecture is critical to the performance of the VE1 preamplifier. The bridge rectifier (VD3 to VD6) converts the AC voltage from the city grid to a usable DC voltage, which is then filtered through capacitors C6 and C7 to smooth out the output. The +270V voltage is essential for the operation of the 6P3P tube, which serves as the output stage for the audio signal. The regulation provided by VT and VD11 ensures that fluctuations in the input voltage do not adversely affect the performance of the preamplifier.
The additional +250V supply for the anode is crucial for maintaining the operating point of the 6N6 tubes, allowing for optimal amplification without introducing noise. The design's secondary filtering stage, utilizing R7 and C5, generates a +200V supply for the SRPP configuration, which is vital for maintaining the integrity of the audio signal.
The filament supply design, utilizing both a dedicated IC regulator and a separate winding from the transformer, ensures that the tubes receive stable heating voltage. This is important for extending the lifespan of the tubes and maintaining consistent audio performance. The overall layout of the power supply minimizes electromagnetic interference, which can be detrimental to audio quality.
In summary, the VE1 preamplifier is a sophisticated audio device that employs advanced tube technology and thoughtful power supply design to achieve high fidelity and low distortion. The integration of various components, from the rectifiers to the filtering capacitors, is meticulously planned to create an efficient and reliable audio amplification solution.Preamplifier VE1 the machine with low muscle low R double triode 6N6 (left and right audio channels each with its half). Working state design in the CPI. Promote the use of high-level VE2 households, low R-made tubes EN11J, electric low distortion all the way in the form of consensus and wide SRPP (Shunt Regulated Push groan ull) 6 final amplifier circuit VE3 taken directly from the tube anode power supply AC 220V City grid. Electricity through VD3 ~ VD6 bridge rectifier, C 6 C7 filtered after wave t to obtain + 270v voltage power pole tube 6P3P screen, screen grid power; + 270V fork by VT VD11.
VDZ produce the adjusted regulated + 250V power supply is pre-VE1 anode feed; + 2sov then by R 7, c 5 secondary filter is formed + 200v voltage SRPP circuits. This can be taken directly electrically Tsui simplify the power supply transformer TP TP t to reduce size, weight and production cost Zhuo very useful because there is no single-ended amplifier CMRR (common mode rejection) effect, and therefore the power supply requirements are relatively harsh.
therefore. Anode power supply with dual capacitor filter; in addition t after all filament current supply by q wherein front and push through IC (VA78H06) Regulators fed A filament; another group AC 12V, 2A winding through rectifier bridge VD ~ VD14 , C14 ~ C16 filter in X, Y terminals generate about 1 2.4V voltage two-channel amplifier tube filament power supply port power transformer TP using the "voice of the" finished product (5; OVA ~ 12vx 21220V)
The VE1 preamplifier circuit is designed to provide high-quality audio amplification with minimal distortion. The use of a double triode 6N6 allows for effective signal processing in both audio channels, ensuring that stereo sound remains balanced and clear. The SRPP configuration is particularly beneficial for enhancing linearity and reducing harmonic distortion, making it suitable for high-fidelity audio applications.
The power supply architecture is critical to the performance of the VE1 preamplifier. The bridge rectifier (VD3 to VD6) converts the AC voltage from the city grid to a usable DC voltage, which is then filtered through capacitors C6 and C7 to smooth out the output. The +270V voltage is essential for the operation of the 6P3P tube, which serves as the output stage for the audio signal. The regulation provided by VT and VD11 ensures that fluctuations in the input voltage do not adversely affect the performance of the preamplifier.
The additional +250V supply for the anode is crucial for maintaining the operating point of the 6N6 tubes, allowing for optimal amplification without introducing noise. The design's secondary filtering stage, utilizing R7 and C5, generates a +200V supply for the SRPP configuration, which is vital for maintaining the integrity of the audio signal.
The filament supply design, utilizing both a dedicated IC regulator and a separate winding from the transformer, ensures that the tubes receive stable heating voltage. This is important for extending the lifespan of the tubes and maintaining consistent audio performance. The overall layout of the power supply minimizes electromagnetic interference, which can be detrimental to audio quality.
In summary, the VE1 preamplifier is a sophisticated audio device that employs advanced tube technology and thoughtful power supply design to achieve high fidelity and low distortion. The integration of various components, from the rectifiers to the filtering capacitors, is meticulously planned to create an efficient and reliable audio amplification solution.Preamplifier VE1 the machine with low muscle low R double triode 6N6 (left and right audio channels each with its half). Working state design in the CPI. Promote the use of high-level VE2 households, low R-made tubes EN11J, electric low distortion all the way in the form of consensus and wide SRPP (Shunt Regulated Push groan ull) 6 final amplifier circuit VE3 taken directly from the tube anode power supply AC 220V City grid. Electricity through VD3 ~ VD6 bridge rectifier, C 6 C7 filtered after wave t to obtain + 270v voltage power pole tube 6P3P screen, screen grid power; + 270V fork by VT VD11.
VDZ produce the adjusted regulated + 250V power supply is pre-VE1 anode feed; + 2sov then by R 7, c 5 secondary filter is formed + 200v voltage SRPP circuits. This can be taken directly electrically Tsui simplify the power supply transformer TP TP t to reduce size, weight and production cost Zhuo very useful because there is no single-ended amplifier CMRR (common mode rejection) effect, and therefore the power supply requirements are relatively harsh.
therefore. Anode power supply with dual capacitor filter; in addition t after all filament current supply by q wherein front and push through IC (VA78H06) Regulators fed A filament; another group AC 12V, 2A winding through rectifier bridge VD ~ VD14 , C14 ~ C16 filter in X, Y terminals generate about 1 2.4V voltage two-channel amplifier tube filament power supply port power transformer TP using the "voice of the" finished product (5; OVA ~ 12vx 21220V)