Basic reference transistor bias circuit - Mixed Negative feedback
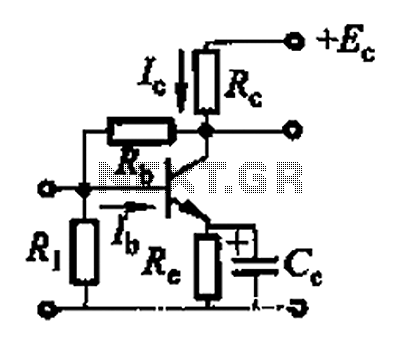
Basic reference transistor bias circuit - Mixed Negative feedback
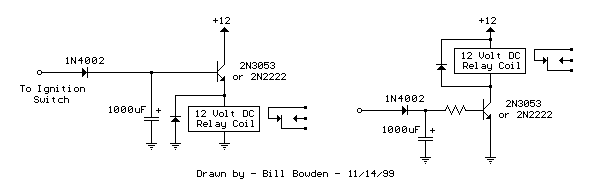
The basic reference transistor bias circuit utilizing mixed negative feedback is a fundamental electronic configuration designed to stabilize the operating point of a transistor. This circuit typically employs a combination of resistive feedback and emitter degeneration to enhance linearity and thermal stability.
In this configuration, a transistor is connected in a common-emitter arrangement, where the input signal is applied to the base terminal. The collector is connected to a power supply, while the emitter is connected through a resistor to ground. The mixed negative feedback is achieved by incorporating resistors that connect the collector to the base, providing a fraction of the output voltage back to the input. This feedback mechanism helps to reduce the gain sensitivity to variations in transistor parameters and temperature changes.
The biasing network is crucial for ensuring that the transistor operates in the active region, preventing it from entering saturation or cutoff during signal variations. The design of the resistor values is critical, as they determine the biasing current and, consequently, the quiescent point (Q-point) of the transistor. Proper selection of these components allows for a stable operation over a range of conditions, making this circuit widely used in amplifier designs and other applications requiring reliable transistor performance.
In summary, the basic reference transistor bias circuit with mixed negative feedback is essential for achieving stable and linear transistor operation, which is vital for a variety of electronic applications. Basic reference transistor bias circuit - Mixed Negative feedback
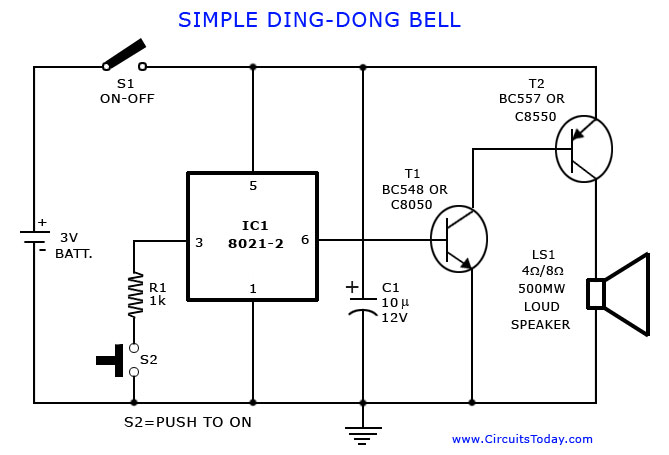
The basic reference transistor bias circuit utilizing mixed negative feedback is a fundamental electronic configuration designed to stabilize the operating point of a transistor. This circuit typically employs a combination of resistive feedback and emitter degeneration to enhance linearity and thermal stability.
In this configuration, a transistor is connected in a common-emitter arrangement, where the input signal is applied to the base terminal. The collector is connected to a power supply, while the emitter is connected through a resistor to ground. The mixed negative feedback is achieved by incorporating resistors that connect the collector to the base, providing a fraction of the output voltage back to the input. This feedback mechanism helps to reduce the gain sensitivity to variations in transistor parameters and temperature changes.
The biasing network is crucial for ensuring that the transistor operates in the active region, preventing it from entering saturation or cutoff during signal variations. The design of the resistor values is critical, as they determine the biasing current and, consequently, the quiescent point (Q-point) of the transistor. Proper selection of these components allows for a stable operation over a range of conditions, making this circuit widely used in amplifier designs and other applications requiring reliable transistor performance.
In summary, the basic reference transistor bias circuit with mixed negative feedback is essential for achieving stable and linear transistor operation, which is vital for a variety of electronic applications. Basic reference transistor bias circuit - Mixed Negative feedback