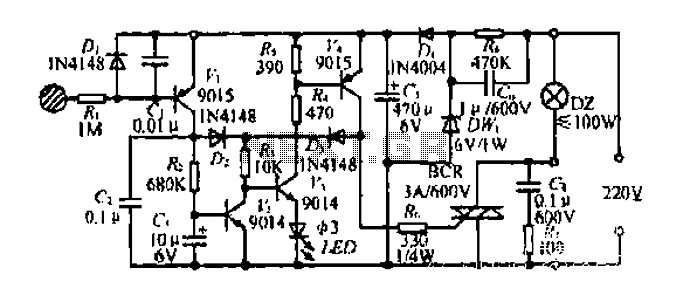
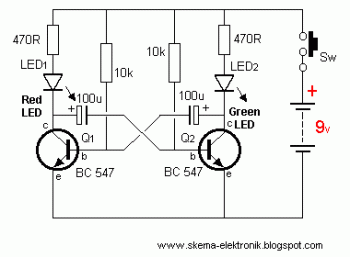
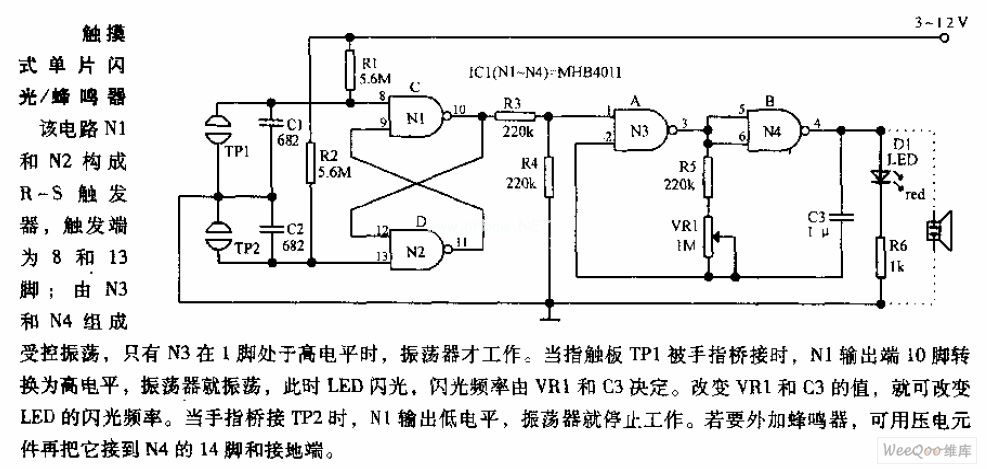
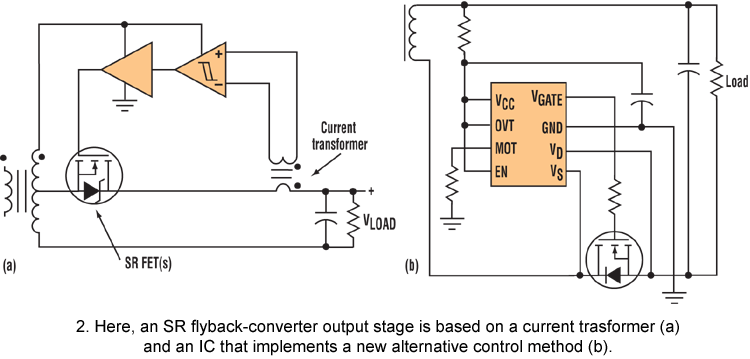
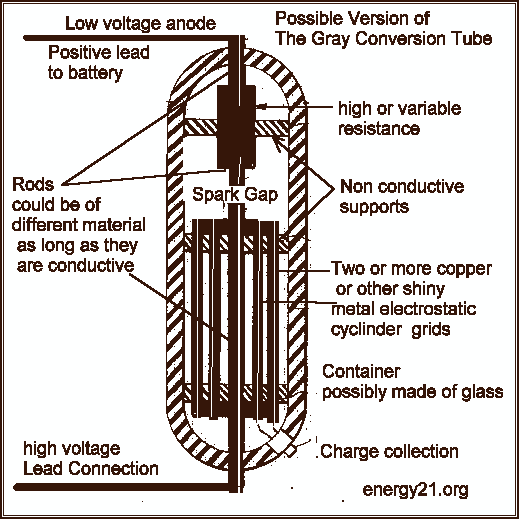
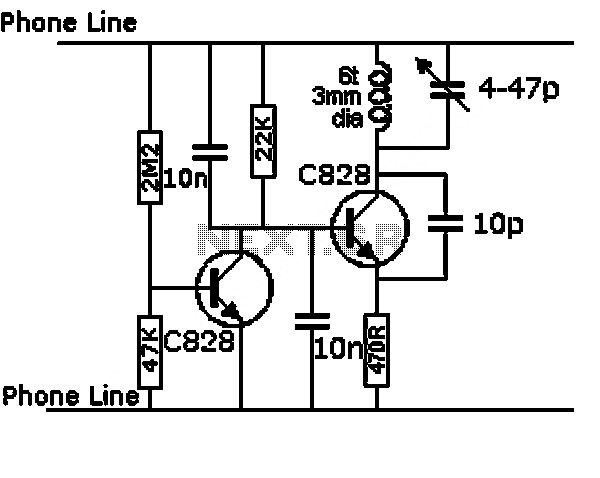
A circuit diagram of an amplifier circuit to enhance the output current and voltage

Amplifying circuit diagram to enhance the output current and voltage.
An amplifying circuit is designed to increase the amplitude of an input signal, resulting in a higher output current and voltage. This type of circuit is commonly utilized in various electronic applications, such as audio systems, instrumentation, and communication devices.
The basic components of an amplifying circuit typically include transistors (BJT or FET), resistors, capacitors, and sometimes operational amplifiers (op-amps). The configuration of these components can vary based on the desired amplification characteristics, such as gain, bandwidth, and input/output impedance.
In a common transistor amplifier configuration, the transistor operates in its active region, where it can effectively amplify the input signal. The input signal is applied to the base (or gate) of the transistor, while the output is taken from the collector (or drain). Resistors are used to set the biasing conditions of the transistor, ensuring it remains in the active region during operation. Coupling capacitors may be employed to block DC components while allowing AC signals to pass through, thereby isolating different stages of amplification.
For further enhancement of performance, feedback mechanisms can be introduced. Negative feedback can stabilize the gain and improve linearity, while positive feedback can be used in specific applications to increase gain further. The choice of components and configuration will ultimately depend on the specific requirements of the application, including the desired frequency response and power handling capabilities.
In summary, an amplifying circuit is crucial for boosting signal strength in various electronic applications, and careful design considerations are necessary to achieve optimal performance.Amplifying circuit diagram to enhance the output current and voltage:
An amplifying circuit is designed to increase the amplitude of an input signal, resulting in a higher output current and voltage. This type of circuit is commonly utilized in various electronic applications, such as audio systems, instrumentation, and communication devices.
The basic components of an amplifying circuit typically include transistors (BJT or FET), resistors, capacitors, and sometimes operational amplifiers (op-amps). The configuration of these components can vary based on the desired amplification characteristics, such as gain, bandwidth, and input/output impedance.
In a common transistor amplifier configuration, the transistor operates in its active region, where it can effectively amplify the input signal. The input signal is applied to the base (or gate) of the transistor, while the output is taken from the collector (or drain). Resistors are used to set the biasing conditions of the transistor, ensuring it remains in the active region during operation. Coupling capacitors may be employed to block DC components while allowing AC signals to pass through, thereby isolating different stages of amplification.
For further enhancement of performance, feedback mechanisms can be introduced. Negative feedback can stabilize the gain and improve linearity, while positive feedback can be used in specific applications to increase gain further. The choice of components and configuration will ultimately depend on the specific requirements of the application, including the desired frequency response and power handling capabilities.
In summary, an amplifying circuit is crucial for boosting signal strength in various electronic applications, and careful design considerations are necessary to achieve optimal performance.Amplifying circuit diagram to enhance the output current and voltage: