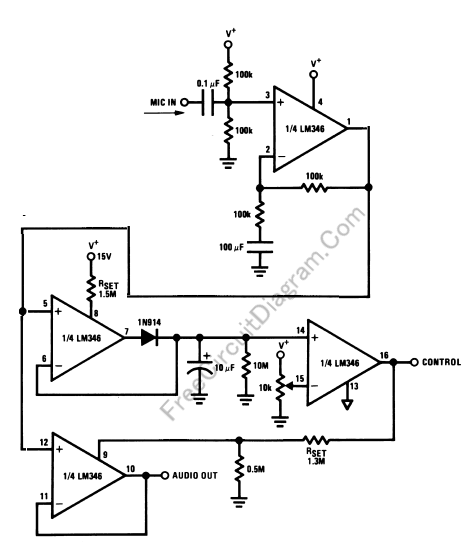
A combination of common-source grounded base amplifier formed by cascaded amplifier
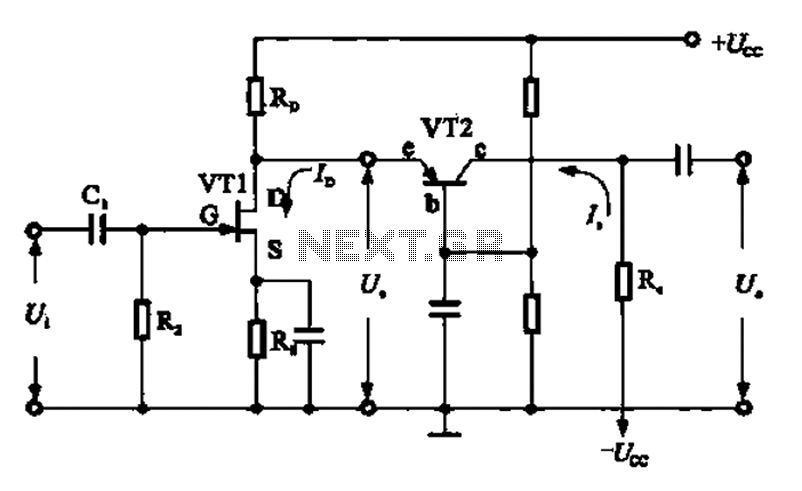
A combination of a common-source grounded base amplifier formed by cascaded amplifiers. The source is grounded, and a common base amplifier is combined into a cascaded amplifier. The graph below shows the low noise characteristics of the FET common-base amplifier, which is used for amplifying high-frequency adaptive end units. This configuration is often employed as a wideband low noise preamplifier.
The described circuit configuration consists of a cascaded amplifier system that integrates a common-source amplifier with a common-base amplifier. The common-source amplifier provides high voltage gain and is characterized by its input impedance, which is typically high. This makes it suitable for interfacing with various signal sources. The grounded source configuration ensures stability and minimizes distortion, making it ideal for low-noise applications.
The common-base amplifier, on the other hand, is known for its low input impedance and high output impedance. This configuration is particularly effective for high-frequency applications, as it provides a wide bandwidth and is less susceptible to the Miller effect, which can limit bandwidth in other amplifier configurations. The cascading of these two amplifier types allows for the benefits of each to be utilized, creating a hybrid amplifier that is capable of amplifying weak signals while maintaining low noise levels.
In practical applications, such as adaptive end units, this cascaded amplifier configuration serves as a preamplifier. It is designed to enhance the signal level before further processing, ensuring that the subsequent stages of the system can operate effectively with a strong, low-noise signal. The low noise characteristics of the FET (Field Effect Transistor) used in the common-base stage are crucial for maintaining signal integrity, especially in high-frequency environments.
Overall, the combination of a grounded source common-source amplifier and a common-base amplifier in a cascaded configuration results in a versatile and efficient low-noise preamplifier suitable for a variety of applications, particularly in telecommunications and signal processing.A combination of common-source grounded base amplifier formed by cascaded amplifier The source is grounded and common base amplifier combined into a cascaded amplifier. The gra ph below shows the low noise of the FET, common- base amplifier for amplifying the high frequency adaptive end units produced cascaded amplifier, often as a wideband low noise preamplifier amplifier.
The described circuit configuration consists of a cascaded amplifier system that integrates a common-source amplifier with a common-base amplifier. The common-source amplifier provides high voltage gain and is characterized by its input impedance, which is typically high. This makes it suitable for interfacing with various signal sources. The grounded source configuration ensures stability and minimizes distortion, making it ideal for low-noise applications.
The common-base amplifier, on the other hand, is known for its low input impedance and high output impedance. This configuration is particularly effective for high-frequency applications, as it provides a wide bandwidth and is less susceptible to the Miller effect, which can limit bandwidth in other amplifier configurations. The cascading of these two amplifier types allows for the benefits of each to be utilized, creating a hybrid amplifier that is capable of amplifying weak signals while maintaining low noise levels.
In practical applications, such as adaptive end units, this cascaded amplifier configuration serves as a preamplifier. It is designed to enhance the signal level before further processing, ensuring that the subsequent stages of the system can operate effectively with a strong, low-noise signal. The low noise characteristics of the FET (Field Effect Transistor) used in the common-base stage are crucial for maintaining signal integrity, especially in high-frequency environments.
Overall, the combination of a grounded source common-source amplifier and a common-base amplifier in a cascaded configuration results in a versatile and efficient low-noise preamplifier suitable for a variety of applications, particularly in telecommunications and signal processing.A combination of common-source grounded base amplifier formed by cascaded amplifier The source is grounded and common base amplifier combined into a cascaded amplifier. The gra ph below shows the low noise of the FET, common- base amplifier for amplifying the high frequency adaptive end units produced cascaded amplifier, often as a wideband low noise preamplifier amplifier.