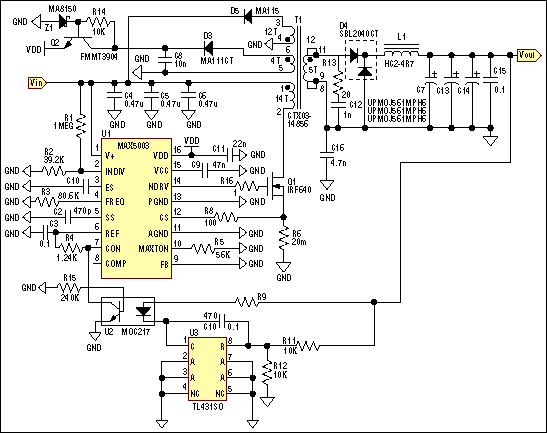
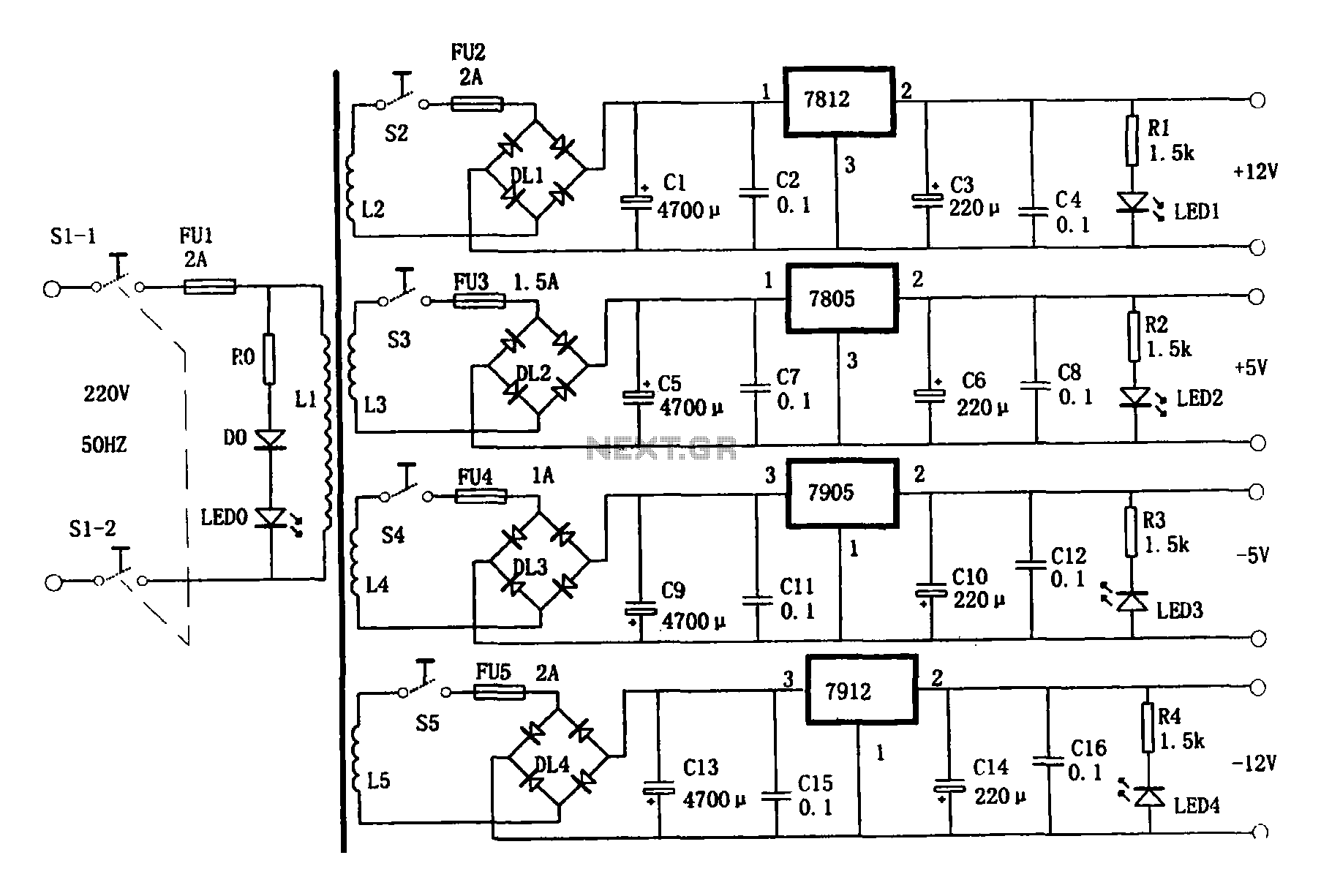
A typical computer motherboard CPU power supply circuit
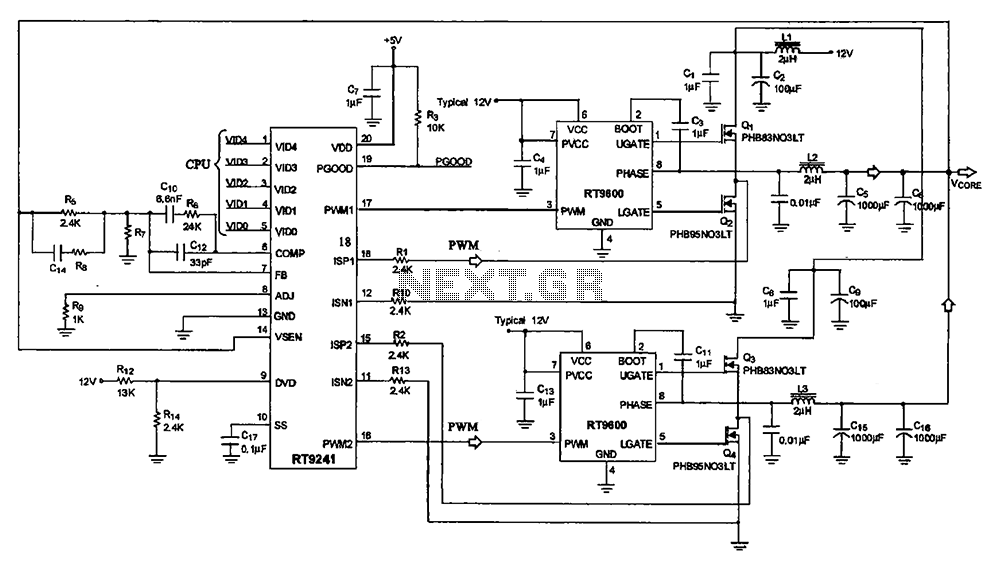
A typical computer motherboard CPU power supply circuit is primarily composed of the main power supply management chip RT9241 and additional components from the power management chip RT9600. The voltage command signal from the CPU is input into the RT9241, where it undergoes circuit identification processing. The chip outputs two different phase PWM pulse signals, which are then processed by the two power management circuits, each outputting two opposite phase PWM signals. These signals control the field effect transistors Q1, Q2, and Q3, which supply power to the CPU.
The CPU power supply circuit on a computer motherboard is a critical component designed to ensure stable and efficient power delivery to the processor. The main power management chip, RT9241, plays a pivotal role in regulating the voltage supplied to the CPU. It receives a voltage command signal from the CPU itself, which is essential for dynamic voltage scaling, allowing the processor to adjust its power consumption based on workload demands.
The RT9241 processes this command signal through an internal circuit identification mechanism, which determines the appropriate voltage levels required for optimal CPU operation. It generates two distinct phase PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signals that are crucial for controlling the power output. The use of two different phases helps in reducing ripple voltage and improving efficiency, as well as enhancing the overall performance of the power supply circuit.
These PWM signals are then routed to the power management components, particularly the RT9600 chip, which further processes these signals. The RT9600 is responsible for driving the external field effect transistors (FETs), specifically Q1, Q2, and Q3. These FETs act as electronic switches that modulate the power delivered to the CPU based on the PWM signals received.
By alternating the states of Q1, Q2, and Q3 in response to the PWM signals, the circuit effectively manages the power flow, ensuring that the CPU receives the necessary voltage and current levels for operation while minimizing energy loss. This arrangement not only supports the CPU's performance but also contributes to the overall power efficiency of the motherboard, which is increasingly important in modern computing environments where energy consumption is a significant concern.
In conclusion, the CPU power supply circuit on a motherboard, utilizing the RT9241 and RT9600 chips, exemplifies a sophisticated approach to power management, ensuring that the CPU operates reliably and efficiently under varying loads.A typical computer motherboard CPU power supply circuit A typical computer motherboard CPU power supply circuit, which is mainly composed of the main power supply management ch ip RT9241, two from the power source management and other parts of the chip RT9600. Voltage command signal from the CPU from the RT9241 O ~ feet into by the chip circuit identification processing, by pin output two different phases PWM pulse signals, respectively, by the two from power management Cang backsheet each output processing of two opposite phase PWM signal, the field effect transistors Qi, Q2 and Q3, Q after power to the CPU.
The CPU power supply circuit on a computer motherboard is a critical component designed to ensure stable and efficient power delivery to the processor. The main power management chip, RT9241, plays a pivotal role in regulating the voltage supplied to the CPU. It receives a voltage command signal from the CPU itself, which is essential for dynamic voltage scaling, allowing the processor to adjust its power consumption based on workload demands.
The RT9241 processes this command signal through an internal circuit identification mechanism, which determines the appropriate voltage levels required for optimal CPU operation. It generates two distinct phase PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signals that are crucial for controlling the power output. The use of two different phases helps in reducing ripple voltage and improving efficiency, as well as enhancing the overall performance of the power supply circuit.
These PWM signals are then routed to the power management components, particularly the RT9600 chip, which further processes these signals. The RT9600 is responsible for driving the external field effect transistors (FETs), specifically Q1, Q2, and Q3. These FETs act as electronic switches that modulate the power delivered to the CPU based on the PWM signals received.
By alternating the states of Q1, Q2, and Q3 in response to the PWM signals, the circuit effectively manages the power flow, ensuring that the CPU receives the necessary voltage and current levels for operation while minimizing energy loss. This arrangement not only supports the CPU's performance but also contributes to the overall power efficiency of the motherboard, which is increasingly important in modern computing environments where energy consumption is a significant concern.
In conclusion, the CPU power supply circuit on a motherboard, utilizing the RT9241 and RT9600 chips, exemplifies a sophisticated approach to power management, ensuring that the CPU operates reliably and efficiently under varying loads.A typical computer motherboard CPU power supply circuit A typical computer motherboard CPU power supply circuit, which is mainly composed of the main power supply management ch ip RT9241, two from the power source management and other parts of the chip RT9600. Voltage command signal from the CPU from the RT9241 O ~ feet into by the chip circuit identification processing, by pin output two different phases PWM pulse signals, respectively, by the two from power management Cang backsheet each output processing of two opposite phase PWM signal, the field effect transistors Qi, Q2 and Q3, Q after power to the CPU.