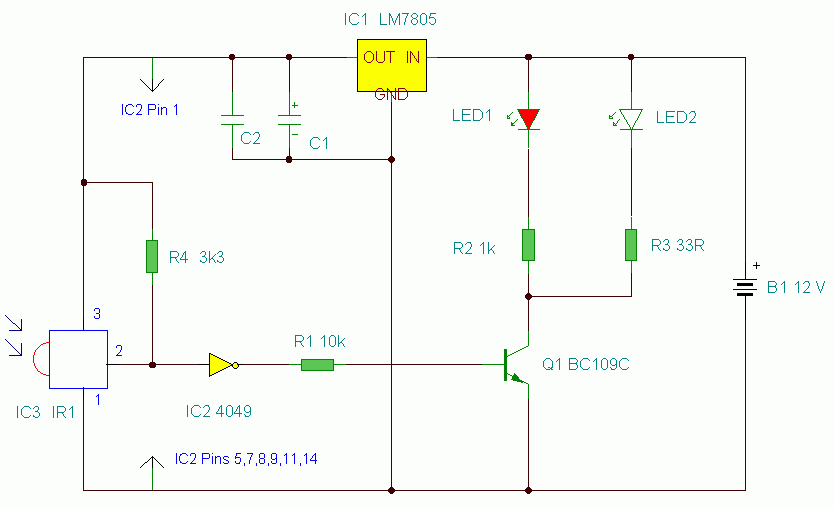
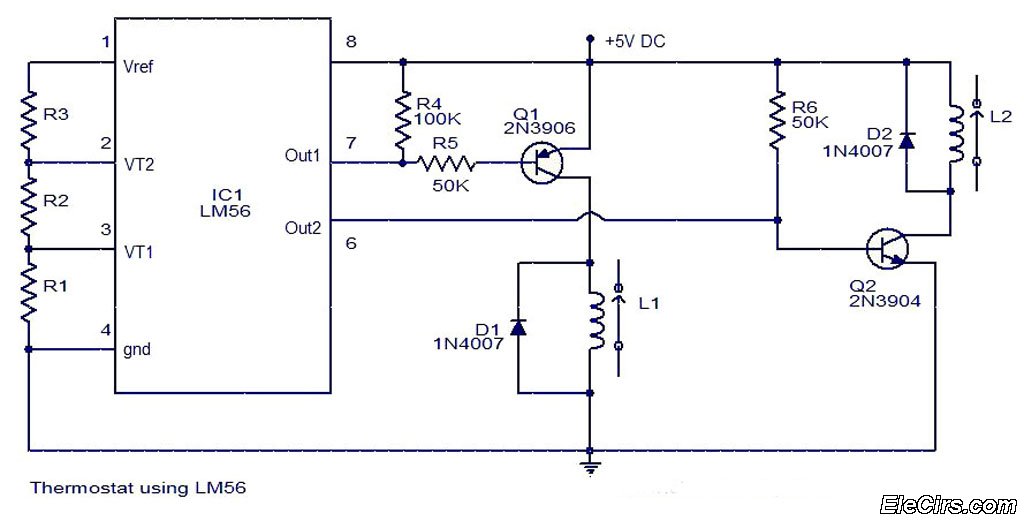
AC voltmeter circuit
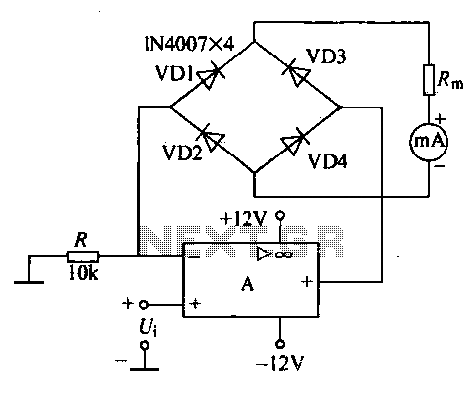
An operational amplifier, a diode bridge rectifier, and DC mA AC voltmeter tables are illustrated in the figure. The operational amplifier used is the LM324. The measured AC voltage is applied to the inverting terminal of the operational amplifier, which has a high input impedance. Negative feedback is utilized to minimize the nonlinear effects in the feedback loop, and the diode bridge is incorporated into the feedback operational amplifier circuit to mitigate the impact of the non-linear characteristics of the diodes. The current flowing through the bridge is determined solely by the input voltage (Ui) divided by the resistance (R), rendering it independent of the parameters of the bridge and the operational amplifier (including the non-linear diode dead zone parameters). The total current through the rectified output is proportional to the average measured voltage of Ui. The measured voltage is influenced by the frequency band and the upper limit of the operational amplifier circuit's rise time.
The circuit comprises an LM324 operational amplifier configured in an inverting amplifier setup. The input AC voltage is connected to the inverting terminal, while the non-inverting terminal is grounded. The high input impedance of the LM324 ensures minimal loading on the input source, allowing for accurate voltage measurements without significant signal degradation. The feedback loop incorporates a diode bridge rectifier, which serves to convert the AC input into a DC output.
The diode bridge consists of four diodes arranged in a bridge configuration, allowing for full-wave rectification. This arrangement enables the circuit to handle both halves of the AC waveform, resulting in a smoother DC output. The operational amplifier's feedback path includes these diodes, which helps to counteract the non-linear behavior typically exhibited by diodes in rectifier circuits.
The output current from the bridge rectifier, which is the rectified version of the input AC voltage, is expressed as the input voltage divided by the resistance in the feedback loop. This relationship indicates that the output current is independent of the non-linear characteristics of the diodes, thus providing a more stable and reliable measurement.
The average voltage measured at the output is directly proportional to the input AC voltage, making the circuit suitable for applications requiring accurate voltage measurements. Additionally, the performance of the operational amplifier is influenced by the frequency of the input signal and the rise time of the operational amplifier circuit, which must be considered in high-frequency applications. Overall, this configuration is effective for precise voltage measurement in various electronic applications, ensuring both accuracy and stability in the output readings.An operational amplifier, a diode bridge rectifier and DC mA AC voltmeter tables as shown in FIG. The figure, the operational amplifier LM324. Ul measured AC voltage is applied to the inverting terminal of the operational amplifier, it has a high input impedance, and because a negative feedback can reduce the feedback loop nonlinear effects, so the diode bridge and the head in the feedback operational amplifier circuit, in order to reduce the effect of non-linear diode itself. I all current flow path across the bridge, its value only Ui / R, related to nothing to do with the bridge and the head parameters (non-linear diode dead zone parameters).
Table full head crossing rectified current is proportional to the average measured voltage of Ui. The measured voltage depends on the frequency band and the upper limit of the operational amplifier circuit of rising rates.
The circuit comprises an LM324 operational amplifier configured in an inverting amplifier setup. The input AC voltage is connected to the inverting terminal, while the non-inverting terminal is grounded. The high input impedance of the LM324 ensures minimal loading on the input source, allowing for accurate voltage measurements without significant signal degradation. The feedback loop incorporates a diode bridge rectifier, which serves to convert the AC input into a DC output.
The diode bridge consists of four diodes arranged in a bridge configuration, allowing for full-wave rectification. This arrangement enables the circuit to handle both halves of the AC waveform, resulting in a smoother DC output. The operational amplifier's feedback path includes these diodes, which helps to counteract the non-linear behavior typically exhibited by diodes in rectifier circuits.
The output current from the bridge rectifier, which is the rectified version of the input AC voltage, is expressed as the input voltage divided by the resistance in the feedback loop. This relationship indicates that the output current is independent of the non-linear characteristics of the diodes, thus providing a more stable and reliable measurement.
The average voltage measured at the output is directly proportional to the input AC voltage, making the circuit suitable for applications requiring accurate voltage measurements. Additionally, the performance of the operational amplifier is influenced by the frequency of the input signal and the rise time of the operational amplifier circuit, which must be considered in high-frequency applications. Overall, this configuration is effective for precise voltage measurement in various electronic applications, ensuring both accuracy and stability in the output readings.An operational amplifier, a diode bridge rectifier and DC mA AC voltmeter tables as shown in FIG. The figure, the operational amplifier LM324. Ul measured AC voltage is applied to the inverting terminal of the operational amplifier, it has a high input impedance, and because a negative feedback can reduce the feedback loop nonlinear effects, so the diode bridge and the head in the feedback operational amplifier circuit, in order to reduce the effect of non-linear diode itself. I all current flow path across the bridge, its value only Ui / R, related to nothing to do with the bridge and the head parameters (non-linear diode dead zone parameters).
Table full head crossing rectified current is proportional to the average measured voltage of Ui. The measured voltage depends on the frequency band and the upper limit of the operational amplifier circuit of rising rates.