Across The Track Infrared Detectors
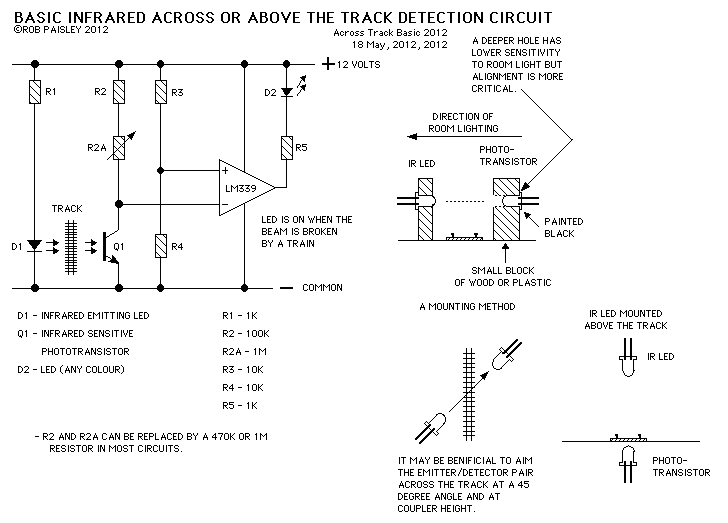
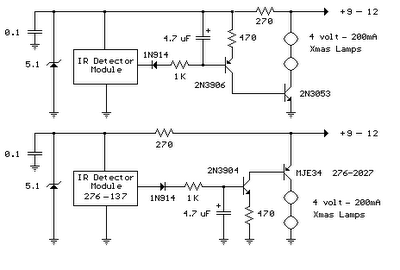
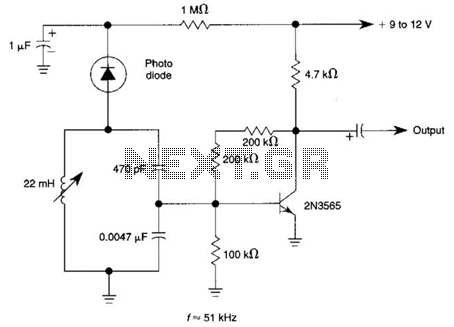
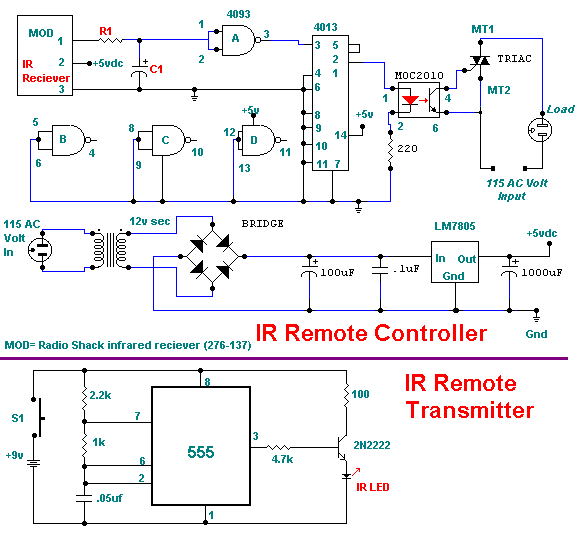
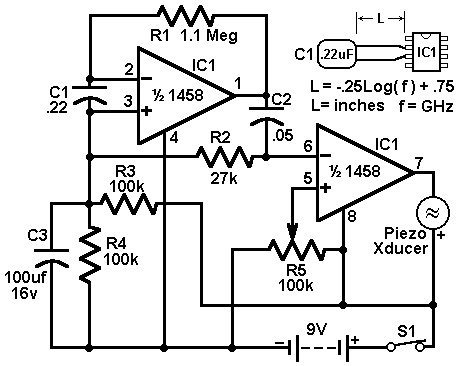
This page presents information on infrared - Across The Track train detection circuits. The circuits are designed around the LM339 comparator chip and can use a wide assortment of matched infrared - emitter / detector pairs. The basic circuit shown below has been tested with sensor gaps as wide as 12 inches but a distance of 8 inches or less is more practical.
The infrared "Across The Track" train detection circuit utilizes the LM339 comparator as its core component, which is a quad comparator capable of comparing multiple voltage levels. This circuit is particularly effective in detecting trains as they pass through a designated area, employing infrared emitter and detector pairs that work in tandem to create an invisible barrier.
In a typical configuration, the infrared emitter transmits a continuous beam of infrared light, which is received by the infrared detector positioned directly opposite. When a train enters the detection zone, it interrupts the infrared beam, causing a change in voltage at the output of the detector. This change is then fed into one of the LM339 comparator inputs.
The LM339 is configured with a reference voltage at another input, which sets the threshold for detection. When the voltage from the detector drops below this reference level, the LM339 outputs a low signal, which can be used to trigger an alarm, activate lights, or interface with other control systems.
The circuit can be adjusted for various distances between the emitter and detector. While the basic design has been tested effectively with gaps up to 12 inches, it is recommended to maintain a practical distance of 8 inches or less for optimal performance and reliability. Additionally, the choice of matched infrared emitter and detector pairs is crucial, as their characteristics will influence the sensitivity and response time of the circuit.
In terms of power supply, the LM339 operates on a wide voltage range, typically from 2V to 36V, allowing for flexibility in deployment. Proper decoupling capacitors should be placed close to the power pins of the LM339 to minimize noise and ensure stable operation.
Overall, the infrared "Across The Track" train detection circuit offers a reliable and efficient solution for monitoring train movements, enhancing safety and operational awareness in rail systems.This page presents information on infrared - `Across The Track` train detection circuits. The circuits are designed around the LM339 comparator chip and can use a wide assortment of matched infrared - emitter / detector pairs. The basic circuit shown below has been tested with sensor gaps as wide as 12 inches but a distance of 8 inches or less is more practical.
🔗 External reference
The infrared "Across The Track" train detection circuit utilizes the LM339 comparator as its core component, which is a quad comparator capable of comparing multiple voltage levels. This circuit is particularly effective in detecting trains as they pass through a designated area, employing infrared emitter and detector pairs that work in tandem to create an invisible barrier.
In a typical configuration, the infrared emitter transmits a continuous beam of infrared light, which is received by the infrared detector positioned directly opposite. When a train enters the detection zone, it interrupts the infrared beam, causing a change in voltage at the output of the detector. This change is then fed into one of the LM339 comparator inputs.
The LM339 is configured with a reference voltage at another input, which sets the threshold for detection. When the voltage from the detector drops below this reference level, the LM339 outputs a low signal, which can be used to trigger an alarm, activate lights, or interface with other control systems.
The circuit can be adjusted for various distances between the emitter and detector. While the basic design has been tested effectively with gaps up to 12 inches, it is recommended to maintain a practical distance of 8 inches or less for optimal performance and reliability. Additionally, the choice of matched infrared emitter and detector pairs is crucial, as their characteristics will influence the sensitivity and response time of the circuit.
In terms of power supply, the LM339 operates on a wide voltage range, typically from 2V to 36V, allowing for flexibility in deployment. Proper decoupling capacitors should be placed close to the power pins of the LM339 to minimize noise and ensure stable operation.
Overall, the infrared "Across The Track" train detection circuit offers a reliable and efficient solution for monitoring train movements, enhancing safety and operational awareness in rail systems.This page presents information on infrared - `Across The Track` train detection circuits. The circuits are designed around the LM339 comparator chip and can use a wide assortment of matched infrared - emitter / detector pairs. The basic circuit shown below has been tested with sensor gaps as wide as 12 inches but a distance of 8 inches or less is more practical.
🔗 External reference