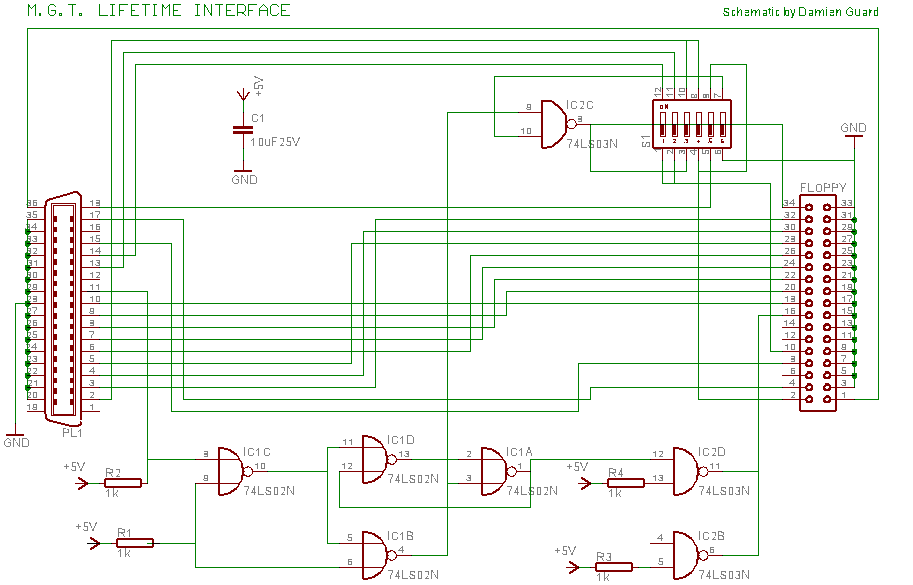
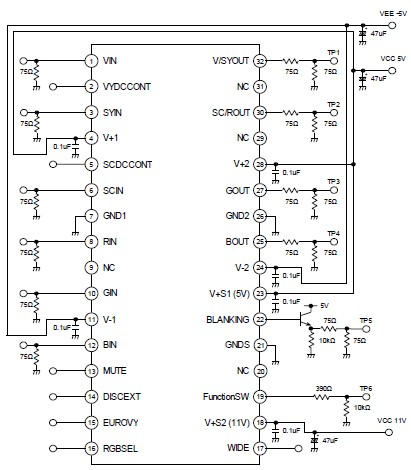
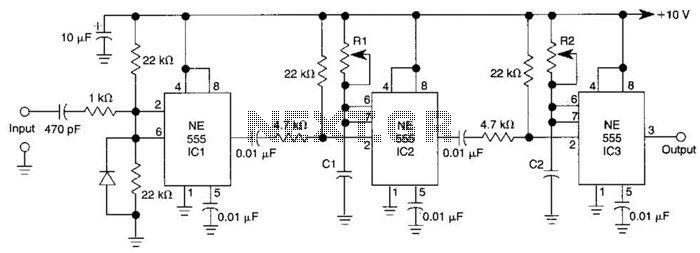
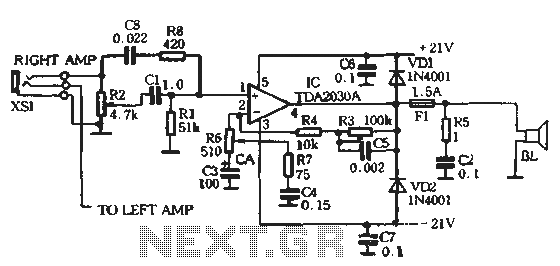
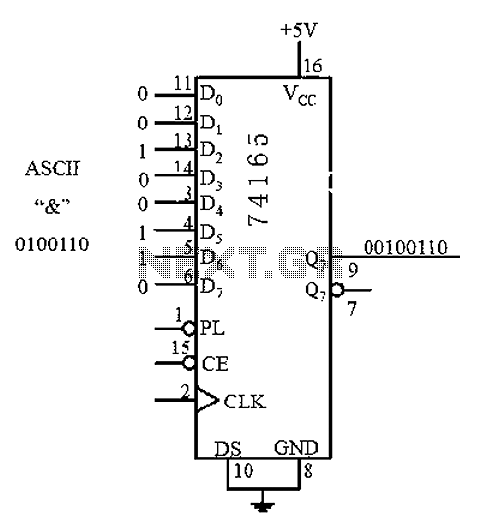
Add a Discrete Jack-Sensing Circuit to the MAX13330/MAX13331 Automotive Headphone Amplifier
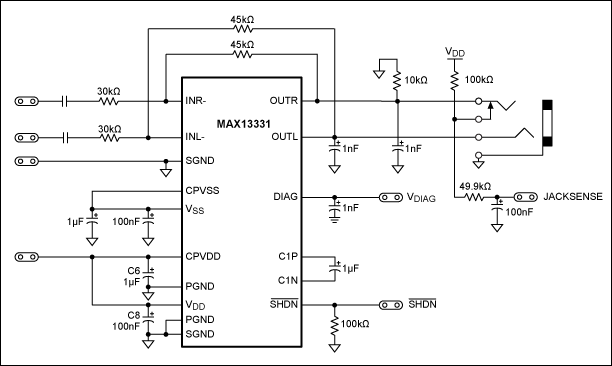
Incorporate a straightforward, economical jack-sensing circuit (JACKSENSE) into a DirectDrive automotive headphone amplifier to detect when headphones are plugged into the audio jack.
The implementation of a jack-sensing circuit (JACKSENSE) in a DirectDrive automotive headphone amplifier is designed to enhance user experience by providing a reliable detection mechanism for headphone insertion. The circuit typically utilizes a combination of resistors, transistors, and possibly a microcontroller to monitor the state of the audio jack.
The circuit functions as follows: when a headphone plug is inserted into the audio jack, it completes a circuit that changes the voltage levels at a designated sensing point. This change can be detected using a voltage divider network or a comparator circuit. The output signal can then be used to enable or disable the audio output to the headphones, ensuring that sound is only directed to the headphones when they are connected.
In a basic design, a pull-down resistor may be connected to the ground, while a signal line is connected to the tip of the headphone jack. When the headphone is inserted, the resistance changes, which can be interpreted by a microcontroller or a simple transistor switch. This allows the amplifier to switch states and prevent audio signals from being sent to the speakers, thereby protecting the equipment and enhancing sound quality.
To ensure reliability, the circuit may also include debounce logic to prevent false triggering from the mechanical contact of the headphone jack. The overall design should prioritize low power consumption, compact size, and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for automotive applications where space and energy efficiency are critical.
In conclusion, the integration of a jack-sensing circuit into a DirectDrive headphone amplifier not only improves functionality but also contributes to a more seamless user interface in automotive audio systems.Add a simple, low-cost, jack-sensing circuit (JACKSENSE) to a DirectDrive automotive headphone amp and detect when a headphone is inserted into the audio jack.. 🔗 External reference
The implementation of a jack-sensing circuit (JACKSENSE) in a DirectDrive automotive headphone amplifier is designed to enhance user experience by providing a reliable detection mechanism for headphone insertion. The circuit typically utilizes a combination of resistors, transistors, and possibly a microcontroller to monitor the state of the audio jack.
The circuit functions as follows: when a headphone plug is inserted into the audio jack, it completes a circuit that changes the voltage levels at a designated sensing point. This change can be detected using a voltage divider network or a comparator circuit. The output signal can then be used to enable or disable the audio output to the headphones, ensuring that sound is only directed to the headphones when they are connected.
In a basic design, a pull-down resistor may be connected to the ground, while a signal line is connected to the tip of the headphone jack. When the headphone is inserted, the resistance changes, which can be interpreted by a microcontroller or a simple transistor switch. This allows the amplifier to switch states and prevent audio signals from being sent to the speakers, thereby protecting the equipment and enhancing sound quality.
To ensure reliability, the circuit may also include debounce logic to prevent false triggering from the mechanical contact of the headphone jack. The overall design should prioritize low power consumption, compact size, and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for automotive applications where space and energy efficiency are critical.
In conclusion, the integration of a jack-sensing circuit into a DirectDrive headphone amplifier not only improves functionality but also contributes to a more seamless user interface in automotive audio systems.Add a simple, low-cost, jack-sensing circuit (JACKSENSE) to a DirectDrive automotive headphone amp and detect when a headphone is inserted into the audio jack.. 🔗 External reference