Address decoder interface circuit
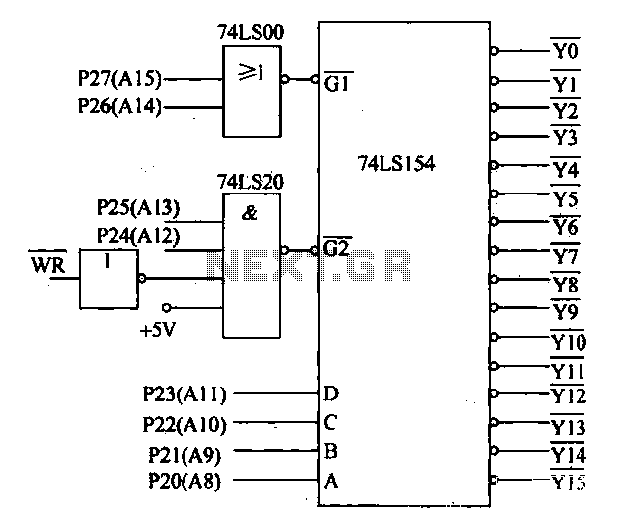
Decoding circuit: To ensure proper functionality of various interfaces, the system must assign IP addresses to all ports. Based on the number of system interfaces, it utilizes the 74LS154 decoder, which can translate up to 16 addresses. The interface circuit is illustrated in Figure 27-50. In this figure, the address bus A15 and A14 control the decoder's G1 control terminal, while A13 and A12 control the G2 terminal. The address lines A8 connect to the decoder's selection control terminals D, C, B, and A, allowing for the analysis of each port address, as detailed in Table 27-2. Additionally, the system incorporates eight D/A conversion circuits to control the brightness output of the processor, converting it into an analog signal sent to the corresponding actuators. The DAC0832 is used for this purpose, providing an output in the range of 4-20 mA.
The decoding circuit plays a critical role in managing the communication between multiple interfaces within a system. By employing the 74LS154, a 4-to-16 line decoder, the circuit can effectively assign unique IP addresses to each of the system's ports. This capability is crucial for ensuring that data packets are directed to the correct destinations, thereby maintaining the integrity of the communication process.
The address bus configuration, particularly the use of A15, A14, A13, and A12, enables the control of the decoder's operation. The G1 and G2 control terminals dictate whether the decoder is active, while the address lines A8 through A0 are responsible for selecting the specific output line corresponding to the desired port. This setup allows for efficient management of up to 16 different ports, facilitating a streamlined communication protocol.
Furthermore, the inclusion of eight D/A conversion circuits enhances the system's functionality by converting digital signals from the processor into analog voltages. The DAC0832 is a key component in this process, providing a reliable output range of 4-20 mA, which is standard for many industrial applications. This output can be used to control various actuators, such as motors or valves, allowing for precise manipulation of physical systems based on digital commands.
Overall, the combination of the decoding circuit and D/A conversion capabilities creates a robust framework for managing multiple interfaces and ensuring effective communication and control within the system. The design considerations and component choices reflect a thorough understanding of electronic principles and practical applications in the field.Decoding circuit: In order to make the various interfaces to work properly, the system needs to assign IP addresses to all ports. According to the number of system interfaces, it adopts the 74LS154, can be translated to 16 addresses, the interface circuit shown in Figure 27-50. The figure, the address bus A15, A14 control decoder control terminal Gl. A13, A12 control decoder control terminal G2. All-A8 connected decoder selection control terminal D, C, B, A. It can analyze each port address, see Table 27-2. In addition, the system also features eight D/A conversion circuit, respectively, to control the amount of output processor brightest converted into analog, sent to the corresponding actuators.
Use DAC0832, the output of 4-20mA.
The decoding circuit plays a critical role in managing the communication between multiple interfaces within a system. By employing the 74LS154, a 4-to-16 line decoder, the circuit can effectively assign unique IP addresses to each of the system's ports. This capability is crucial for ensuring that data packets are directed to the correct destinations, thereby maintaining the integrity of the communication process.
The address bus configuration, particularly the use of A15, A14, A13, and A12, enables the control of the decoder's operation. The G1 and G2 control terminals dictate whether the decoder is active, while the address lines A8 through A0 are responsible for selecting the specific output line corresponding to the desired port. This setup allows for efficient management of up to 16 different ports, facilitating a streamlined communication protocol.
Furthermore, the inclusion of eight D/A conversion circuits enhances the system's functionality by converting digital signals from the processor into analog voltages. The DAC0832 is a key component in this process, providing a reliable output range of 4-20 mA, which is standard for many industrial applications. This output can be used to control various actuators, such as motors or valves, allowing for precise manipulation of physical systems based on digital commands.
Overall, the combination of the decoding circuit and D/A conversion capabilities creates a robust framework for managing multiple interfaces and ensuring effective communication and control within the system. The design considerations and component choices reflect a thorough understanding of electronic principles and practical applications in the field.Decoding circuit: In order to make the various interfaces to work properly, the system needs to assign IP addresses to all ports. According to the number of system interfaces, it adopts the 74LS154, can be translated to 16 addresses, the interface circuit shown in Figure 27-50. The figure, the address bus A15, A14 control decoder control terminal Gl. A13, A12 control decoder control terminal G2. All-A8 connected decoder selection control terminal D, C, B, A. It can analyze each port address, see Table 27-2. In addition, the system also features eight D/A conversion circuit, respectively, to control the amount of output processor brightest converted into analog, sent to the corresponding actuators.
Use DAC0832, the output of 4-20mA.