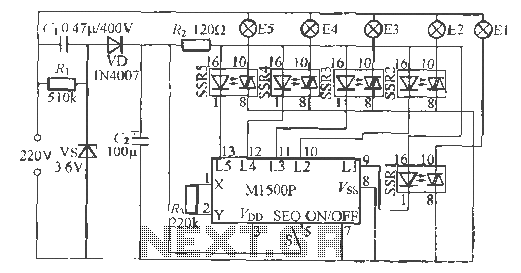
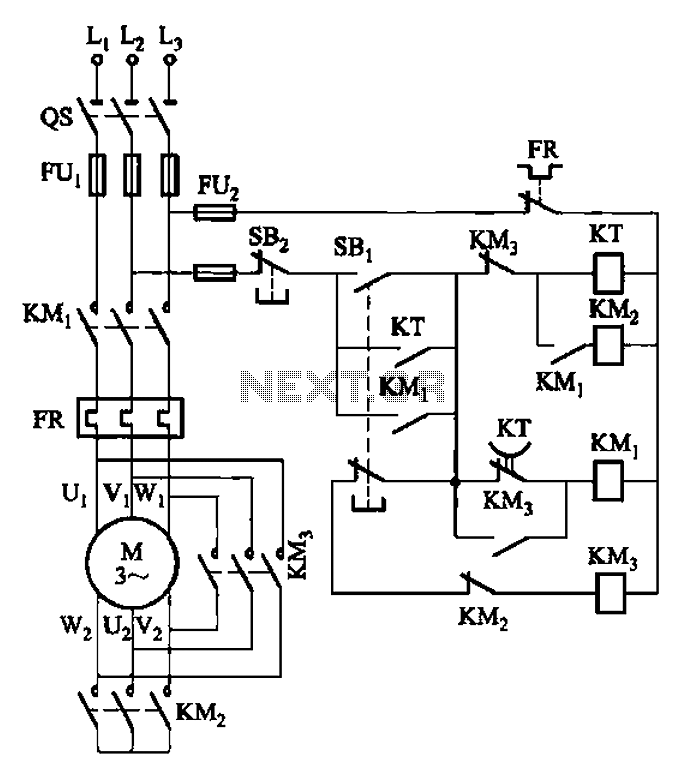
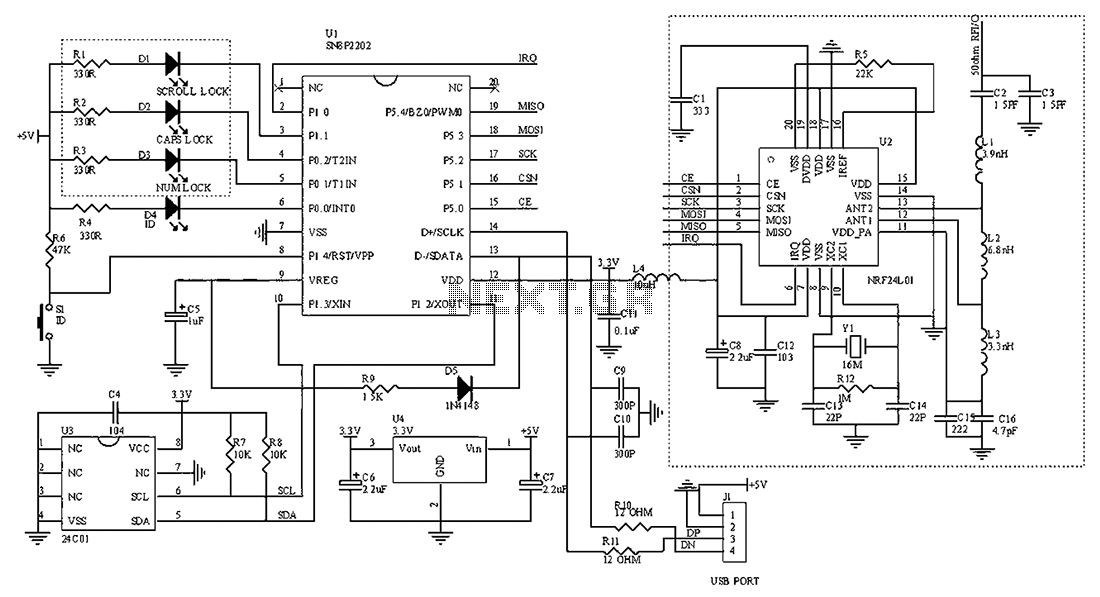
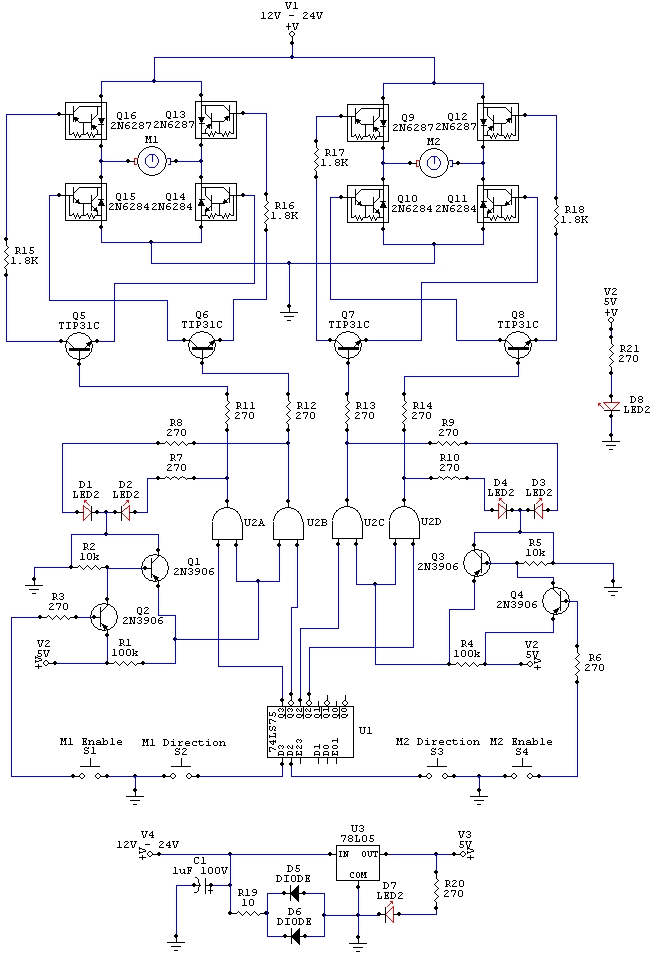
Small Metal detector schematic circuit
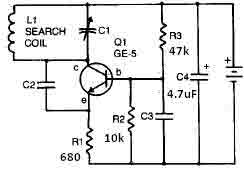
This metal detector circuit needs to be powered using a 9 volts power supply (DC) or a 9 volts battery. The C1 capacitor is a variable capacitor with a value of 365 pF, C2 is a 100 pF silver mica capacitor, C3 is a 0.05 uF disc capacitor, and the C4 is a 4.7 uF capacitor. The Q1 transistor can be RCA SK3011 npn transistor or equivalent type, and all resistors need to be ½ watts. More: This metal detector schematic circuit is based on a transistor radio as a detector. With the radio tuned to a weak station, you must adjust the variable capacitor C1 until the locator oscillator beats against the received signal. If a metal is detected, the inductance of the L1 coil is changed, changing the frequency of the locator oscillators, resulting in a change in the beat tone radio. The L1 search coil of the metal detector circuit must have 18 turns from a 0.65 mm enameled wire scrambled on a 4-inch diameter support.
The metal detector circuit operates on a simple principle of frequency modulation, utilizing a combination of capacitors, inductors, and a transistor to detect changes in the electromagnetic field caused by nearby metallic objects. The circuit is powered by a 9-volt DC supply, which can be sourced from either a battery or an external power supply.
The variable capacitor, C1, has a capacitance range of up to 365 pF, allowing for fine-tuning of the oscillator frequency. This is crucial for achieving the desired detection sensitivity. The fixed capacitors, C2, C3, and C4, serve specific roles in the circuit. C2, a 100 pF silver mica capacitor, is typically used for stability in high-frequency applications, while C3, a 0.05 uF disc capacitor, may be used for coupling or bypassing, ensuring that unwanted frequencies do not affect the circuit's operation. C4, with a capacitance of 4.7 uF, is likely employed for power supply filtering, smoothing out any voltage fluctuations that could interfere with the circuit's performance.
The transistor Q1, an RCA SK3011 or an equivalent NPN type, acts as an amplifier and is essential for processing the signals generated by the oscillator. The choice of a ½-watt resistor rating throughout the circuit ensures that the components can handle the power levels without overheating, contributing to the circuit's reliability.
The L1 coil, which is a critical component of the metal detector, consists of 18 turns of 0.65 mm enameled wire wound on a 4-inch diameter form. This coil acts as an inductor and is responsible for generating the electromagnetic field. When a metallic object enters this field, the inductance of the coil changes, which in turn alters the frequency of the oscillator. This frequency shift produces a beat tone in the radio receiver, indicating the presence of metal.
The overall design of this metal detector circuit is straightforward, making it suitable for hobbyists and educational purposes, while also demonstrating fundamental electronic principles such as resonance, oscillation, and signal detection.This metal detector circuit needs to be powered using a 9 volts power supply ( DC) or a 9 volts battery . The C1 capacitor is a variable capacitor with a value of 365 pF , C2 is a 100pF silver mica capacitor , C3 is a 0.05 uF disc capacitor and the C4 is a 4.7 uF capacitor .
The Q1 transistor can be RCA SK3011 npn transistor or equivalent type and all resistors need to be ½ watts . This metal detector schematic circuit is based on a transistor radio as an detector . With the radio tuned to a weak station you must adjust the variable capacitor C1 until the locator oscillator beats against the received signal . If a metal is detected the inductance of the L1 coil is changed , changing the frequency of the locator oscillators , resulting a change in the beat tone radio .
The L1 search coil of the metal detector circuit must have 18 turns from a 0.65 mm enameled wire scrambled on a 4 inch diameter support . 🔗 External reference
The metal detector circuit operates on a simple principle of frequency modulation, utilizing a combination of capacitors, inductors, and a transistor to detect changes in the electromagnetic field caused by nearby metallic objects. The circuit is powered by a 9-volt DC supply, which can be sourced from either a battery or an external power supply.
The variable capacitor, C1, has a capacitance range of up to 365 pF, allowing for fine-tuning of the oscillator frequency. This is crucial for achieving the desired detection sensitivity. The fixed capacitors, C2, C3, and C4, serve specific roles in the circuit. C2, a 100 pF silver mica capacitor, is typically used for stability in high-frequency applications, while C3, a 0.05 uF disc capacitor, may be used for coupling or bypassing, ensuring that unwanted frequencies do not affect the circuit's operation. C4, with a capacitance of 4.7 uF, is likely employed for power supply filtering, smoothing out any voltage fluctuations that could interfere with the circuit's performance.
The transistor Q1, an RCA SK3011 or an equivalent NPN type, acts as an amplifier and is essential for processing the signals generated by the oscillator. The choice of a ½-watt resistor rating throughout the circuit ensures that the components can handle the power levels without overheating, contributing to the circuit's reliability.
The L1 coil, which is a critical component of the metal detector, consists of 18 turns of 0.65 mm enameled wire wound on a 4-inch diameter form. This coil acts as an inductor and is responsible for generating the electromagnetic field. When a metallic object enters this field, the inductance of the coil changes, which in turn alters the frequency of the oscillator. This frequency shift produces a beat tone in the radio receiver, indicating the presence of metal.
The overall design of this metal detector circuit is straightforward, making it suitable for hobbyists and educational purposes, while also demonstrating fundamental electronic principles such as resonance, oscillation, and signal detection.This metal detector circuit needs to be powered using a 9 volts power supply ( DC) or a 9 volts battery . The C1 capacitor is a variable capacitor with a value of 365 pF , C2 is a 100pF silver mica capacitor , C3 is a 0.05 uF disc capacitor and the C4 is a 4.7 uF capacitor .
The Q1 transistor can be RCA SK3011 npn transistor or equivalent type and all resistors need to be ½ watts . This metal detector schematic circuit is based on a transistor radio as an detector . With the radio tuned to a weak station you must adjust the variable capacitor C1 until the locator oscillator beats against the received signal . If a metal is detected the inductance of the L1 coil is changed , changing the frequency of the locator oscillators , resulting a change in the beat tone radio .
The L1 search coil of the metal detector circuit must have 18 turns from a 0.65 mm enameled wire scrambled on a 4 inch diameter support . 🔗 External reference