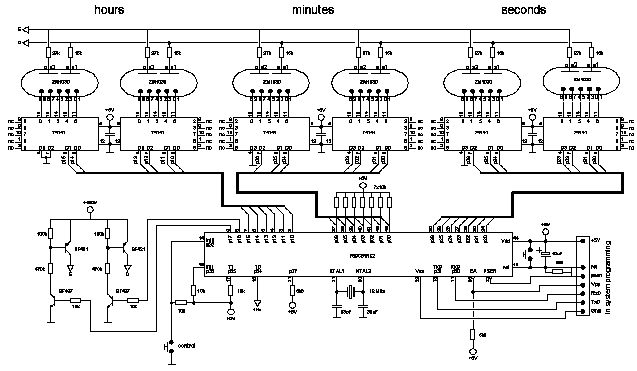
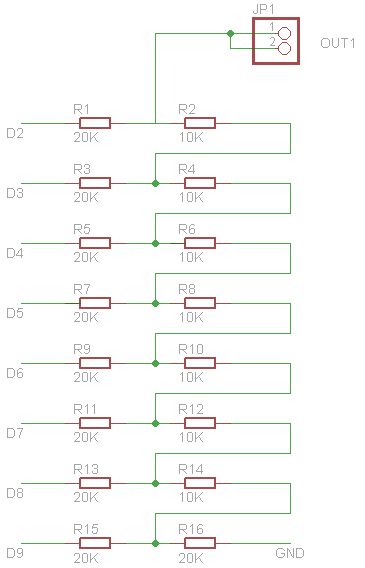
Adjustable TTL clock
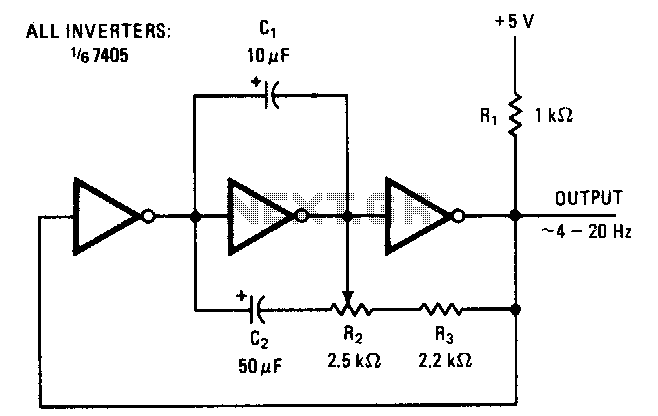
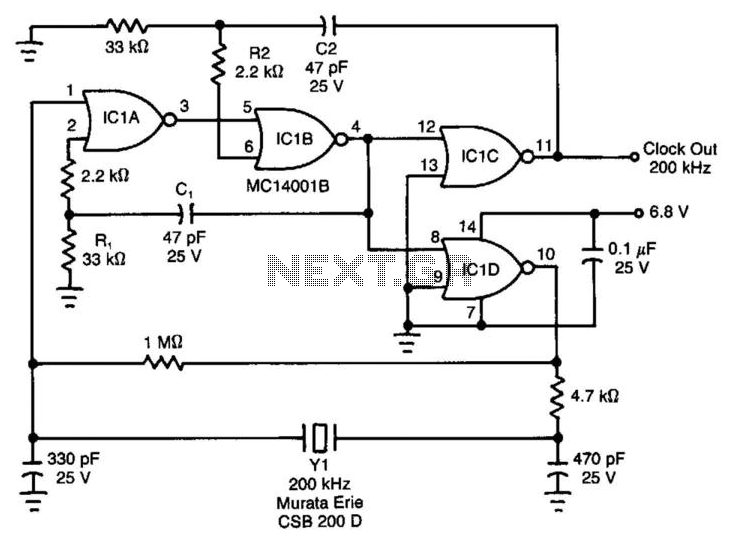
The symmetry of the square-wave output is maintained by connecting the right side of resistor R2 through resistor R3 to the output of the third amplifier stage. This configuration alters the charging current to the capacitors in proportion to the setting of the frequency-adjusting potentiometer R2. Consequently, a duty cycle of 50% is consistent across the entire range of oscillation. The lower frequency limit is determined by capacitor C2. The components illustrated allow the frequency of oscillation to be adjusted by R2 from approximately 4 to 20 hertz. Additional frequency ranges can be achieved by modifying the values of capacitor C1 and resistor R3, which govern the upper limit of oscillation, or capacitor C2, which restricts the low-frequency end.
The described circuit utilizes a square-wave oscillator configuration, where the symmetry of the output waveform is crucial for maintaining a consistent duty cycle. The connection of R2 to the output of the third amplifier stage through R3 facilitates the modulation of the charging current to the capacitors, effectively allowing for precise control over the frequency of oscillation. The frequency-adjusting potentiometer R2 plays a pivotal role in this modulation, enabling the user to vary the frequency within a specified range.
The lower frequency limit of the oscillator is set by capacitor C2, which acts as a timing element in conjunction with the resistors. As the capacitance of C2 influences the time constant of the circuit, it effectively determines the minimum frequency at which the oscillator can operate. The upper frequency limit can be adjusted by changing the values of capacitor C1 and resistor R3. These components define the time constant for the charging and discharging cycles, thus impacting the maximum frequency achievable by the oscillator.
This schematic can be further optimized by selecting appropriate resistor and capacitor values based on the desired frequency range. For instance, if a higher frequency range is needed, reducing the capacitance of C1 or the resistance of R3 will result in shorter time constants, allowing the oscillator to achieve higher frequencies. Conversely, increasing C2 will lower the minimum frequency, providing flexibility in application-specific designs.
In summary, the circuit effectively provides a square-wave output with a stable 50% duty cycle across a range of frequencies from 4 to 20 hertz, with additional tuning capabilities through the careful selection of component values. This design is suitable for various applications where precise frequency control is required, such as in timing circuits, signal generators, and modulation schemes.Symmetry of the square-wave output is maintained by connecting the right side of R2 through resistor R3 to the output of the third amplifier stage. This changes the charging current to the capacitors in proportion to the setting of frequency-adjusting potentiometer R2.
Thus, a duty cycle of 50% is constant over the entire range of oscillation. The lower frequency limit is set by capacitor C2 With the components shown, the frequency of oscillation can be varied by R2 from about 4 to 20 hertz. Other frequency ranges can be obtained by changing the values of Cl and R3, which control the upper limit of oscillation, or C2, which limits the low-frequency end.
The described circuit utilizes a square-wave oscillator configuration, where the symmetry of the output waveform is crucial for maintaining a consistent duty cycle. The connection of R2 to the output of the third amplifier stage through R3 facilitates the modulation of the charging current to the capacitors, effectively allowing for precise control over the frequency of oscillation. The frequency-adjusting potentiometer R2 plays a pivotal role in this modulation, enabling the user to vary the frequency within a specified range.
The lower frequency limit of the oscillator is set by capacitor C2, which acts as a timing element in conjunction with the resistors. As the capacitance of C2 influences the time constant of the circuit, it effectively determines the minimum frequency at which the oscillator can operate. The upper frequency limit can be adjusted by changing the values of capacitor C1 and resistor R3. These components define the time constant for the charging and discharging cycles, thus impacting the maximum frequency achievable by the oscillator.
This schematic can be further optimized by selecting appropriate resistor and capacitor values based on the desired frequency range. For instance, if a higher frequency range is needed, reducing the capacitance of C1 or the resistance of R3 will result in shorter time constants, allowing the oscillator to achieve higher frequencies. Conversely, increasing C2 will lower the minimum frequency, providing flexibility in application-specific designs.
In summary, the circuit effectively provides a square-wave output with a stable 50% duty cycle across a range of frequencies from 4 to 20 hertz, with additional tuning capabilities through the careful selection of component values. This design is suitable for various applications where precise frequency control is required, such as in timing circuits, signal generators, and modulation schemes.Symmetry of the square-wave output is maintained by connecting the right side of R2 through resistor R3 to the output of the third amplifier stage. This changes the charging current to the capacitors in proportion to the setting of frequency-adjusting potentiometer R2.
Thus, a duty cycle of 50% is constant over the entire range of oscillation. The lower frequency limit is set by capacitor C2 With the components shown, the frequency of oscillation can be varied by R2 from about 4 to 20 hertz. Other frequency ranges can be obtained by changing the values of Cl and R3, which control the upper limit of oscillation, or C2, which limits the low-frequency end.