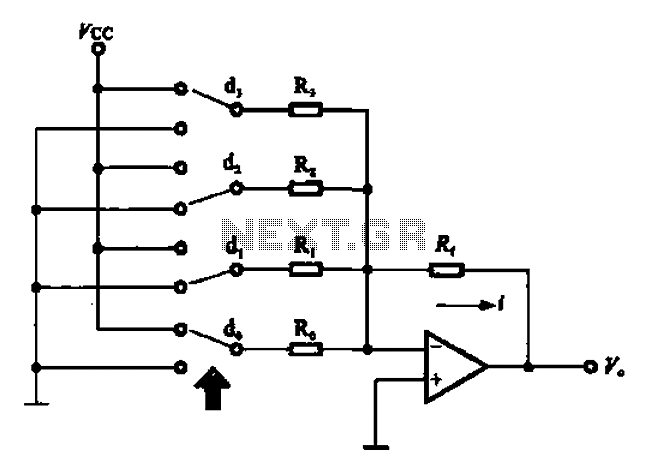
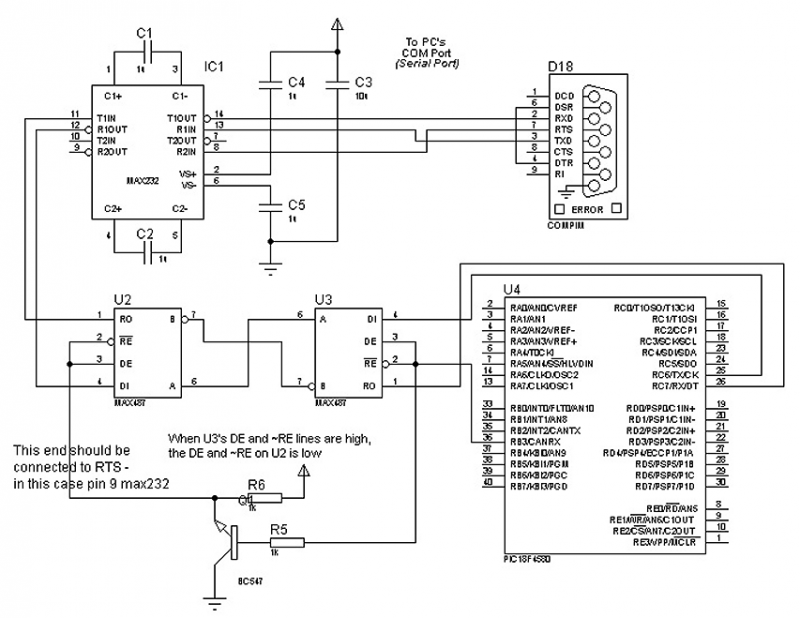
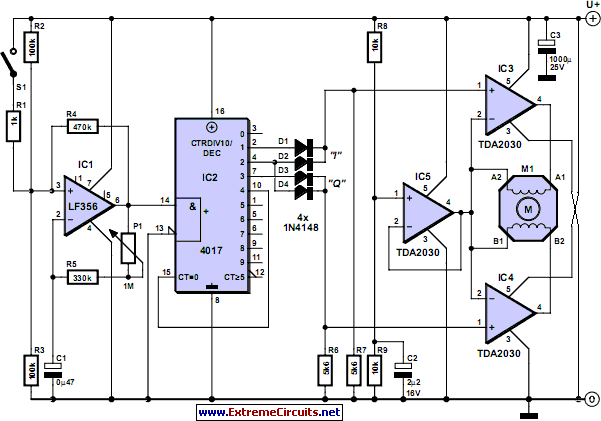
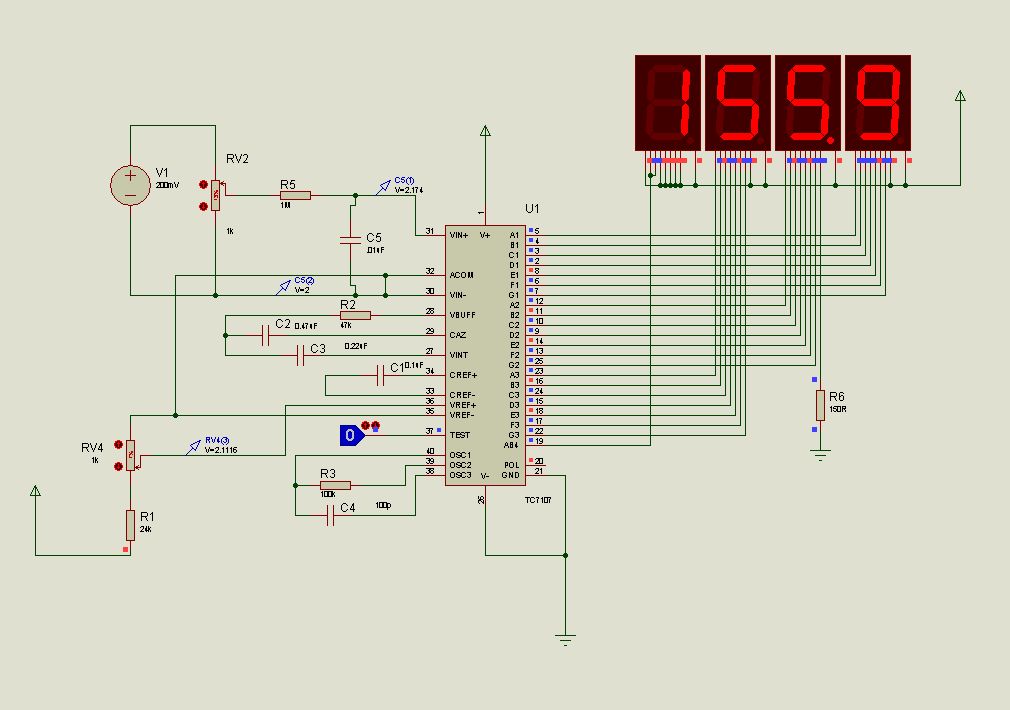
ADP1821 Step Down DC-to-DC Converter
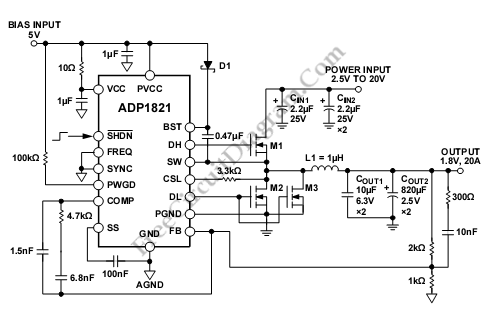
This is an ADP1821 step-down DC-to-DC converter circuit. This circuit utilizes the ADP1821, which is a synchronous pulse-width-modulated (PWM) step-down controller.
The ADP1821 is designed to efficiently convert a higher input voltage to a lower output voltage while maintaining high performance and efficiency. This device operates in a synchronous mode, allowing for reduced power loss and improved efficiency compared to non-synchronous designs. The PWM control scheme enables precise regulation of the output voltage, making the circuit suitable for various applications, including powering microcontrollers, sensors, and other electronic devices.
The circuit typically includes several key components: the ADP1821 IC itself, input and output capacitors, an inductor, and a diode. The input capacitors serve to stabilize the input voltage and reduce voltage ripple, while the output capacitors help maintain a steady output voltage with minimal ripple. The inductor is critical for energy storage and transfer; it smooths the current flowing to the load, helping to maintain a consistent output voltage.
In operation, the ADP1821 modulates the duty cycle of the switching signal to control the amount of energy delivered to the output. The feedback loop monitors the output voltage and adjusts the PWM signal accordingly, ensuring that the output remains stable despite variations in load current or input voltage. This feedback mechanism is essential for maintaining the desired output voltage under different operating conditions.
The design of the circuit should also consider thermal management, as the ADP1821 can generate heat during operation. Adequate heat sinking or thermal vias may be required to ensure reliable performance. Additionally, careful selection of the inductor and capacitors is important to optimize the transient response and minimize output voltage ripple.
Overall, the ADP1821 step-down DC-to-DC converter circuit is a robust solution for efficiently powering electronic devices from higher voltage sources, making it a valuable component in modern electronic design.This is a ADP1821 Step Down DC-to-DC Converter circuit. This circuit uses ADP1821 that is synchronous pulse-width-modulated (PWM), step-down controller,. 🔗 External reference
The ADP1821 is designed to efficiently convert a higher input voltage to a lower output voltage while maintaining high performance and efficiency. This device operates in a synchronous mode, allowing for reduced power loss and improved efficiency compared to non-synchronous designs. The PWM control scheme enables precise regulation of the output voltage, making the circuit suitable for various applications, including powering microcontrollers, sensors, and other electronic devices.
The circuit typically includes several key components: the ADP1821 IC itself, input and output capacitors, an inductor, and a diode. The input capacitors serve to stabilize the input voltage and reduce voltage ripple, while the output capacitors help maintain a steady output voltage with minimal ripple. The inductor is critical for energy storage and transfer; it smooths the current flowing to the load, helping to maintain a consistent output voltage.
In operation, the ADP1821 modulates the duty cycle of the switching signal to control the amount of energy delivered to the output. The feedback loop monitors the output voltage and adjusts the PWM signal accordingly, ensuring that the output remains stable despite variations in load current or input voltage. This feedback mechanism is essential for maintaining the desired output voltage under different operating conditions.
The design of the circuit should also consider thermal management, as the ADP1821 can generate heat during operation. Adequate heat sinking or thermal vias may be required to ensure reliable performance. Additionally, careful selection of the inductor and capacitors is important to optimize the transient response and minimize output voltage ripple.
Overall, the ADP1821 step-down DC-to-DC converter circuit is a robust solution for efficiently powering electronic devices from higher voltage sources, making it a valuable component in modern electronic design.This is a ADP1821 Step Down DC-to-DC Converter circuit. This circuit uses ADP1821 that is synchronous pulse-width-modulated (PWM), step-down controller,. 🔗 External reference